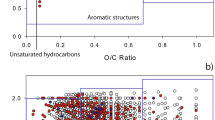
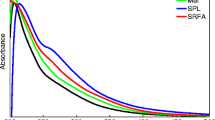
Abstract
In this contribution we present to our knowledge the first investigations of macromolecular, often called humic-like substances (HULIS) in cloud water samples and compare them with water-soluble extracts from atmospheric PM2.5, soils and waters to study its possible origin. Chemical analysis was done using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with UV and diode array detector, and HPLC coupled with ESI-MS (electrospray ionization mass spectrometer). The data have been treated by principle component analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis to state similarities and/or differences between different types of samples. Our results show that the content of organic and inorganic species is distinctly different in smaller and larger droplets suggesting varying origin. We conclude that smaller droplets are formed more from organic containing condensation nuclei (CCN) and larger droplets more from inorganic containing CCN organic compounds. Putting all experimental findings together we state that HULIS in cloud water—and consequently in particulate CCN precursors—are produced in an atmospheric polymerization process from low molecular weighted organics of different origin. Evidence is found that anthropogenic sources contribute to this pathway. Cloud drops may act as reactor in this HULIS formation process but more likely are gas-phase or gas-to-particle interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bank, S. and Castillo, R., 1987: Analysis of organic matter from cloud particles, Geophys. Res. Lett. 1 4, 210–212.
Bauer, H., Giebl, H., Hitzenberger, R., Kasper-Giebl, A., Reischl, G., Zibuschka, F., and Puxbaum, H., 2003: Airborne bacteria as cloud condensation nuclei, J. Geophys. Res. 10 8(D21), 4658, doi:10.1029/2003JD003545, 2003.
Charlson, R. J., Lovelock, J. E., Andreae, M. O., and Warren, S. G., 1987: Oceanic phytoplankton, atmospheric sulphur, cloud albedo, and climate, Nature 32 6, 655–661.
Chen, Z., Wang, Y., Lu, M., Yang, H., and Zhang, Y., 1991: The role of atmospheric organic compounds in the formation of acid rain, Environ. Chem. (Chines e) 1 0, 1–13.
Corrigan, C. E. and Novakov, T., 1999: Cloud condensation nucleus activity of organic compounds: A laboratory study, Atmos. Environ. 3 3, 2662–2668.
Decesari, S., Facchini, M. C., Matta, E., Mircea, M., Fuzzi, S., Chuhtai, A. R., and Smith, D. M., 2002: Water soluble org anic compounds formed by oxidation of soot,Atmos. Environ. 3 6, 1827–1832.
Ellison, G. B., Tuck, A. F., and Vaida, V., 1999: Atmospheric processing of organic aerosol, J. Geophys. Res. 10 4, 11633–11641.
Facchini, M. C., 2001:Organic compounds in clouds: Present knowledge and future perspectives, IGACtivities Newsletter 2 3, 10–13.
Facchini, M. C., Fuzzi, S., Zappoli, S., Andracchio, A., Gelencsér, A., Kiss, G., Krivácsy, Z., Mészáros, E., Hansson, H.-C., Alsberg, T., and Zebuehr, Y., 1999: Partitioning of the organic aerosol component between fog droplets and interstitial air, J. Geophys.l Res. 10 4, 26821–26832.
Feng, J., Prümke, H.-J., Fischer, T., and Möller, D., 2000: Investigation of humic matter with HPLC-UV and mass spectrometry, Paper presented at 7th International Conference on Carbonaceous Particles in the Atmosphere, San Juan, Puerto Rico.
Fuzzi, S., Decesari, S., Facchini, M. C., and Matta, E., 2001: A simplified model of the water soluble organic component of atmospheric aerosols, Geophysl Res. Lett. 2 0, 4079–4082.
Gelencsér, A., Hoffer, A., Krivácsy, Z., Kiss, G., Molnár, A., and Mészáros, E., 2002: On the possible origin of humic matter in fine continental aerosol, J. Geophys. Re s. 10 7, D12, doi:10.1029/2001JD001299.
Gorbunov, B., Hamilton, R., Clegg, N., and Toumi, R., 1998: Water nucleation on aerosol particles containing both organic and soluble inorganic substances, Atmos. Res. 4 7, 271–283.
