Abstract
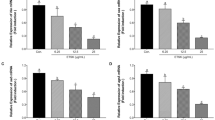
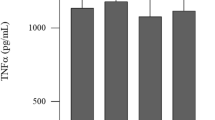
It has been shown that staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) acts through human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to stimulate synthesis or release of pyrogenic cytokines. Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) is thought to play an important role in inflammatory responses through the regulation of genes encoding pro-inflammatory cytokines. The purpose of the present study was to determine whether the NF-κB mechanisms in human PBMC are involved in SEA-induced fever. Western blot evaluation revealed SEA was able to induce nuclear translocation of NF-κB from cytosol to nucleus in PBMC, which could be abolished by a NF-κB inhibitor such as pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), sodium pyrithione (Pyri), N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), or curcumin (Cur). Electrophoretic mobility shift assay also showed that the NF-κB DNA-binding activity was increased in the SEA-treated PBMC. Again, the SEA-induced increased NF-κB binding activity was significantly attenuated by either PDTC, Pyri, NAC or Cur. The pyrogenic responses to supernatant fluids obtained from human PBMC stimulated with SEA were associated with increased levels of interleukin 1-β (IL-1β), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the supernatant fluids. Both the fever and the increased levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in supernatant fluids obtained from the SEA-stimulated PBMC were decreased by incubating SEA-PBMC with either PDTC, Pyri, NAC, or Cur. Furthermore, the fever induced by systemic or central administration of SEA in rabbits were attenuated by pre-treatment with an systemic or central dose of either PDTC, Pyri, NAC, or Cur. The data indicate that inhibition of NF-κB prevents SEA-induced fever. (Mol Cell Biochem 262: 177–185, 2004)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karin M, Ben-NeriahY: Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: The control of NF-?B activity. Ann Rev Immunol 18: 621–663, 2000
O'Neill LAJ, Kaltschmidt C: NF-?B: A crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. TINS 20: 252–258, 1997
YamamotoY, Gaynor RB: Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-?B pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest 107: 135–142, 2001
Collart MA, Baeuerle P, Vassalli P: Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages: Involvement of four ?B-like motifs and constitutive and inducible forms of NF-?B. Mol Cell Biol 10: 1498–1506, 1990
Liberrmann TA, Baltimore D: Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Mol cell Biol 10: 2327–2334, 1990
Shakhov AN, Collart MA, Vassalli P, Nedospasov SA, Jongeneel CV: Kappa B-type enhancers are involved in lipopolysaccharide-mediated transcription activation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene in primary macrophages. J Exp Med 171: 35–47, 1990
Dendorfer U, Oettgen P, Libermann TA: Multiple regulatiory elements in the interleukin-6 gene mediate induction by prostaglandins, cyclic AMP, and lipopolysaccharide. Mol Cell Biol 14: 4443–4454, 1994
Hiscolt J, Marois J, Garoufalis J, D'Addario M, Roulston A, Kwan I, Pepin N, Lacaste J, Nguyen H, Bensi G, Fenton M: Characterization of a functional NF-?B site in the human interleukin-1ßpromoter: Evidence for a positive autorgulatory loop. Md-cell Biol 13: 6231–6240, 1993
Zhang Y, Broser M, Rom WN: Activation of the interleukin-6 gene by Mycobacterium tuberculosis or lipopolysaccharide is mediated by nuclear factors NF-IL6 and NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 2225–2229, 1994
Fantuzzi G, Dinarello LA: The inflammatory response in inteleukin-1ß-deficient mice: Comparison with other cytokine-related knock-out mice. J Leukocyte Biol 59: 489–493, 1996
Kotzin BL, Leung DYM, Kappler J, Marrack P: Superantigens and human disease. Adv Immunol 54: 99–146, 1993
