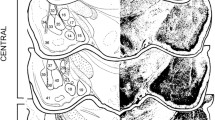
Abstract
The amygdaloid complex, traditionally regarded as part of the system of basal endbrain nuclei, has a unique structure in that it combines the two major principles of organization of the gray matter – the nuclear and the screening. Working from the studies of Zavarzin on the nuclear and screening centers, the authors suggest a classification of its structures into nuclei, paleocortex, and intermediate formations.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
É. Sh. Airapet'yants and T. S. Sotnichenko, The Limbic System [in Russian], Nauka, Leningrad (1967).
I. G. Akmaev and L. B. Kalimullina, The Amygdaloid Complex of the Brain: Functional Morphology and Neuroendocrinology [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1993).
A. A. Zavarzin, Studies on the Theory of Parallelism in the Evolutionary Dynamics of Tissues [in Russian], Nauka, Leningrad (1986).
R. Yu. Il'yuchenok, M. A. Gilinskii, L. V. Loskutov, N. I. Dubrovina, and N. V. Vol'f, The Amygdaloid Complex: Connections, Behavior, and Memory [in Russian], Nauka, Novosibirsk (1981).
L. B. Kalimullina and Z. A. Kalkamanov, Position of Image Recognition Theory in the Practice of Morphological Studies [in Russian], Deposited in the All-Russian Institute of Scientific and Technical Information (VINITI), No. 4961-B89, 24.7.89, Moscow (1989).
A. V. Karpova and L. B. Kalimullina, Structural-Functional Organization of the Cortical Nucleus of the Amygdaloid Complex of the Brain [in Russian], Bashkir State University, Ufa (2001).
I. N. Filimonov, Selected Works [in Russian], Meditsina, Moscow (1974).
S. A. Chepurnov and N. E. Chepurnova, The Amygdaloid Complex of the Brain [in Russian], Moscow State University Press, Moscow (1981).
V. T. Shuvaev and N. F. Suvorov, The Basal Ganglia and Behavior [in Russian], Nauka, St. Petersburg (2001).
M. T. Alkire, A. Vazdarjanova, H. Dickinson-Anson, N. S. White, and L. Cahill, “Lesions of the basolateral amygdala complex block propofol-induced amnesia for inhibitory avoidance learning in rats,” Anesthesiol., 95,No. 3, 708–715 (2001).
D. G. Amaral, R. B. Veazy, and W. M. Cowan, “Some observations on hypothalamo-amygdaloid connections in the monkey,” Brain Res., 252,No. 1, 13–27 (1982).
L. Brothers, B. Ring, and A. Kling, “Response of neurons in the macaque amygdala to complex social stimuli,” Behav. Brain Res., 41,No. 3, 199–213 (1990).
D. P. Cain, S. G. Grant, D. Saucier, E. L. Hargreaves, and E. R. Kandel, “Fyn tyrosine kinase is required for normal amygdala kindling,” Epilepsy Res., 22,No. 2, 107–114 (1995).
M. Davis, The role of the Amygdala: Neurobiological Aspects of Emotion, Memory and Mental Dysfunction, J. P. Aggletov (ed.), Wiley-Liss, New York (1992).
E. S. Faber, R. J. Callister, and P. Sah, “Morphological and electrophysiological properties of principal neurons in the rat lateral amygdala in vitro,” J. Neurophysiol., 85,No. 2, 714–723 (2001).
G. S. Geis and R. D. Wurster, “Horseradish peroxidase localization of cardiac vagal preganglionic somata,” Brain Res., 182,No. 1, 19–30 (1980).
K. A. Goosens and S. Maren, “Contextual and auditory fear conditioning are mediated by the lateral, basal, and central amygdaloid nuclei in rats,” Learn. Mem., 8,No. 3, 148–155 (2001).
M. Heling, “Antisense inhibition of neuropeptide Y (NPY) receptor expression blocks anxiolytic-like action of NPY in amygdala and paradoxically increases feeding,” Regul. Pept., 59,No. 2 201–205 (1995).
B. R. Kaada, “Stimulation and regional ablation of the amygdaloid complex with reference to functional representations,” in: Neurobiology of the Amygdala, B. E. Eleftheriou (ed.), Plenum Press, New York (1972).
I. E. Krettek and I. L. Price, “Projections from amygdaloid complex to the cerebral cortex and thalamus in the rat and cat,” J. Comp. Neurol., 172,No. 4, 687–722 (1977).
M. P. Laakso, K. Partanen, M. Lehtovirta, M. Hallicainen, T. Hynninen, P. Vainio, P. Rikkinen, Sr., and H. Soininen, “MRI of amygdala fails to diagnose early Alzheimer's disease,” Neuroreport, 27,No. 6, 2414–2428 (1995).
P. D. McLean, “The limbic system: visceral brain and emotional behaviour,” Arch. Neurol. Psychiatr., 73,No. 2, 130–134 (1955).
The Amygdala: Structure, Function, Sex Dimorphism: Collection of Articles, Bashkir State University Press, Ufa (1995).
B. I. Morgado, G. M. Torras, and C. I. Portell, “The amygdaloid body: functional implications,” Rev. Neurol., 33,No. 5, 471–477 (2001).
G. M. Murphy, Jr. and W. G. Ellis, “The amygdala in Down's syndrome and familial Alzheimer's disease: four clinicopathological case reports,” Biol. Psychiatry, 30,No. 1, 92–106 (1991).
L. Nitecka and M. Frotscher, “Interconnections of GABAergic and cholinergic elements in the rat amygdaloid nuclei: single-and double-immunolabeling studies,” Biol. Psychiatry, 279,No. 3, 470–488 (1989).
T. Ono, H. Nishijo, and T. Uwano, “Amygdala role in conditioned associative learning,” Prog. Neurobiol., 46,No. 4, 401–422 (1995).
R. M. Pigache, “The anatomy of ‘paleocortex.’ A critical review,” Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol., 43,No. 6, 1–62 (1970).
J. Raber and F. E. Bloom, “IL-2 regulates vasopressin release from the hypothalamus and the amygdala: role of nitric oxide-mediated signaling,” J. Neurosci., 14,No. 10, 6187–6195 (1994).
J. Raber, G. F. Koob, and F. E. Bloom, “Interleukin-2 induces corticotropin-releasing factor release from the amygdala, and involves a nitric oxide-mediated signaling: comparison with the hypothalamic response,” Pharmacol. Exptl. Ther., 272,No. 2, 815–824 (1995).
M. E. Ragozzino and P. E,. Gold, “Task-dependent effects of intra-amygdalar morphine injections: attenuation by intra-amygdalar glucose injections,” Neurosci., 14,No. 12, 78–85 (1994).
J. C. Repa, J. Muller, J. Apergis, T. M. Desrochers, Y. Zhoui, and L. E. Le Doux, “Two different lateral amygdalar cell populations contribute to the initiation and storage of memory,” Nat. Neurosci., 4,No. 7, 724–731 (2001).
S. K. Sanders and A. Shekhar, “Regulation of anxiety by GABA-receptors in the amygdala,” Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 52,No. 4, 701–706 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalimullina, L.B., Akhmadeev, A.V., Minibaeva, Z.R. et al. Structural Organization of the Amygdaloid Complex of the Rat Brain. Neurosci Behav Physiol 34, 551–555 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEAB.0000028283.55130.69
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEAB.0000028283.55130.69