Gulbrand, L., Jorgen, G., and Nina, G., 1977: Organic micropollutants in precipitation in Norway, Atmos. Environ. 1 1, 1007–1014.
Havers, N., Burba, P., Lambert, P., and Klockow, D., 1998: Spectroscopic characterization of humic-like substances in airborne particulate matter, J. Atmos. Chem. 2 9, 45–54.
Hudson, J. G., 1991: Observation of anthropogenic cloud condensation nuclei, Atmos. Env. 25 A, 2449–2451.
Jaenicke, R., 1982: Atmosphärische Spurenstoffe Ergebnisse aus dem gleichnamigen Son-derforschungsbereich, in Reihe Sonderforschungsbereiche (DFG),Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 443 pp.
Jennings, S. G., 2000: Atmospheric aerosol measurements at Mace Head, Ireland, J. Aerosol Sci. 3 1, S580–S583.
Junge, C. E., 1957:Chemical analysis of aerosol particles and of gas traces on the island of Hawaii, Tellus 9, 528–537.
Junge, C. E., 1963: Air Chemistry and Radioactivit y, Academic Press, New York and London.
Kalberer, M., Paulson, D., Sax, M., Steinbacher, M., Dommen, J., Prevot, A. S. H., Fisseha, R., Weingartner, E., Frankevich, V., Zenobi, R., and Baltensperger, U., 2004: Identification of poly-mers as major component of atmospheric organic aerosols, Science 30 3, 1659–1662.
Keen, W. C., Galloway, J. N., and Holden, J. D. J., 1983: Measurement of weak organic acidity in precipitation from remote area of the world, J. Geophys. Res. 8 8, 5122–5130.
Kimitaka, K. and Paplan, I. R., 1984: Capillary gas chromatography determination of volatile organic acids in rain and fog samples, Anal. Chem. 5 6, 1616–1620.
Kiss, G., Tombácz, E., Varga, B., Alsberg, T., and Persson, L., 2003: Estimation of the average molecular weight of humic-like substances isolated from fine atmospheric aerosol, Atmos. Environ. 3 7, 3783–3794.
Krivácsy, Z., Kiss, G., Varga, B., Galambos, I., Sarvari, Z., Gelencsér, A., Molnar, A., Fuzzi, S., Facchini, M. C., Zappoli, S., Andracchio, A., Alsberg, T., Hansson, H. C., and Persson, L., 2000: Study of humic-like substances in fog and interstitial aerosol by size-exclusion chromatography and capillary electrophoresis, Atmos. Environ. 3 4, 4273–4281.
Krivácsy, Z., Hoffer, A., Sárvári, Zs., Temesi, D., Baltensperger, U., Nyeki, S. D., Weingartner, E., Kleefeld, S., and Jennings, S. G., 2001: Role of organic and black carbon in the chemical com-position of atmospheric aerosol at European background sites, Atmos. Enviro n. 3 5, 6231–6244.
Likens, G. E., Edgerton, E. S., and Galloway, J. N., 1983: The composition and decomposition of organic carbon in precipitation, Tellus 35 B, 16–24.
Lüttke, J., Levsen, K., Acker, K., Wieprecht, W., and Möller, D., 1999: Phenols and nitrated phenols in clouds at Mt. Brocken. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 7 4, 69–99.
Matsumoto, G. and Hanya, T., 1980: Organic constituents in atmospheric fallout in the Tokyo area, Atmos. Environ. 1 4, 1409–1419.
Mászáros, E., 1968: The size distribution of water soluble particles in the atmosphere, Tellus 2 0, 443–448.
Mászáros, E., 1992: Structure of continental clouds before the industrial era: A mystery to be solved, Atmos. Environ. 26 A, 2469–2470.
Mászáros, E., Barcza, T., Gelencsér, A., Hlavay, J., Kiss, G., Krivácsy, Z., Molnar, A., and Polyak, K., 1997: Size distribution of inorganic and organic species in the atmospheric aerosol in Hungary, J. Aerosol Sci. 2 8, 1163–1175.
Möller, D., 1977: Atmosphärische chemische Reaktionen von Schwefeldioxid, Z. Che m. 1 7, 393–405.
