Abstract
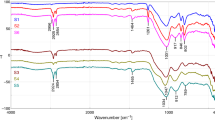
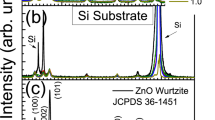
Coatings were obtained on borosilicate glass and fused silica substrates with thicknesses of up to 230 nm from solutions with compositions along the Zn--Sn--O tie line. The preparation of the sols was accomplished by combinatorial chemistry with a robotic sample processor using different ZnI I, SnI I and SnI V salts and alkoxides, as well as salts of different doping agents (e.g. SbV, TaV, InI II) dissolved in various solvents and additives. The films were made by spin-coating followed by a thermal treatment in air, inert or reducing atmosphere at temperatures up to 1000°C. Except for a few cases, mixed crystalline phases of ZnO, SnO2 and ZnSnO3 or Zn2SnO4 are usually observed within the range 0.4 < [Zn]/([Zn] + [Sn]) < 0.75. Pure Zn2SnO4 and ZnSnO3 coatings exhibit good optical properties with a haze <0.2% and a transmission in the visible range >85%. In contrast to literature, results obtained for similar coatings by sputtering and pulsed laser deposition, all the sol–gel coatings showed a high resistivity of ρ > 3 Ωcm even after a forming gas treatment and/or doping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Minami, Material Res. Soc. Bull. 25,38(2000).
D.L. Young, T.J. Coutts, and D.L. Williamson, Material Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 666, F3.8.1 (2001
J. Perkins, J. del Cueto, J. Alleman, C. Warmsingh, B. Keyes, L. Gedvilas, P. Parilla, B. To, D. Readey, and D.S. Ginley, Thin Solid Films 411, 152 (2002).
C.M. Cardile, A.J. Koplick, R. McPherson, and B.O. West, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 8, 370 (1989).
M. Jayachandran, B. Subramanian, M.J. Chockalingam, and A.S. Lakshmanan, Bull. Materials Sci. 17, 989 (1994).
T. Sei, Y. Nomura, and T. Tsuchiya, J. Non-Crystalline Solids 218, 135 (1997).
W.S. Dabney, N.E. Antolino, B.S. Luisi, A.P. Richard, and D.D. Edwards, Thin Solid Films, 411, 192 (2002).
I. Stambolova, K. Konstantinov, M. Khristova, and P. Peshev, Phys. Status Solidi a-Appl. Res. 167, R11 (1998).
G. Fu, H. Chen, Z.X. Chen, J.X. Zhang, and H. Kohler, Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical 81, 308 (2002).
E. Ruf, Deutsches Patentamt, DE4005135 A1, Deutschland, 1990, p. 1.
M.J. Hampden-Smith, T.A. Wark, and C.J. Brinker, Coord. Chem. Rev. 112,81(1992).
D.L. Young, Dissertation Thesis, Colorado School of Mines (Golden), 2000.
A.A. Al-Shahrani, S. Abboudy, and A.W. Brinkman, J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 29, 2165 (1996).
G.B. Palmer, K.R. Poeppelmeier, and T.O. Mason, J. Solid State Chem. 134, 192 (1997).
A.A. Al-Shahrani, Phys. Low-Dimens. Struct. 3/4,67(2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurz, A., Aegerter, M. Transparent Conducting Films in the Zn--Sn--O Tie Line. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 31, 267–271 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JSST.0000048001.35242.4b
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JSST.0000048001.35242.4b