Abstract
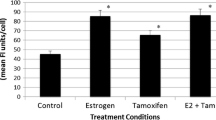
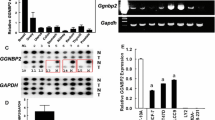
17β-Estradiol (17β-E2) augments VEGF-A expression in various estrogen targeted organs and cells including breast tumor derived cell lines, via an ER-α mediated pathway. Ironically, 17β-E2 is able to regulate some genes via ER-α independent pathways. In the present study, we sought to determine whether 17β-E2 can modulate VEGF-A expression in absence of ER-α, and therefore, three different cell lines including ER-α+ MCF-7, and ER-α SKBR-3 and HMEC were used for this study. The present study demonstrates that 17β-E2 also induces VEGF-A mRNA expression in ER-negative SKBR-3 breast tumor cells in a manner similar to that observed in ER-positive MCF-7 cells. Blocking the induced-expression by antiestrogen ICI 182,780 indicates the induction pathway is ER dependent. While ER-α mRNA is absent in both HMEC and SKBR-3 cells, the impact of estrogen was found only in SKBR-3 cells, suggesting the existence of an analogue to ER-α or overlapping signal in these cells. Consistent with this suggestion, the present studies demonstrate the existence of an ER-αvar2 protein in MCF-7 and in SKBR-3 cells. This variant is predominantly localized in the nuclei of SKBR-3 cells. Importantly, specific binding of 17β-E2 by these cells suggest the ER-αvar2 may act as active receptor in SKBR-3 cells. (Mol Cell Biochem 262: 215–224, 2004)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrara N, Houck K, Jakeman L, Leung DW: Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins.Endocr Rev 13: 18–32, 1992
Ferrara N: The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in pathological angiogenesis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 36: 127–137, 1995
Bachelder RE, Crago A, Chung J, Wendt MA, Shaw LM, Robinson G, Mercurio AM: Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine survival factor for neuropilin-expressing breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 61: 5736–5740, 2001
Tian X, Song S, Wu J, Meng L, Dong Z, Shou C: Vascular endothelial growth factor: Acting as an autocrine growth factor for human gastric adenocarcinoma cell MGC803. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286: 505–512, 2001
Tischer E, Mitchell R, Hartman T, Silva M, Gospodarowicz D, Fiddes JC, Abraham JA: The human gene for vascular endothelial growth factor.Multiple protein forms are encoded through alternative exon splicing. J Biol Chem 266: 11947–11954, 1991
Poltorak Z, Cohen T, Sivan R, Kandelis Y, Spira G, Vlodavsky I, Keshet E, Neufeld G: VEGF145, a secreted vascular endothelial growth factor isoform that binds to extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem 272: 7151–7158, 1997
Stalmans I, Lambrechts D, De Smet F, Jansen S, Wang J, Maity S, Kneer P, Von Der OM, Swillen A, Maes C, Gewillig M, Molin DG, Hellings P, Boetel T, Haardt M, Compernolle V, Dewerchin M, Plaisance S, Vlietinck R, Emanuel B, Gittenberger-De Groot AC, Scambler P, Morrow B, Driscol DA, Moons L, Esguerra CV, Carmeliet G, Behn-Krappa A, Devriendt K, Collen D, Conway SJ, Carmeliet P: VEGF: A 223 modifier of the del22q11 (DiGeorge) syndrome? Nat Med 9: 173–182, 2003
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J: The biology of VEGF and its receptors.Nat Med 9: 669–676, 2003
Kieser A, Weich HA, Brandner G, Marme D, Kolch W: Mutant p53 potentiates protein kinase C induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Oncogene 9: 963–969, 1994
Banerjee SK, Zoubine MN, Mullick M, Weston AP, Cherian R, Campbell DR: Tumor angiogenesis in chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Impact of K-ras mutations. Pancreas 20: 248–255, 2000
Norman AW, Litwack G: Estrogens and Progestins Hormones. Academic Press, New York, 1997, pp 361–386
Banerjee SK, Sarkar DK, Weston AP, De A, Campbell DR: Over expression of ascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor during the development of estrogen-induced rat pituitary tumors may mediate estrogen-initiated tumor angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis 18: 1155–1161, 1997
