Abstract
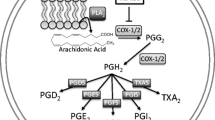
Prostaglandins (PG) produced by activated non-parenchymal liver cells regulate the function of parenchymal cells through six classes of G-protein-coupled receptors (-R): four receptor subtypes for PGE2, EP1-R–EP4-R and one type each for PGD2, DP-R, and PGF2α, FP-R. The mechanisms by which prostaglandins modulate the hepatocyte responding phenotype are poorly characterized. We have studied the concentration and time effect of PGE2, PGD2 and PGF2α on the mRNA expression level of their own receptors in the presence or absence of the inflammatory signal interleukin 6 (IL-6). The mRNA levels were determined in primary adult rat hepatocytes upon treatment with either prostaglandin (5 μM or 50 μM), or IL-6 (100 ng/ml), or both, for 4–24 h. A marked, concentration-dependent induction of EP2-R mRNA expression was promoted by PGE2, PGD2 or PGF2α after 4 h, whereas EP1-R, EP3-R and EP4-R transcript levels were unaffected. This expression pattern changed substantially upon 24 h. The induction of EP2-R mRNA, persisted, though attenuated. Furthermore, EP1-R mRNA upregulated two–three fold and EP3-R mRNA decreased modestly by 50 μM prostaglandin. None of the treatments affected the FP-R mRNA level, while that of DP-R mRNA was undetectable. In the presence of IL-6, prostaglandins had no such effects, but they did attenuate the IL-6-mediated changes in prostaglandin receptor mRNA expression. The findings indicate that prostaglandins modulate the prostaglandin receptor gene expression programme in primary adult rat hepatocytes in a manner that is specific to the receptor, the concentration and time of exposure, and the inflammatory condition of the cell (Mol Cell Biochem 266: 183–189, 2004)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hespeling U, Jungermann K, Puschel GP: Feedback inhibition of glucagon-stimulated glycogenolysis in hepatocyte-Kupffer cell cocultures by glucagon-elicited prostaglandin production in Kupffer cells. Hepatology 22: 1577–1583, 1995
Athari A, Hänecke K, Jungermann K: Prostaglandin F2β and D2 release from primary Ito cell cultures after stimulation with noradrenaline and ATP but not adenosine. Hepatology 20: 142–148, 1992
Casteleijn E, Kuiper J, Van Rooij HC, Kamps JA, Koster JF, Van Berkel TJ: Endotoxin stimulates glycogenolysis in the liver by means of intra-cellular communication. J Biol Chem 263: 6953–6955, 1988
Peters T, Karch U, Decker K: Interdependence of tumour necrosis factor, prostaglandin E2 and protein synthesis in lipopolysacharide-exposed rat Kupffer cells. Eur J Biochem 191: 583–589, 1990
Enomoto N, Ikejima K, Yamashina S, Enomoto A, Nishiura T, Nishimura T, Brenner DA, Schemmer P, Bradford BU, Rivera CA, Zhong Z, Thurman RG: Kupffer cell-derived prostaglandin E2 is involved in alcohol-induced fat accumulation in rat liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279: G100–G106, 2000
Püschel GP, Christ B: Inhibition by PGE2 of glucagon-induced increase in phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA and acceleration of mRNA degradation in cultured hepatocytes. FEBS Lett 351: 353–356, 1994
Püschel GP, Kirchner C, Schröder A, Jungermann K: Glycogenolytic and antiglycogenolytic prostaglandin-E(2) actions in rat hepatocytes are mediated via different signalling pathways. Eur J Biochem 218: 1083–1089, 1993
Athari A, Jungermann K: Direct activation by prostaglandin F2β but not thromboxane A2 of glycogenolysis via an increase in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163: 1235–1242, 1989
Negishi M, Sugimoto Y, Ichikawa A: Molecular mechanisms of diverse actions of prostanoid receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1259: 109–119, 1995
Narumiya S, Sugimoto Y, Ushikubi F: Prostanoid receptors: structures, properties, and functions. Physiol Rev 79: 1193–1226, 1999
Nataraj C, Thomas DW, Tilley SL, Nguyen MT, Mannon R, Koller BH, Coffman TM: Receptors for prostaglandin E2 that regulate cellular immune responses in the mouse. J Clin Invest 108: 1229–1235, 2001
Breyer RM, Bagdassarian CK, Myers SA, Breyer MD: Prostanoid receptors: subtypes and signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41: 661–690, 2001
