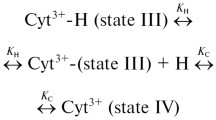Abstract
We have carried out a systematic investigation of salts- and alcohols-induced conformational alterations on the trifluoroacetic acid (TFA)-treated ferricytochrome c by soret absorption spectroscopy, far UV circular dichroism (CD), tryptophan fluorescence, and 1-anilino-8-naphthalene sulfonate (ANS) binding. TFA induces the unfolding of native cytochrome c obtained from horse heart leading to loss of secondary structure. The addition of increasing concentration of salts and alcohols leads to increase in MRE value at 222 and 208 nm indicating an increase in the α-helical content leading to formation of compact dimensional structure. Cytochrome c is a heme protein in which the resonance energy of tryptophan is transferred to heme resulting in quenched tryptophan fluorescence. Addition of alcohols leads to increase in tryptophan and ANS fluorescence. The tryptophan and ANS fluorescence in case of salts shows decreased fluorescence intensity. TFA-induced unfolded cytochrome c showed the soret absorption maximum at 394 nm. However, an intermediate state in presence of alcohols and salts showed the absorption maxima at 398 nm and 402 nm, respectively. Among all the salts and alcohols studied, K3Fe(CN)6 and butanol were found to be most effective as examined by the above-mentioned spectroscopic techniques. The order of effectiveness of alcohols was found to be butanol > propanol > ethanol > methanol. The following effective trend in the case of salts was obtained: K3Fe(CN)6 > K2SO4>KClO4 > KCl. These results suggest that alcohols induce an intermediate with molten globule–like conformation on the TFA unfolded state, whereas salts induce a refolded intermediate approaching native-like conformation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, A., Madhusudana, K. P., and Bhakuni, V. (2000). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1480: 201–210.
Antalik, M., and Sedlak, E. (1999). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1434: 347–355.
Barrick, D., and Baldwin, R. L. (1993). Protein Sci. 2: 869–876.
Chen, Y. H., Yang, J. T., and Martinez, H. M. (1972). Biochemistry. 11: 4120–4131.
Dyson, H. J., and Beattie, J. K. (1982). J. Biol. Chem. 257: 2267–2273.
Davis Searles, P. R., Morar, A. S., Saunderes, A. J., Eri, D. A., and Pielak, G. J. (1998). Biochemistry 37: 17048–17053.
Fink, A. L., Calciano, C. T., Goto, Y., Kurotsv, T., and Palleros, D. R. (1994). Biochemistry 33: 12504–12511.
Gekko, H., and Ito, H. (1990). J. Biochem. 109: 572–577.
Gekko, K., and Timasheff, S. N. (1981). Biochemistry 20: 4677–4686.
Gupta, P., Khan, R. H., and Saleemuddin, M. (2003). Arch Biochem. Biophys. 413: 199–206.
Goto, Y., and Nishikiori, S. (1991). J. Mol. Biol. 222: 679–686.
Goto, Y., Calciano, L. J., and Fink, A. L. (1990a). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 87: 573–577.
Goto, Y., Takahashi, N. and Fink, A. L. (1990b) Biochemistry 29: 3480–3488.
Hamada, D., Hoshino, M., Kataoka, M., Fink, A. L., and Goto, Y. (1993). Biochemistry 32: 10351–10358.
Hiramatsu, K., and Yang, J. T. (1983). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 743: 106–114.
Haq, S. K., Rasheedi, S., and Khan, R. H. (2002). Eur. J. Biochem. 269: 47–52.
Haq, S. K., Ahmad, M. F., and Khan, R. H. (2003). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 303: 685–692.
Hagihara, Y., Tan, Y., and Goto, Y. (1994). J. Mol. Biol. 237: 336–348.
Jeng, M. F., Englander, S. W., Elove, G. A., Wand, A. J., and Roder, H. (1990). Biochemistry 29: 10433–10437.
Jordan, T., Eads, J. C., and Spiro, T. G. (1995). Protein Sci. 4: 716–728.
Khan, F., Khan, R. H., and Muzammil, S. (2000). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1481: 229–236.
Kataoka, M., Hagihara, Y., Mihara, K., and Goto, Y. (1993). J. Mol. Biol. 229: 591–596.
Kamatari, Y. O., Takashi, K., Kataoka, M., and Akasaka, K. (1996). J. Mol. Biol. 259: 512–523.
Marmorino, J. L., and Pielak, G. J. (1995). Biochemistry 34: 3140–3143.
Marmorino, J. L., Lehti, M., and Pielak, G. J. (1998). J. Mol. Biol. 275: 379–388.
Naseem, F., Khan, R. H., Haq, S. K., and Naeem, A. (2003). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1649: 164–170.
Ptitsyn, O. B. (1995). Adv. Protein Chem. 47: 83–229.
Ptitsyn, O. B. (1996). Nat. Struct. Biol. 3: 488–490.
Pascher, T., Winkler, J. P., and Grey, H. B. (1996). Science 271: 1558–1560.
Santucci, R., Bongiovanni, C., Mei, G., Ferri, T. P., Polizio, F., and Desideri, A. (2000). Biochemistry 39: 12632–12638.
Santucci, R., Polizio, F., and Desideri, A. (1999). Biochemie 81: 745–751.
Stryer, L. (1968). Science 162: 526–540.
Williams, G., Moore, G. R., and R. J. P. (1985). Comments Inorg. Chem IV: 55–98.Author: Please Supply Missing Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naeem, A., Akram, M. & Khan, R.H. Conformational States of Trifluoroacetic Acid–Treated Cytochrome c in the Presence of Salts and Alcohols. J Protein Chem 23, 185–195 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOPC.0000026414.34366.33
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOPC.0000026414.34366.33