Won SJ, HuangWT, Lai YS, Lin MT: Staphylococcal enterotoxinAacts through nitric oxide synthase mechanisms in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to stimulate synthesis of pyrogenic cytokines. Infect Immun 68: 2003–2008, 2000
Huang WT, Lin MT, Won SJ: Staphylococcal enterotoxin A-induced fever is associated with increased circulating levels of cytokines in rabbits. Infect Immun 65: 2656–2662, 1997
Barnes PJ, Karin M: Nuclear factor-?B, a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 336: 1066–1071, 1997
Clark BD, Collins KL, Grandy MS, Webb AC, Auron PE: Genomic sequence for human prointeleukin 1 beta: Possible evolution from a reverse transcribed prointerleukin 1 alpha gene. Nucleic Acids Res 14: 7897–7914, 1986
Geng Y, Zhang B, Lotz M: Protein tyrosine kinase activation is regulated for lipopolysaccharide induction of cytokines in human blood monocytes. J Immunol 151: 6692–6700, 1993
Trede NS, Geha RS, Chatila T: Transcriptional activation of IL-1ßand tumor necrosis factor-agenes by MHC class II ligands. J Immunol 146: 2310–2315, 1991
Stadler J, Stafanovic-Racic M, Billiar TR, Cunan RD, McIntyre LA, Georgescu HI, Simmons RL, Evans CH: Articular chondrocytes synthesize nitric oxide in reponse to cytokine and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol 147: 3915–3920, 1991
Feng SH, Lo SC: Lipid extract of Mycoplasma penetrans proteinase Kdigested lipid-associated membrane proteins rapidly activates NF-?B and activator protein 1. Infect Immun 67: 2951–2956, 1999
Franzoso G, Bours V, Park S, Tomita-yamaguchi M, Kelly K, Siebenlist U: The candidate oncoprotein Bcl-3 is an antagonist of p50/NF-?B mediated inhibition. Nature 359: 339–342, 1992
Sawyer GH, Everett JW, Green JD: The rabbit diencephalons in stereotaxic coordinates. J Comp Neurol 101: 801–824, 1954
Huang WT, Lin MT, Won SJ: Mechanisms and sites of pyrogenic action exerted by staphylococcal enterotoxin A in rabbits. Neurosci Lett 236: 53–56, 1997
O'Neill LAJ, Kaltschmidt C: NF-?B: A crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. TINS 20: 252–258, 1997
Valliires L, Rivest S: Regulation of the genes encoding interleukin-6 its receptor, and gp130 in the rat brain in response to the immune activator lipopolysaccharide and proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1ß. J Neurochem 69: 1668–1683, 1997
Breder CD, Hazuka C, Ghayur T, Kung C, Huginin M, Yasuda K, Teng M, Saper CB: Regional induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in the mouse brain after systemic lipopolysaccharide administration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 22: 11393–11397, 1994
Buttini M, Boddeke: Peripheral lipopolysaccharide stimulation induces interleukin-1 beta messenger RNA in rat brain microglial cells. Neuroscience 65: 523–530, 1995
Nadeau S, Rivest S: Regulation of the gene encoding tumor necrosis factor alpha in rat brain and pituitary in response to different models of systemic immune challenge. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58: 61–77, 1999
Quan N, Whiteside M, Herkenham M: Time course and localization patterns of interleukin-1ßmRNA expression in the brain and pituitary after peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide. Neuroscience 83: 281–293, 1997
Blatteis CM, Sehic E, Li S: Pyrogen sensing and signaling: Old views and new concepts. Clin Infect Dis 31 (suppl 5): S168–S177, 2000
Hashimoto M, Ueno T, Iriki M: What roles does the organum vasculosum laminae terminalis play in fever in rabbits? Pfliigers Arch Eur J Physiol 429: 50–57, 1994
Stitt JT: Evidence for the involvement of the organum vasculosum laminae terminalis in the febrile response of rabbits and rats. J Physiol 368: 501–511, 1985
Vane JR: Inducible isoforms of cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase in inflammation. Proc Acad Sci USA 91: 2046–2050, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, DZ., Lee, JJ., Huang, WT. et al. Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B prevents staphylococcal enterotoxin A-induced fever. Mol Cell Biochem 262, 177–185 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000038233.20276.e0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000038233.20276.e0