Fennekohl A, Schieferdecker HL, Jungermann K, Püschel GP: Differential expression of prostanoid receptors in hepatocytes, Kupffer cells, sinusoidal endothelial cells and stellate cells of rat liver. J Hepatol 30: 38–47, 1999
Fennekohl A, Lucas M, Püschel GP: Induction by interleukin 6 of Gs-coupled prostaglandin E2 receptors in rat hepatocytes mediating a prostaglandin E2-dependent inhibition of the hepatocyte's acute phase response. Hepatology 31: 1128–1134, 2000
Kitanaka J, Hasimoto H, Sugimoto Y, Negishi M, Aino H, Gotoh M, Ichikawa A, Baba A: Cloning and expressión of a cDNA for rat prostaglandin F2β receptor. Prostaglandins 48: 31–41, 1994
Boie Y, Stocco R, Sawyer N, Slipetz DM, Ungrin MD, Neuschäfer-Rube F, Püschel GP, Metters KM, Abramovitz M: Molecular cloning and characterization of the four rat prostaglandin E2 prostanoid receptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol 340: 227–241, 1997
Wright DH, Nantel F, Metters KM, Ford-Hutchinson AW: A novel biological role for prostaglandin is suggested by distribution studies of the rat DP prostanoid receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 377: 101–115, 1999
Kimura M, Osumi S, Ogihara M: Prostaglandin E2 (EP1) receptor agonist-induced DNA synthesis and proliferation in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes: The involvement of TGF-β.Endocrinology 142: 4428–4440, 2001
Gabay C, Kushner I: Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 340: 448–454, 1999
Ramadori G, Christ B: Cytokines and the hepatic acute-phase response. Semin Liver Dis 19: 141–155, 1999
Castell JV, Gómez-Lechón MJ, David M, Andus T, Geiger T, Trullenque R, Fabra R, Heinrich PC: Interleukin-6 is the major regulator of acute phase protein synthesis in adult human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett 242: 237–239, 1989
Tilg H, Dinarelloo CA, Mier JW: Interleukin-6 and acute-phase proteins: Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive mediators. Immunol Today 18: 428–432, 1997.
Kunkel SL, Spengler M, May MA, Spengler R, Larrick J, Remick D: Prostaglandin E2 regulates macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor gene expression. J Biol Chem 263: 5380–5384, 1988
Fennekohl A, Sugimoto Y, Segi E, Maruyama T, Ichikawa A, Püschel GP: Contribution of the two Gs-coupled PGE2-receptors EP2-receptor and EP4-receptor to the inhibition by PGE2of the LPS-induced TNF?-formation in Kupffer cells from EP2-or EP4-receptor-deficient mice. Pivotal role for the EP4-receptor in wild type Kupffer cells. J Hepatol 36: 328–334, 2002
Isusi E, Aspichueta P, Liza M, Hernández ML, Díaz C, Hernández G, Martínez MJ, Ochoa B: Short-and long-term effects of atorvastatin, lovastatin and simvastatin on the cellular metabolism of cholesteryl esters and VLDL secretion in rat hepatocytes. Atherosclerosis 153: 283–294, 2000
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989
Neuschäfer-Rube F, Möller U, Püschel GP: Structure of the 5' flanking region of the rat prostaglandin F2β receptor gene and its transcriptional control functions in hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 278: 278–285, 2000
Kuiper J, Zijlstra FJ, Kamps JAAM, van Berkel TJC: Identification of prostaglandin D2as the major eicosanoid from liver endothelial and Kupffer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 959: 143–152, 1988
Regan JW, Bailey TJ, Pepperi DJ, Pierce KL, Bogardus AM, Donello JE, Fairbairn CE, Kedzie KM, Woodward DF, Gil DW: Cloning of a novel human prostaglandin receptor with characteristics of the pharmacologically defined EP2 subtype. J Biol Chem 269: 213–220, 1994
Neuschäfer-Rube F, Püschel GP, Jungermann K: Characterization of prostaglandin F2β-binding sites on rat hepatocyte plasma membranes. Eur J Biochem 211: 163–169, 1993
Mater MK, Thelen AP, Jump DB: Arachidonic acid and PGE2 regulation of hepatic lipogenic gene expression. J Lipid Res 40: 1045–1052, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez, S., Maldonado, E.N., Aspichueta, P. et al. Differential modulation of prostaglandin receptor mRNA abundance by prostaglandins in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 266, 183–189 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000049159.09349.02
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000049159.09349.02