Abstract
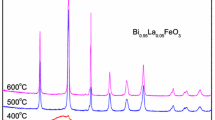
Polycrystalline samples of Bi-modified PLZT, [Pb0.92(La1−zBiz)0.08][Zr0.60Ti0.40]0.98O3 (abbreviated as PLBZT) for z = 0.0, 0.3, 0.6, 0.9 and 1 were prepared through a metal-alkoxide/sol-gel route. Preliminary X-ray diffraction study of the compounds confirmed the formation of single-phase tetragonal compounds. Scanning electron-microscopic (SEM) study of pellet samples of PLBZT shows uniform distribution of grains (spherical) throughout the sample surfaces. Detailed studies of dielectric parameters (dielectric constant, tangent loss) of PLBZT as a function of temperature (30 to 450°C) at 10 kHz reveal that the compounds have diffuse phase transitions. Large variation (first increase and then decrease) in dielectric constant and shift of transition temperature towards higher temperature side with increasing Bi concentration was also observed in PLBZT. The nature of variation of dc resistivity shows that the titled compounds have negative temperature coefficient of resistance (NTCR). Pyroelectric coefficient of the PLBZT compound (z = 0.0 to 1.0) increases with increase of Bi content in PLZT. The transition temperature obtained in this study is very much consistent with that obtained from our dielectric studies. Piezoelectric d 33 coefficient of the compound at 100 Hz was found to be 385, 272, 301, 248 and 291 pc/N for z = 0.0, 0.3, 0.6, 0.9 and 1 respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. H. Parker and A. F. Tasch, IEEE Circuits and Devices Mag 6 (1990) 17.
D. Stansfield, “Underwater Electroacoustic Transducers” (Bath University, Bath, United Kingdom, 1991).
M. Einat, D. Shur, E. Jerby and G. Rosenman, J. Appl. Phys. 89 (2001) 548.
K. K. Deb, Ferroelectrics 82 (1988) 45.
M. E. Lines and A. M. Glass, “Principles and Applications of Ferroelectrics and Related Materials” (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1977).
R. Ostertag, G. Rinn, G. Tunker and H. Schmidt, Electroceramics Feb. (1989) 41.
P. Roychoudhary and S. B. Deshmukh, Ind. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 17 (1981) 71.
S. L. Fu, S. Y. Cheng and C. C. Wei, Ferroelectrics 67 (1986) 93.
R. Lal, S. C. Sharma and R. Dayal, ibid. 100 (1989) 43.
K. L. Yadav and R. N. P. Choudhary, ibid. 141 (1993) 227.
S. R. Shannigrahi, R. N. P. Choudhary, H. N. Acharya and T. P. Sinha, J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 32 (1999) 1539.
K. L. Yadav and R. N. P. Choudhary, Bull. Pure Appl. Sci. 14 (1995) 23.
G. Yi, Z. Wu and M. Sawyer, J. Appl. Phys. 64 (1988) 2717.
P. Klug and L. E. Alexander, “X-ray Diffraction Procedure of Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials” (John Wiely and Sons, New York, 1974).
“Source Book of Pyroelectricity,” edited by S. B. Lang (Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, London, 1974).
E. Wu, Powd, An Interactive Powder Diffraction Data Interpration and Indexing Program, Ver 2.1, School of Physical Science Flinders University of South Australia Bedford Park S.A J042 AU.
B. N. Rolov, Sov. Phys. Solid State 6 (1965) 1676.
S. Miga and K. Wojeik, Ferroelectrics 100 (1987) 167.
V. M. Gurevich, “Electric conductivity of Ferroelectrics” (Israel Translation, Jerusalem-1971).
W. D. Kingery, “Introduction to Ceramics” (Wiely-Inter-sciences, New York, 1960).
E. H. Putley, “Semiconductors and Semimetals” (Academic Press, New York, 1970) Vol. 5, Chap. 6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, S., Choudhary, R.N.P. & Sinha, P.K. Ferroelectric phase transition in sol-gel derived Bi-doped PLZT ceramics. Journal of Materials Science 39, 3129–3135 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000025842.46451.64
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000025842.46451.64