Maity A, Sall W, Koch CJ, Oprysko PR, Evans SM: Low pO2 and betaestradiol induce VEGF in MCF-7 and MCF-7-5C cells: Relationship to in vivo hypoxia. Breast Cancer Res Treat 67: 51–60, 2001
Ochoa AL, Mitchner NA, Paynter CD, Morris RE, Ben Jonathan N: Vascular endothelial growth factor in the rat pituitary: Differential distribution and regulation by estrogen. J Endocrinol 165: 483–492, 2000
Sengupta K, Banerjee S, Saxena N, Banerjee SK: Estradiol-induced vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression in breast tumor cells is biphasic and regulated by estrogen receptor-alpha dependent pathway.Int J Oncol 22: 609–614, 2003
Sengupta K, Banerjee S, Saxena N, Banerjee SK: Estrogen-induced down regulation of thrombospondin-1 in rat pituitary tumor cells and in rat pituitaries may be associated with estrogen-induced tumor cell growth and angiogenesis, abstr. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 44: 103, 2003
Mueller MD, Vigne JL, Minchenko A, Lebovic DI, Leitman DC, Taylor RN: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene transcription by estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 10972–10977, 2000
Moggs JG, Orphanides G: Estrogen receptors: Orchestrators of pleiotropic cellular responses. EMBO Rep 2: 775–781, 2001
Simoncini T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Brazil DP, Ley K, Chin WW, Liao JK: Interaction of oestrogen receptor with the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature 407: 538–541, 2000
Honda K, Sawada H, Kihara T, Urushitani M, Nakamizo T, Akaike A, Shimohama S: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediates neuroprotection by estrogen in cultured cortical neurons. J Neurosci Res 60: 321–327, 2000
Lobenhofer EK, Huper G, Iglehart JD, Marks JR: Inhibition of mitogenactivated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in MCF-7 cells prevents estrogen-induced mitogenesis. Cell Growth Differ 11: 99–110, 2000
Eing-Mei T, Shao-Chun W, JauNan L, Mien-Chie L: Akt activation by estrogen in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61: 8390–8392, 2001
Singh M, Setalo Jr G, Guan X, Frail DE, Toran-Allerand CD: Estrogeninduced activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in the cerebral cortex of estrogen receptor-alpha knock-out mice. J Neurosci 20: 1694–1700, 2000
Lee TH, Chuang LY, Hung WC: Induction of p21WAF1 expression via Sp1-binding sites by tamoxifen in estrogen receptor-negative lung cancer cells. Oncogene 19: 3766–3773, 2000
Banerjee S, Saxena N, Sengupta K, Banerjee SK: 17Alpha-estradiolinduced VEGF-A expression in rat pituitary tumor cells is mediated through ER independent but PI3K-Akt dependent signaling pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 300: 209–215, 2003
Taylor CM, Blanchard B, Zava DT: A simple method to determine whole cell uptake of radiolabelled oestrogen and progesterone and their subcellular localization in breast cancer cell lines in monolayer culture.J Steroid Biochem 20: 1083–1088, 1984
Sadovsky Y, Riemer RK, Roberts JM: The concentration of estrogen receptors in rabbit uterine myocytes decreases in culture. Am J Obstet Gynecol 167: 1631–1635, 1992
Scatchard G: The attractions of proteins for small molecules and ions.Ann NY Acad Sci USA 2: 660–672, 1959
DeFriend DJ, Anderson E, Bell J, Wilks DP, West CM, Mansel RE, Howell A: Effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen and a novel pure antioestrogen (ICI 182780) on the clonogenic growth of human breast cancer cells in vitro. Br J Cancer 70: 204–211, 1994
DeFriend DJ, Howell A, Nicholson RI, Anderson E, Dowsett M, Mansel RE, Blamey RW, Bundred NJ, Robertson JF, Saunders C: Investigation of a new pure antiestrogen (ICI 182780) in women with primary breast cancer. Cancer Res 54: 408–414, 1994
Hahnel R, Twaddle E: Estimation of the association constant of the estrogen-receptor complex in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 33: 559–566, 1973
Hahnel R, Twaddle E, Ratajczak T: The influence of synthetic antiestrogens on the binding of tritiated estradiol-17beta by cytosols of human uterus and human breast carcinoma. J Steroid Biochem 4: 687–695, 1973
