Abstract
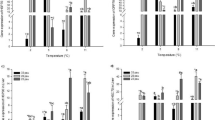
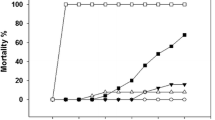
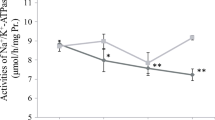
The stimulation of p38-MAPK signal transduction pathway by various stressful stimuli was investigated in the marine bivalve M. galloprovincialis. Oxidative stress (5 μM H2O2) induced a biphasic pattern of p38-MAPK phosphorylation with maximal values attained at 15 min (8.1-fold) and 1 h (8.0-fold) of treatment respectively. Furthermore, 1 μM SB203580 abolished the p38-MAPK phosphorylation induced by oxidative stress. Aerial exposure also induced a biphasic pattern of p38-MAPK phosphorylation, with maximal values attained at 1 h (6.8-fold) and 8 h (4.9-fold) respectively. Re-oxygenation following a 15 min of aerial exposure resulted in the progressive dephosphorylation of the kinase. Treatment with 0.5 M sorbitol (in normal seawater) induced the rapid kinase phosphorylation (9.2-fold) and this effect was reversible. Seawater salinities varying between 100–60% had no effect, whereas a salinity of 50% induced a significant p38-MAPK phosphorylation. Furthermore, hypertonicity (120% seawater) resulted in a moderate kinase phosphorylation. All the above results demonstrate for the first time in a marine invertebrate imposed to environmental and other forms of stress as an intact, living organism, that the p38-MAPK pathway is specifically activated by various stressful stimuli which this animal can often face and sustain in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheehan D, Power A: Effects of seasonality on xenobiotic and antioxidant defense mechanism of bivalve molluscs. Comp Biochem Physiol 123C: 193-199, 1999
De Zwaan A, Eertman RHM: Anoxic or aerial survival of bivalves and other euryoxic invertebrates as a useful response to environmental stress. A comprehensive review. Comp Biochem Physiol 113C: 299-312, 1996
Hochachka PW, Lutz PL: Mechanism, origin, and evolution of anoxia tolerance in animals. Comp Biochem Physiol 130B: 435-459, 2001
De Zwaan A, Cortesi P, Van der Thillart G, Roos J, Storey KB: Differential sensitivities to hypoxia by two anoxia-tolerant marine mollusks: A biochemical analysis. Mar Biol 111: 343-351, 1991
Viarenco A, Burlando B, Cavaletto M, Marchi B, Ponzano E, Blasco J: Role of metallothionein against oxidative stress in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Am J Physiol 277: R1612-R1619, 1999
Cavaletto M, Ghezzi A, Burlando B, Evangelisti V, Ceratto N, Viarengo A: Effect of hydrogen peroxide on antioxidant enzymes and metallothionein level in the digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis. Comp Biochem Physiol 131C: 447-455, 2002
Karin M: The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem 270: 16483-16486, 1995
Muller JM, Krauss B, Kaltschmidt C, Baeuerle PA, Rupec RA: Hypoxia induces c-fos transcription via a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 272: 23435-23439, 1997
Ladare K, Nimigan A, Storey KB: Transcription pattern of birosomal protein L26 during anoxia exposure in Littorina littorea. J Exp Zool 290: 759-768, 2001
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J: Sounding the alarm: Protein kinase cascades activated by stress and inflammation. J Biol Chem 271: 24313-24316, 1996
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J: Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81: 807-869, 2001
Page C, Doubell AF: Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in cardiac tissues. Mol Cell Biochem 157: 49-57, 1996
Seger R, Krebs EG: The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J 9: 726-735, 1995
Cohen P: The search for physiological substrates of MAP and SAP kinases in mammalian cells. Trends Cell Biol 7: 353-361, 1997
Schaeffer HT, Weber MJ: Mitogen-activated protein kinases: Specific messages from ubiquitous messengers. Mol Cell Biol 19: 2435-2444, 1999
Pearson G, Robinson F, Gibson TB, Xu RE, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22: 153-183, 2001
Widmann C, Gibson S, Jarpe MB, Johnson GL: Mitogen-activated protein kinase: Conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol Rev 79: 143-180, 1999
