Abstract
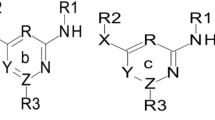
Structure-anti HIV activity relationships were established for a sample of 801-[2-hydroxyethoxy-methyl]-6-(phenylthio)thymine(HEPT) using a three-layer neural network (NN). Eight structural descriptors and physicochemical variables were used to characterize the HEPT derivatives under study. The network's architecture and parameters were optimized in order to obtain good results. All the NN architectures were able to establish a satisfactory relationship between the molecular descriptors and the anti-HIV activity. NN proved to give better results than other models in the literature. NN have been shown to be particularly successful in their ability to identify non-linear relationships.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dunne, A. L., Siregar, H., Mills, J. and Crowe, S. M, HIV replication in chronically infected macrophages is not inhibited by the Tat inhibitors Ro-5-3335 and Ro-24-7429, J. Leukocyte Biology, 56 (1994) 369–373.
Rosenberg, Y. J., Anderson, A. O. and Pabst, R., Decline in blood CD4/CD8 ratios during HIV infections: viral killing or altered lymphocyte trafficking, Immunolo. Today, 19 (1998) 10–17.
Garg, R., Gupta, S. P., Gao, H., Babu, M. S., Debnath, A. K. and Hansch, C, Comparative quantitative structure-activity relationship studies on anti-HIV drugs, Chem. Rev., 99 (1999) 3525–3601.
Hannongbua, S., Nivesanond, K., Lawtrakul, L., Pungpo, P. and Wolschann, P, 3-D-quantitative structure-activity relationships of HEPT derivatives as HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors based on ab initio calculations, J. Inf. Comp. Sci., 41 (2001) 848–855.
Manallack, D. T. and Livingston, D. J., Neural network in drug discovery: have they lived up their promise?, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 34 (1999) 195–208.
Hatrik, S. and Zahradnik, P., Neural network approach to the prediction of the toxicity of benzothiazolium salts from molecular structure, J. Chem. Comput. Sci., 36 (1996) 992–995.
So, S. and Karplus, M., Three-dimentional quantitative structure-activity relationships from molecular similarity matrixes and genetic neural network. 1. Method and validation, J. Med. Chem., 40 (1997) 4360–4359.
Elkhou, K., Afifi, A., Kabbaj, M., Villemin, D. and Cherqaoui, D., QSAR analysis of estrogen receptor ligands using neural networks, ACH Models in Chemistry, 137(5–6) (2000) 633–642.
Mghazli, S., Jaouad, A., Mansour, M., Villemin, D. and Cherqaoui, D., Neural networks studies: quantitative structure-activity relationships of antifungal 1-[2-(substituted phenyl)allyl]imidazoles and related compounds, Chemosphere, 43 (2001) 385–390.
Zakarya, D., Cherqaoui, D., Esseffar, M., Villemin, D. and Cense, J. M., Application of neural networks to structure-sandalwood odour relationships, J. Phys. Org. Chem., 10 (1997) 612–622.
Cherqaoui, D., Esseffar, M., Villemin, D., Cense, J. M., Chastrette, M. and Zakarya, D., Structure-musk Odour relationship studies of tetralin and indan compounds using neural networks, New J. Chem., (1998) 839–843.
Bodour, N., Harget, A. and Huang, M. J., Neural network studies. 1. Estimation of aqueous solubility of organic compounds, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 113 (1991) 9480–9484.
Cherqaoui, D., Villemin, D. and Kvasnicka, V., Application of neural network approach for prediction of some thermochemical properties of alkanes, Chem. and Intell. Labor. Sys., 24 (1994) 117–128.
Cense, J.-M., Diawara, B., Legendre, J. J. and Roullet, G., Neural networks prediction of partition coefficients, Chem. and Intell. Labor. Sys., 23 (1994) 301–308.
Simon, V., Gasteiger, J. and Zupan, J., A combined application of two different neural network types for the prediction of chemical reactivity, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115 (1993) 9148–9159.
Zakarya, D., Farhaoui, L. and Fkih-Tetouan, S., Structure-enantioselectivity relationships using neural networks for the reduction of carbonyl compounds with Backer's yeast, Tetrahedron Lett., 35 (1994) 4985–622.
Aires-de-Sousa, J., Hemmer, M. C. and Gasteiger, J., Prediction of 1HNMR chemical shifts using neural networks, Anal. Chem., 74 (2001) 80–90.
Munk, M. E., Madison, M. S. and Robb, E. W., Neural network models to infrared spectrum interpretation, Mikrochim Acta [Wien], 2 (1991) 505–514.
Miyashita, Y., Yoshida, H., Yaegashi, O., Kimura, T., Nishiyama, H. and Sasaki, S., Non-linear modelling of 13 C NMR chemical shift data using artificial neural networks and partial least squares method, J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem), 311 (1994) 241–245.
Curry, B. and Rumelhart, D. E, MS net: A neural network that classifies mass spectra, Tetrahedron Comput. Methodol., 3 (1990) 213–237.
Holley, L. H. and Karplus, M., Protein secondary structure prediction with a neural network, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 86 (1989) 152–156.
Jalali-Heravi, M. and Parastar, F., Use of artificial neural network in a QSAR study of anti-HIV activity for a large group of HEPT derivatives, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 40 (2000) 147–154.
Bazoui, H., Zahouily, M., Boulaajaj, S., Sebti, S. and Zakarya, D., QSAR for anti-HIV activity of HEPT derivatives, SAR QSAR Environ. Res., 13(6) (2002), 567–577.
Luco, J. and Ferretti, F., QSAR based on multiple linear regression and PLS methods for the anti-HIV activity of a large group of HEPT derivatives, J. Chem. Comput. Sci., 37 (1997) 392–401.
Zupan, J. and Gasteiger, J., Neural Networks for Chemists. An Introduction, VCH Publishers, Weinheim, (1993).
Cherqaoui, D. and Villemin, D., Use of a neural network to determine boiling point of alkanes, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans., 90 (1994) 97–102.
Freeman, J. A. and Skapura, D. M., Neural Networks Algorithms, Applications, and Programming Techniques, Addition Wesley Publishing Company, Reading, (1991).
So, S. and Richards, W. G., Application of neural networks: quantitative structure-activity relationships of the derivatives of 2, 4 diamino (substituted-benzyl) pyrimidines as DHFR inhibitors, J. Med. Chem., 35 (1992) 3201–3207.
Andrea, T. A. and Kalayeh, H., Application of neural networks in quantitative structure-activity relationships of dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors, J. Med. Chem., 34 (1991) 2824–2836.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Douali, L., Villemin, D., Zyad, A. et al. Artificial neural networks: Non-linear QSAR studies of HEPT derivatives as HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Mol Divers 8, 1–8 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MODI.0000006753.11500.37
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MODI.0000006753.11500.37