Abstract
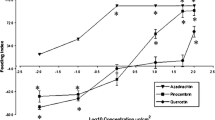
The phagostimulatory sensitivity of diabroticite (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae, Galerucinae) species to cucurbitacins is not correlated with Cucurbitaceae specialization, indicating that other factors, including the absence of feeding deterrents, may influence host–plant affinities among these beetles. Quinoline, indole, and isoquinoline alkaloids and sesquiterpene lactones believed to antagonize γ-aminobutyric acid/glycine Cl− ionophores mediating chemoreception were tested on squash blossom disks for antifeedant activity to four diabroticite species with different host plant specializations. Most alkaloids were antifeedant below 30 nmol/disk. Antifeedant concentrations of sesquiterpene lactones were higher than alkaloids for all species. Oligophagous Diabrotica virgifera virgifera was more sensitive to quinoline alkaloids than polyphagous D. undecimpuntata howardi. Diabrotica virgifera virgifera was also more sensitive to the indole alkaloids strychnine, brucine, eburnamonine, and vincamine than D. u. howardi. The closely related D. barberi had sensitivities similar to those of D. v. virgifera but the more distantly related Acalymma vittatum was less sensitive to the antifeedants than D. v. virgifera The isoquinoline alkaloid hydrastine was uniformly antifeedant to all diabroticites. All the GABA/glycine neurotoxicams tested against diabroticites were feeding deterrents and suggest that beetles share a common antifeedant mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
BERNAYS, E. A., and CHAPMAN, R. F. 1977. Deterrent chemicals as a basis of oligophagy in Locusta migratoria (L.). Ecol. Entomol. 2:1–18.
BERNAYS, E. A., and CHAPMAN, R. F. 1994. Host Plant Selection by Phytophagous Insects. Chapman and Hall, New York, 312 pp.
CHOU, J.-C., and MULLIN, C. A. 1993. Distribution and antifeedant associations of sesquiterpene lactones in cultivated sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) on western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte). J. Chem. Ecol. 19:1439–1452.
CHYB, S., EICHENSEER, H., HOLLISTER, B., MULLIN, C. A., and FRAZIER, J. L. 1995. Identification of sensilla involved in taste mediation in adult western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte). J. Chem. Ecol. 21:313–329.
COTTEE, P. K., BERNAYS, E. A., and MORDUE, A. J. 1988. Comparisons of deterrence and toxicity of selected secondary plant compounds to an oligophagous and polyphagous acridid. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 46:241–247.
DETHIER, V. G. 1980. Evolution of receptor sensitivity to secondary plant substances with special reference to deterrents. Am. Nat. 115:45–66.
DETHIER, V. G., and BOWDAN, E. 1989. The effect of alkaloids on sugar receptors and the feeding behaviour of the blowfly. Physiol. Entomol. 14:127–136.
DETZEL, A., and WINK, M. 1993. Attraction, deterrence or intoxication of bees (Apis mellifera) by plant allelochemicals. Chemoecology 4:8–18.
EICHENSEER, H., and MULLIN, C. A. 1996. Maxillary appendages used by western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera, to discriminate between a phagostimulant and-deterrent. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 78:237–242.
FRAZIER, J. F., and CHYB, S. 1995. Use of feeding inhibitors in insect control, pp. 364–381, in G. deBoer and R. F. Chapman (eds.). Regulatory Mechanisms of Insect Feeding. Chapman and Hall, New York.
HOUSER, J. S., and BALDUF, W. V. 1925. The striped cucumber beetle, Diabrotica vittata F. Bull. Ohio Agr. Exp. Stat. No. 388.
JAIN, D. C., and TRIPATHI, A. K. 1993. Potential of natural products as insect antifeedants. Phytother. Res. 7:327–334.
JERMY, T. 1966. Feeding inhibitors and food preference in chewing phytophagous insects. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 9:1–12.
JERMY, T. 1990. Prospects of antifeedant approach to pest control—A critical review. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:3151–3166.