Canesi L, Betti M, Ciacci C, Gallo C: Insulin effect of zinc in Mytilus digestive gland cells: Modulation of tyrosine kinase-mediated cell signaling. Gen Comp Endocrinol 122: 60-66, 2001
Canesi L, Betti M, Ciacci C, Scarpato A, Citterio B, Pruzzo C, Gallo G: Signaling pathways involved in the physiological response of mussel hemocytes to bacterial challenge: the role of stress-activated p38 MAP kinases. Dev Comp Immunol 26: 325-334, 2002
Abele D, Burlando B, Viarengo A, Portner HO: Exposure to elevated temperatures and hydrogen peroxide elicits oxidative stress and antioxidant response in the Antarctic intertidal limpet Nacella concinna. Comp Biochem Physiol 120B: 425-435, 1998
Takemoto Y, Yoshiyama M, Takeuchi K, Omura T, Komatsu R, Izumi Y, Kim S, Yoshikawa J: Increased JNK, AP-1 and NF-κB DNA binding activities in isoproterenol-induced cardiac remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31: 2017-2030, 1999
Aggeli IKS, Gaitanaki C, Lazou A, Beis I: Stimulation of multiple MAPK pathways by mechanical overload in the amphibian heart. Am J Physiol 281: R1689-1698, 2001a
Aggeli IKS, Gaitanaki C, Lazou A, Beis I: Activation of multiple MAPK pathways (ERK, JNKs, p38-MAPK) by diverse stimuli in the amphibian heart. Mol Cell Biochem 221: 63-69, 2001b
Lang F, Busch GL, Ritter M, Volkl H, Waldegger S, Gulbins E, Haussinger D: Functional significance of cell volume regulatory mechanisms. Phys Rev 78: 247-306, 1998
Somero GN, Yancey PH: Osmolytes and cell volume regulation: Physiological and evolutionary principles. In: J.F. Hoffmann, J.D. Jamieson (eds). Handbook of Physiology, section 14, Cell Physiology. Oxford University Press, New York, 1997, pp 441-484
Winston GW, DiGiulio RT: Prooxidant and antioxidant mechanisms in aquatic organisms. Aquat Toxicol 19: 137-161, 1991
Livingstone DR: Biotechnology and pollution monitoring. Use of molecular biomarkers in the aquatic environment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 57: 195-211, 1993
Regoli F, Winston GW: Applications of a new method for measuring the total oxyradical scavenging capacity in marine invertebrates. Mar Environ Res 46: 439-442, 1998
Gaitanaki C, Stathopoulou K, Stavridou C, Beis I: Oxidative stress activates multiple MAPK signal transduction pathways and the phosphorylation of the small HSP27 in the amphibian heart. J Exp Biol 206: 2759-2769, 2003
Yin T, Sandhu G, Wolfgang CD, Burrier A, Webb RL, Rigel DF, Hai T, Whelan J: Tissue-specific pattern of stress kinase activation in ischemic/reperfused heart and kidney. J Biol Chem 272: 19943-19950, 1997
Greenway SC, Storey KB: Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases during natural freezing and thawing in wood frog. Mol Cell Biochem 209: 29-37, 2000
Greenway SC, Storey KB: Mitogen-activated protein kinases and anoxia tolerance in turtles. J Exp Zool 287: 477-484
Cowan KJ, Storey KB: Mitogen-activated protein kinases: New signaling pathways functioning in cellular responses to environmental stress. J Exp Biol 206: 1107-1115
Aggeli IKS, Gaitanaki C, Lazou A, Beis I: Hyperosmotic and thermal stresses activate p38-MAPK in the perfused amphibian heart. J Exp Biol 205: 443-454, 2002
Sadoshima J, Qiu Z, Morgan JP, Izumo S: Tyrosine kinase activation is an immediate and essential step in hypotonic cell swelling-induced ERK activation and c-fos gene expression in cardiac myocytes. EMBO J 15: 5535-5546, 1996
Kulitz D, Avila K: Mitogen-activated protein kinases are in vivo transducers of osmosensory signals in fish gill cells. Comp Biochem Physiol 129B: 821-829, 2001
Walker ST, Mantle D, Bythell JC, Thomason JC: Oxidative stress: Comparison of species specific and tissue specific effects in the marine bivalves Mytilus edulis (L.) and Dosinia lupinus (L.). Comp Biochem Physiol 127B: 347-355, 2000
Mizukami Y, Yoshioka K, Morimoto S, Yoshida K: A novel mechanism of JNK1 activation. J Biol Chem 272: 16657-16662, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaitanaki, C., Kefaloyianni, E., Marmari, A. et al. Various stressors rapidly activate the p38-MAPK signaling pathway in Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lam.). Mol Cell Biochem 260, 119–127 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000026064.73671.91
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000026064.73671.91