Abstract
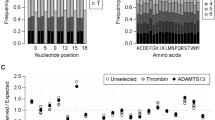
We have developed a substrate-phage approach for examining the substrate specificities of an important group of proteases involved in apoptosis—the caspases. After establishing selection conditions with caspases-3 and caspase-8 vs control substrate-phage, we sorted X4 and X6 diversity libraries, identified consensus motifs that agree with previously defined caspase substrate motifs, confirmed the selection of active substrates using synthetic peptide rate assays under a range of buffer conditions, and compared kinetic parameters for selected substrates. The libraries produced some variations on the canonical motifs. From caspase-3 selections, a phage-derived synthetic peptide, DLVD, was hydrolyzed up to 170% faster than the canonical substrate DEVD. The P4 Asp residue was essential for good protease-sensitivity, but even substrates with substitutions at P4 were selected by phage and shown to be hydrolyzed. Caspase-8 selections, as expected, yielded predominantly clones containing a Glu at P3. In this case, the most frequent phage-derived peptide, LEVD, was cleaved at a rate of only 20% of the canonical caspase-8 substrate LETD. However, based on substitutions observed in the phage selectants at P4, a substrate peptide, AETD, was designed and shown to be hydrolyzed up to 160% faster than LETD. We consider factors that may contribute to differences in caspase substrate-phage selections vs synthetic peptide studies on the caspases, and suggest that the two approaches may offer complementary information.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Back, S. H., Shin, S., and Jang, S. K. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277: 27200–27209.
Barry, M. A., and Eastman, A. (1992). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 186: 782–789.
Dall'Acqua, W., Halin, C., Rodrigues, M. L., and Carter, P. (1999). Protein Eng. 12: 981–987.
Earnshaw, W. C., Martins, L. M., and Kaufmann, S. H. (1999). Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68: 383–424.
Engelman, D. M., Steitz, T. A., and Goldman, A. (1986). Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 15: 321–353.
Ethell, D. W., Bossy-Wetzel, E., and Bredesen, D. E. (2001). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1541: 231–238.
Galloway, C. J., Dean, G. E., Marsh, M., Rudnick, G., and Mellman, I. (1983). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 80: 3334–3338.
Garcia-Calvo, M., Peterson, E. P., Rasper, D. M., Vaillancourt, J. P., Zamboni, R., Nicholson, D. W., and Thornberry, N. A. (1999). Cell Death Differ. 6: 362–369.
Germain, M., Affar, E. B., D'Amours, D., Dixit, V. M., Salvesen, G. S., and Poirier, G. G. (1999). J. Biol. Chem. 274: 28379–28384.
Harris, J. L., Backes, B. J., Leonetti, F., Mahrus, S., Ellman, J. A., and Craik, C. S. (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 7754–7759.
Kipp, M., Schwab, B. L., Przybylski, M., Nicotera, P., and Fackelmayer, F. O. (2000). J. Biol. Chem. 275: 5031–5036.
Kuida, K., Zheng, T. S., Na, S., Kuan, C., Yang, D., Karasuyama, H., Rakic, P., and Flavell, R. A. (1996). Nature 384: 368–372.
Lowman, H. B., and Wells, J. A. (1993). J. Mol. Biol. 234: 564–578.
Lowman, H. B. (1998). Methods Mol. Biol. 87: 249–264.
Matthews, D. J., Goodman, L. J., Gorman, C. M., and Wells, J. A. (1994). Protein Sci. 3:1197–1205.
Matthews, D. J., and Wells, J. A. (1993). Science 260: 1113–1117.
Mittl, P. R. E., Di Marco, S., Krebs, J. F., Bai, X., Karanewsky, D. S., Priestle, J. P., Tomaselli, K. J., and Grutter, M. G. (1997). J. Biol. Chem. 272: 6539–6547.
Moretti, A., Weig, H. J., Ott, T., Seyfarth, M., Holthoff, H. P., Grewe, D., Gillitzer, A., Bott-Flugel, L., Schomig, A., Ungerer, M., and Laugwitz, K. L. (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 99: 11860–11865.
Nicholson, D. W., Ali, A., Thornberry, N. A., Vaillancourt, J. P., Ding, C. K., Gallant, M., Gareau, Y., Griffin, P. R., Labelle, M., Lazebnik, Y. A., et al.(1995). Nature 376: 37–43.
Salvesen, G. S. (2002). Essays Biochem. 38: 9–19.
Samejima, K., Svingen, P. A., Basi, G. S., Kottke, T., Mesner, P. W., Jr., Stewart, L., Durrieu, F., Poirier, G. G., Alnemri, E. S., Champoux, J. J., Kaufmann, S. H., and Earnshaw, W. C. (1999). J. Biol. Chem. 274: 4335–4340.
Schechter, I., and Berger, A. (1967). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 27: 157–162.
Slee, E. A., Adrain, C., and Martin, S. J. (2001). J. Biol. Chem. 276: 7320–7326.
Stennicke, H. R., Renatus, M., Meldal, M., and Salvesen, G. S. (2000). Biochem. J. 350: 563–568.
Stennicke, H. R., and Salvesen, G. S. (2000). Methods Enzymol. 322: 91–100.
Talanian, R. V., Quinlan, C., Trautz, S., Hackett, M. C., Mankovich, J. A., Banach, D., Ghayur, T., Brady, K. D., and Wong, W. W. (1997). J. Biol. Chem. 272: 9677–9682.
Thornberry, N. A., Chapman, K. T., and Nicholson, D. W. (2000). Methods Enzymol. 322: 100–110.
Thornberry, N. A., Rano, T. A., Peterson, E. P., Rasper, D. M., Timkey, T., Garcia-Calvo, M., Houtzager, V. M., Nordstrom, P. A., Roy, S., Vaillancourt, J. P., Chapman, K. T., and Nicholson, D. W. (1997). J. Biol. Chem. 272: 17907–17911.
Uren, A. G., O'Rourke, K., Aravind, L. A., Pisabarro, M. T., Seshagiri, S., Koonin, E. V., and Dixit, V. M. (2000). Molec. Cell 6: 961–967.
Watt, W., Koeplinger, K. A., Mildner, A. M., Heinrikson, R. L., Tomasselli, A. G., and Watenpaugh, K. D. (1999). Struct. Fold Des. 7: 1135–1143.
Woo, M., Hakem, R., Soengas, M. S., Duncan, G. S., Shahinian, A., Kagi, D., Hakem, A., McCurrach, M., Khoo, W., Kaufman, S. A., Senaldi, G., Howard, T., Lowe, S. W., and Mak, T. W. (1998). Genes Dev. 12: 806–819.
Zheng, T. S., Hunot, S., Kuida, K., and Flavell, R. A. (1999). Cell Death Differ. 6: 1043–1053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lien, S., Pastor, R., Sutherlin, D. et al. A Substrate-Phage Approach for Investigating Caspase Specificity. J Protein Chem 23, 413–425 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOPC.0000039555.92058.51
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOPC.0000039555.92058.51