Abstract
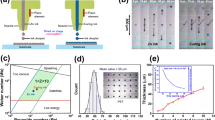
NdFeB films with thickness between 10 and 50 μm are prepared by screen printing of standard inks containing 70–80 wt % of NdFeB powder (MQP-B). The coarse MQ-powder is fine-milled to give a mean particle size of about 10 μm in order to obtain well-printable inks and homogeneous films. Typically, remanent inductions of 200–320 mT are obtained. The maximum loading of magnetic powder in the ink is increased to 85–90 wt % by optimizing the powder-particle packing. Mixtures of MQ-powders of different grain size were prepared in order to maximize the powder's tap density and reduce the interparticle volume. Inks prepared from such powder mixtures display an increased remanence of up to 500 mT. Screen-printed NdFeB thick films are important components for miniature actuators or micro-electromechanical systems. In miniature systems the magnetic component has to provide a strong field without having a large size. Therefore, the reported enhancement of the remanence of NdFeB inks for screen printing of magnetic thick films represents dramatic progress compared to standard NdFeB inks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Yuan, A. J. Williams, T. C. Shields, S. Blackburn, C. B. Ponton, J. S. Abell and I. R. Harris, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 247 (2002) 257.
B. Pawlowski and J. Topfer, J. Mater. Sci. (in press).
B. Pawlowski, S. Schwarzer, A. Rahmig and J. TOPFER, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 265 (2003) 337.
W. B. Fuller and S. E. Thomsen,Eng. News. Rec. 57 (1907) 599.
R. Litzow, Glastechn. Ber. 8 (1930) 149.
A. H. M. Andreasen and J. Anderson, Kolloid Z. 50 (1930) 217.
Product Catalogue, Magnequench International, Inc.
R. K. Mcgeary, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 44 (1961) 513.
J. E. Funk and D. R. Dinger, Interceram. 41 (1992) 10.
F. S. Ortega, R. G. Pileggi, P. Sepulveda and V.C. Pandolfelli, Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 78 (1999) 106.
E. Kallenbach, H. Kube, V. Zoppig, K. Feindt, R. Hermann and F. Beyer, Mechatronics 9 (1999) 769.
H. Kube, E. Kallenbach, B. Pawlowski and J. Topfer, in iProceedings of the Fourteenth ASPE Annual Meeting, Monterey, CA, USA (1999) 579.
J. Topfer, in Proceedings of the Fifth Symposium "Magnetoresistive Sensors: Basics, Preparation and Applications", 10./ 11.03.99, Wetzlar, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarzer, S., Pawlowski, B., Rahmig, A. et al. Permanent magnetic thick films from remanence optimized NdFeB-inks. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 15, 165–168 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSE.0000011356.95343.98
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSE.0000011356.95343.98