Hahnel R, Twaddle E, Ratajczak T: The specificity of the estrogen receptor of human uterus. J Steroid Biochem 4: 21–31, 1973
Cullinan-Bove K, Koos RD:Vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor expression in the rat uterus: Rapid stimulation by estrogen correlates with estrogen-induced increases in uterine capillary permeability and growth. Endocrinology 133: 829–837, 1993
Takei H, Lee ES, Jordan VC: In vitro regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by estrogens and antiestrogens in estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer 9: 39–42, 2002
Hyder SM, Nawaz Z, Chiappetta C, Stancel GM: Identification of functional estrogen response elements in the gene coding for the potent angiogenic factor vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res 60: 3183–3190, 2000
Das SK, Tan J, Raja S, Halder J, Paria BC, Dey SK: Estrogen targets genes involved in protein processing, calcium homeostasis, and Wnt signaling in the mouse uterus independent of estrogen receptor-alpha and-beta. J Biol Chem 275: 28834–28842, 2000
Frigo DE, Tang Y, Beckman BS, Scandurro AB, Alam J, Burow ME, McLachlan JA: Mechanism of AP-1-mediated gene expression by select organochlorines through the p38MAPKpathway. Carcinogenesis, 2003
Charpentier AH, Bednarek AK, Daniel RL, Hawkins KA, Laflin KJ, Gaddis S, MacLeod MC, Aldaz CM: Effects of estrogen on global gene expression: Identification of novel targets of estrogen action. Cancer Res 60: 5977–5983, 2000
Rishi AK, Gerald TM, Shao ZM, Li XS, Baumann RG, Dawson MI, Fontana JA: Regulation of the human retinoic acid receptor alpha gene in the estrogen receptor negative human breast carcinoma cell lines SKBR-3 and MDA-MB-435. Cancer Res 56: 5246–5252, 1996
Roman SD, Ormandy CJ, Manning DL, Blamey RW, Nicholson RI, Sutherland RL, Clarke CL: Estradiol induction of retinoic acid receptors in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 53: 5940–5945, 1993
Sheikh MS, Shao ZM, Li XS, Dawson M, Jetten AM, Wu S, Conley BA, Garcia M, Rochefort H, Fontana JA: Retinoid-resistant estrogen receptor-negative human breast carcinoma cells transfected with retinoic acid receptor-alpha acquire sensitivity to growth inhibition by retinoids.J Biol Chem 269: 21440–21447, 1994
Fontana JA: Interaction of retinoids and tamoxifen on the inhibition of human mammary carcinoma cell proliferation. Exp Cell Biol 55: 136–144, 1987
van der BB, van der Leede BM, Kwakkenbos-Isbrucker L, Salverda S, de Laat SW, van der Saag PT: Retinoic acid resistance of estradiolindependent breast cancer cells coincides with diminished retinoic acid receptor function. Mol Cell Endocrinol 91: 149–157, 1993
Kos M, Reid G, Denger S, Gannon F: Minireview: Genomic organization of the human ER-a gene promoter region. Mol Endocrinol 15: 2057–2063, 2001
Weigel RJ, Crooks DL, Iglehart JD, de Coninck EC: Quantitative analysis of the transcriptional start sites of estrogen receptor in breast carcinoma.Cell Growth Differ 6: 707–711, 1995
Klotz DM, Castles CG, Fuqua SA, Spriggs LL, Hill SM: Differential expression of wild-type and variant ER mRNAs by stocks of MCF-7 breast cancer cells may account for differences in estrogen responsiveness. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 210: 609–615, 1995
Kos M, Denger S, Reid G, Gannon F: Upstream open reading frames regulate the translation of the multiple mRNA variants of the estrogen receptor alpha. J Biol Chem 277: 37131–37138, 2002
Grandien K, Backdahl M, Ljunggren O, Gustafsson JA, Berkenstam A: Estrogen target tissue determines alternative promoter utilization of the human estrogen receptor gene in osteoblasts and tumor cell lines.Endocrinology 136: 2223–2229, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sengupta, K., Banerjee, S., Saxena, N.K. et al. Differential expression of VEGF-A mRNA by 17β-estradiol in breast tumor cells lacking classical ER-α may be mediated through a variant form of ER-α. Mol Cell Biochem 262, 215–224 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000038237.33875.d0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000038237.33875.d0