Abstract
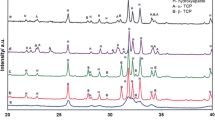
Temporary bone replacement materials on the basis of calcium phosphates and hydroxyapatite (HAP) are used in surgery for filling bone defects. Components which are able to control the nucleation and crystal growth of HAP through their functional groups and which can additionally activate bone cells may be helpful in the development of materials with enhanced remodelling in vivo. In this study, the influence of O-phospho-L-serine (PS) on the materials properties of calcium phosphate bone cement composites was investigated. For up to an addition of 25 mg/g PS a strong increase in the stability of the cements under load was determined. The material was studied by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. A more dense microstructure and a plate-like morphology of the HAP-crystals were detected in the modified composites compared with the non-modified samples. By X-ray powder diffraction an inhibition of the dissolution of α-tricalcium phosphate (α-TCP) and dicalciumphosphate anhydrous (DCPA) particles was found. α-TCP and DCPA are the main constituents of the cement precursor. The results of cell culture studies using rat calvaria osteoblasts demonstrate a good viability of the cells on the PS-modified material. Furthermore, the proliferation and differentiation were found to be enhanced on the PS-modified material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Mann, in “Biomineralisation -Principles and Concepts in Bioinorganic Materials Chemistry” (Oxford University Press, 2001).
W. T. Butler, A. L. Ridall and M. D. Mckee, in “Principles of Bone Biology” (Bilezikian, Academic Press, New York, 1996) 167.
B. Ganss, R. H. Kim and J. Sodek, Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 10 (1999) 79.
J. Sodek, B. Ganss and M. D. Mckee, ibid. 11 (2000) 279.
E. S. Sorensen, P. Horup and T. E. Petersen, Protein Sci. 4 (1996) 2040.
G. K. Hunter, P. V. Hauschka, A. R. Poole, L. C. Rosenberg and H. A. Goldberg, Biochem. J. 317 (1996) 59.
G. K. Hunter and H. A. Goldberg, ibid. 302 (1994) 175.
R. A. Saavedra, BioEssays 16 (1994) 913.
T. Uemura, A. Nemoto, Y. Liu, H. Kojima and J. Dong, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 17 (2001) 33.
A. L. Boskey, L. Speviak, E. Paschalis, S. B. Doty and M. D. Mckee, Calcif. Tissue Int. 71 (2002) 145.
T. Aoba and E. C. Moreno, J. Coll. Interface Sci. 106 (1985) 110.
D. N. Misra, ibid. 194 (1997) 249.
L. Benaziz, A. Barroug, A. Legrouri, C. Rey and A. Lebugle, ibid. 238 (2001) 48.
A. L. Boskey and B. L. Dick, Calcif. Tissue Int. 49 (1991) 193.
N. Spanos, P. G. Klepitsianis and P. G. Koutsoukoson, J. Coll. Interface Sci. 236 (2001) 260.
S. Dahlin, J. Angström and A. Linde, Eur. J. Oral. Sci. 106 (1998) 239.
N. L. Huq, K. J. Cross and E. C. Reynolds, J. Mol. Model 6 (2000) 35.
B. Knepper-Nicolai, A. Reinstorf, I. Hofinger, K. Flade, R. Wenz and W. Pompe, Biomol. Eng. 19 (2002) 227.
F. C. M. Driessens, I. Khairoun, M. G. Boltong and J. A. Planell, in Proceedings of the 10th Internatinal Symposium on Ceramics in Medicine (Seydel & Rey, Paris) 1997, p. 279.
J. H. Bradt, M. Mertig, A. Teresiak and W. Pompe, Chem. Mater. 11 (1999) 2694.
F. C. M. Driessens, M. G. Boltong, O. Bermudez and J. A. Planell, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 4 (1993) 503.
Standard Test Method for Time of Setting of Hydraulic-Cement Paste by Gillmore Needles, Document Number: ASTM C266-99, ASTM International, 01-Nov-1999.
Powder Diffraction File -cards of the International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD).
M. Roth, Anal. Chem. 43 (1971) 880.
U. Geißler, U. Hempel, C. Wolf, D. Scharnweber, H. Worch and K.-W. Wenzel, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 5 (2000) 752.
A. Scutt, A. Berg and H. Mayer, Anal. Biochem. 203 (1992) 290.
G. A. Currie, Br. J. Cancer 43 (1981) 335.
M. Tanahashi and T. Matsuda, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 34 (1997) 305.
M. S. Mohan and E. H. Abbott, Inorg. Chem. 17 (1978) 2203.
F. C. M. Driessens, J. A. Planell, M. G. Boltong, I. Khairoun and M. P. Ginebra, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part: H J. Eng. Med. 207 (1993) 87.
D. H. Kohn, M. Sarmadi, J. I. Helman and P. H. Krebsbach, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 60 (2002) 292.
C. Knabe, F. C. M. Driessens, J. A. Planell, R. Gildenhaar, G. Berger, D. Reif and R. Fitzner, ibid. 52 (2000) 498.
D. Becker, U. Geißler, U. Hempel, S. Bierbaum, D. Scharnweber, H. Worch and K.-W. Wenzel, ibid. 59 (2002) 516.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinstorf, A., Ruhnow, M., Gelinsky, M. et al. Phosphoserine – a convenient compound for modification of calcium phosphate bone cement collagen composites. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 15, 451–455 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSM.0000021119.14870.3d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSM.0000021119.14870.3d