Mukai, A. and Ambe, Y., 1986: Characterization of himic-like acid brown substance in airborne particulate matter and tentative identification of its origin, Atmos. Environ. 2 0, 813–819.
Norton, R. B., Roberts, J. M., and Huebert, B. J., 1983: Tropospheric oxalate, Geophys. Res. Lett. 1 0, 517–520.
Osan, J., de Hoog, J., Worobiec, A., Ro, C. U., Oh, K. Y., Szaloki, I., and Van-Grieken, R., 2001: Application of chemometric method for classification of atmospheric particles based on thin-window electron probe microanalysis data, Analytica Chemica Acta 44 6, 211–222.
Otto, M., 1997: Chemometrie-Statistik und Computereinsatz, in der Analyti k,Weinheim.
Przybylski, M. and Glocker, M. O., 1996: Elektrospray-Massenspektrometrie von biomakro-molekülkomplexen mit nichtkovalenten Wechselwirkungen-neue analytische Perspektiven f ür supramolekulare Chemie und molekulare Erkennungprozesse, Angew. Chem. 10 8, 878–899.
Rogge, W. F., Mazurek, M. A., Hildeman, L. M., and Gass, G. R., 1993: Quantification of organic urban aerosol at molecular level: Identification, abundance and reasonal variation, Atmos. Environ. 27 A, 1309–1330.
Saxena, P., Hildeman, L. M., Murry, P. H., and Seinfeld, J. H., 1995: Organics alter the atmospheric behaviour of hygroscopic particles, J. Geophys. Res. 10 0, 18755–18770.
Saxena, P. and Hildemann, L. M., 1996: Water-soluble organics in atmospheric particles: A critical review of the literature and application of thermodynamics to identify candidate compounds, J. Atmos. Chem. 2 4, 57–109.
Schell, D., Maser, R., Wobrock, W., Jaeschke, W., Georgii, H.-W., Kos, G. P. A., Arends, B. G., Beswick, K. M., Bower, K. N., and Gallagher, M. W., 1997: A two-stage impactor for fog droplet collection: Design and performance, Atmos. Enviro n. 3 1, 2671–2679.
Sempere, R. and Kawamura, K., 1994: Comparative distribution of dicarboxylic acids and related polar compounds in snow, rain and aerosol from urban atmosphere, Atmos. Environ. 2 8, 449–459.
Temesi, D., Molnar, A., Mészáros, E., Feczkó, T. Gelencsér, A. Kiss, G., and Krivásy, Z., 2001: Size resolved chemical mass balance of aerosl particles over rural Hungary, Atmos. Enviro n. 3 5, 4347–4355.
Twomey, S., 1991: Aerosol, clouds and radiation, Atmos. Environ. 25 A, 2435–2442.
Went, F. W., 1960: Blue haze in the atmosphere, Nature 18 7, 641–643.
Winkler, P., 1992: Design and calibration of a fog water collector. Instruments and observing method s. Report WMO/TD-No. 462, Geneve, pp. 17–21.
Woelki, G., Friedrich, S., Hanschmann, G., and Salzer, R., 1997: HPLC fractionation and structural dynamics of humic acids, Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 35 7, 548–552.
Xu, S. and Hu, M., 2000: The advances of water-soluble organic compounds in atmospheric particles, Res. Environ. Sci. (Chinese) 1 3, 50–53.
Yu, S., 2000: Role of organic acids (formic, acetic, pyruvic and oxalic) in the formation of cloud condensation nuclei (CCN): A review, Atmos. Res. 5 3, 185–217.
Zappoli, S., Andracchio, A., Fuzzi, S., Facchini, M. C., Gelencsér, A., Kiss, G., Krivácsy, Z., Molnar, A., Mészáros, E., Hansson, H. C., Rosman, K., and Zebuehr, Y., 1999: Inorganic, organic and macromolecular components of fine aerosol in different areas of Europe in relation to their water solubility, Atmos. Environ. 3 3, 2733–2743.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, J., Möller, D. Characterization of Water-Soluble Macromolecular Substances in Cloud Water. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry 48, 217–233 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOCH.0000044377.93748.e4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOCH.0000044377.93748.e4