KRUG, E., and PROKSCH, P. 1993. Influence of dietary alkaloids on survival and growth of Spodoptera littoralis. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 21:749–756.
KRYSAN, J. L. 1986. Introduction: Biology, distribution, and identification of pest Diabrotica, pp. 1–23, in J. L. Krysan and T. A. Miller (eds.). Methods for the Study of Pest Diabrotica. Springer, New York.
LANDIS, D. A., and GOULD, F. 1989. Investigating the effectiveness of feeding deterrents against the southern corn rootworm, using behavioral bioassays and toxicity testing. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 51:163–174.
METCALF, R. L., METCALF, R. A., and RHODES, A. M. 1980. Cucurbitacins as kairomones for Diabroticite beetles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:3769–3772.
MITCHELL, B. K. 1988. Adult leaf beetles as models for exploring the chemical basis of host plant recognition. J. Insect Physiol. 34:213–225.
MULLIN, C. A., ALFATAFTA, A. A., HARMAN, J. L., SERINO, A. A., and EVERETT, S. L. 1991. Corn rootworm feeding on sunflower and other compositae: Influence of floral terpenoid and phenolic factors, pp. 278–292, in P. A. Hedin (ed.). Naturally Occurring Pest Bioregulators, ACS Symposium Series No. 449. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
MULLIN, C. A., MASON, C. H., CHOU, J.-C., and LINDERMAN, J. R. 1992. Phytochemical antagonism of γ-aminobutyric acid based resistances in Diabrotica, pp. 288–308, in C. A. Mullin and J. G. Scott (eds.). Molecular Mechanisms of Insecticide Resistance: Diversity Among Insects, ACS Symposium Series No. 505. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
MULLIN, C. A., CHYB, S., EICHENSEER, H., HOLLISTER, B., and FRAZIER, J. L. 1994. Neuroreceptor mechanisms in insect gustation: a pharmacological approach. J. Insect Physiol. 40:913–931.
SCHNEIDER, D., and WINK, M. 1990. Fate of plant-derived secondary metabolites in three moth species (Syntomis mogadorensis, Syntomeida epilais, and Creatonotos transiens). J. Comp. Physiol. B 160:389–400.
SCHOONHOVEN, L. M. 1982. Biological aspects of antifeedants. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 31:57–69.
SCHOONHOVEN, L. M., BLANEY, W. M., and SIMMONDS, M. S. J. 1992. Sensory coding of feeding deterrents in phytophagous insects, pp. 59–79, in E. A. Bernays (ed.). Insect-Plant Interactions Vol 4. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
SIMMONDS, M. S. J., BLANEY, W. M., DELLE MONACHE, F., and MARININ BETTOLO, G. B. 1990. Insect antifeedant activity associated with compounds isolated from species of Lonchocarpus and Tephrosia. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:365–380.
TALLAMY, D. W., and KRISCHIK, V. A. 1989. Variation and function of cucurbitacins in Cucurbita: An examination of current hypotheses. Am. Nat. 133:766–786.
WINK, M. 1993. Allelochemical properties or the raison d'être of alkaloids, pp. 1–118, in G. A. Cordell (ed.). The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Pharmacology, Vol. 43. Academic, San Diego, CA.
XIE, Y. S., ARNASON, J. T., PHILOGENE, B. J. R., LAMBERT, J. D. H., KAMINSKI, J., MORAND, P., TIMMINS, G., and WERSTIUK, N. H. 1991. Effects of azadirachtin on the western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera (LeConte) (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). Can. Entomol. 123:707–710.
XIE, Y. S., ARNASON, J. T., PHILOGENE, B. J. R., ATKINSON, J., and MORAND, P. 1992. Behavioral responses of western corn rootworm larvae to naturally occurring and synthetic hydroxamic acids. J. Chem. Ecol. 18:945–957.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eichenseer, H., Mullin, C.A. Antifeedant Comparisons of GABA/Glycinergic Antagonists for Diabroticite Leaf Beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J Chem Ecol 23, 71–82 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOEC.0000006346.94240.f9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOEC.0000006346.94240.f9