Abstract
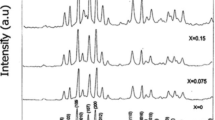
The phase diagram of the cuprate superconductors at low doping and low temperatures in the non-superconducting state is dominated by magnetic correlations. When increasing the hole concentration in the CuO2-planes from zero an antiferromagnetic (AF) insulating phase is followed for hole concentrations greater than approximately 0.08 by the superconducting phase. For the range of doping in between the situation is less clear and several models exist. For Bi2Sr2Y x Ca1−xCu2O8 in the range of Y-concentrations 0.9 < x < 0.0 the evolution of the electronic structure starting from the AF phase at x = 0.9, which in this respect can be regarded as the parent compound of the superconducting phase, and its gradual development into the superconducting range can be studied on one system. In this series the CuO2-planes are kept embedded in a nearly identical environment for each hole concentration. Especially the results from the AF phase deviate from former reports attained mainly from oxychlorides.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
C. Dürr, S. Legner, R. Hayn, S. V. Borisenko, Z. Hu, A. Theresiak, M. Knupfer, M. S. Golden, J. Fink, S. Haffner, F. Ronning, Z.-X. Shen, H. Eisaki, S. Uchida, C. Janowitz, R. Müller, R. L. Johnson, K. Rossnagel, G. Reichardt, Phys. Rev. B 63 014505 (2000) and references therein.
T. Tohyama and S. Maekawa, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 13 R17 (2001).
C. Janowitz, R. Müller, T. Plake, A. Müller, A. Krapt, H. Dwelk, and R. Manzke, Physica B 259 1134 (1999).
C. Janowitz, R. Müller, T. Plake, Th. Böker, and R. Manzke J. Electr. Spectr. Relat. Phen. 105 43 (1999).
K. Roβnagel, L. Kipp, M. Skibowski, and S. Harm, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 467 1485 (2001).
D. S. Marshall, D. S. Dessan, A. G. Loeser, C. H. Park, A. Y. Matsnnra, J. N. Eckstein, I. Bozovic, P. Fournier, A. Kapitulnik, W. E. Spices, Z. X. Shen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 4841 (1996); A. G. Loeser, Z. X. Shen, D. S. Dessan, D. S. Marshall, C. H. Park, P. Fournier, A. Kapitulnik, Science 273 3235 (1996).
P. Aebi, J. Osterwalder, P. Schwaller, and L. Schlapbach, Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 17 (1994).
B. O. Wells, Z. X. Shen, A. Matsuura, D. M. King, M. A. Kastner, M. Geven, and R. J. Birgenean, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 6 (1995).
V. Gavrichkov, A. Borisov, and S. G. Ovchinnikov, Phys. Rev. B 64 235124 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janowitz, C., Seidel, U., Unger, RS. et al. Evolution of the Electronic Structure of Y-Bi-2212 from the Antiferromagnetic to the Superconducting Regime. Journal of Superconductivity 17, 49–52 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOSC.0000011839.86643.9f
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOSC.0000011839.86643.9f