Abstract
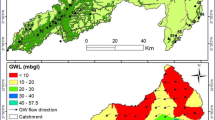
The salt and water balances at Konanki pilot area in Nagarjunasagar project right canal command in Andhra Pradesh State of India were analysed using SALTMOD. The model was calibrated by using two-year data collected in the pilot area. From the calibration, the leaching efficiencies of the root and transition zone were estimated as 65% and the out going natural sub-surface drainage was determined as 50 mm per year. The model predicts that the root zone soil water salinity will be reduced to 4, 3 and 2.5 dS/m (from an initial value of 11.5 dS/m) during the first, second and third seasons within six years after installation of the drainage system. Next, the situation prior to the installation of the drainage system was reconstructed using the model. Finally, sensitivity analyses were made to study the effects of varying drain depth, spacing and amount of irrigation water applied on root zone salinity and depth to water table. Here, the model predicted that closer than the present spacing or further deepening of the drains from the present depth of 1 m to 1.4 m will not have any better influence on the reduction of the root zone salinity than in the present situation. These simulations also suggested that by applying 80% of the present amount of irrigation water, the root zone salinity can be brought down to 5 and 4 dS/m by second and fourth years, respectively and this will in turn reduce the problem of water logging and salinity to some extent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreu L., Moreno F., Jarvis N.J. & Vachaud G. 1994. Application of the model MACRO to water movement and salt leaching in drained and irrigated marsh soils, Maismas, Spain. Agricultural Water Management 25: 71–88.
Andreu L., Jarvis N.J., Moreno F. & Vachaud G. 1996. Simulating the impact of irrigation management on the water and salt balance in drained marsh soils, Marismas, Spain. Soil Use and Management 12(3): 109–116.
Beekma J., Kelleners T.J., Boers Th.M. & Raza Z.I. 1995. Application of SWATRE to evaluate drainage of an irrigated field in the Indus Plain, Pakistan. In: L.S. Pereira et al. (Eds) Crop-Water-Simulation Models in Practice (pp 141–160). Wageningen Press, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Kelleners T.J. 1994. Use of SWATRE to simulate water and salt balance of an irrigated field in the Indus Plain of Pakistan. IWASRI Report 140. Lahore, Pakistan. 42 pp.
Kijne J.W. 1996. Water and salinity balances for irrigated agriculture in Pakistan. Research Report No. 6. International Irrigation Management Institute, Colombo, Sri Lanka. 17 pp.
NRSA 1996. Satellite assessment of water logging and soil salinity/alkalinity in Nagarjunasagar right canal command area Part-C. Assessment of water logging and soil salinity/alkalinity. National Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderabad, India. pp. 2–3.
Oosterbaan R.J. & Abu Senna M. 1989. Using SALTMOD to predict drainage and salinity in the Nile Delta. In: Annual Report (pp 63–74). ILRI, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Oosterbaan R.J. 2000. SALTMOD. Description of Principles, User Manual and Examples of Application. Special Report. ILRI, Wageningen, The Netherlands. 80 pp.
Rao K.V.G.K., Ramesh G., Chauhan H.S. & Oosterbaan R.J. 1992. Salt and Water Balance Studies to Evaluate Remedial Measures for Water Logged Saline Irrigated Soils (pp 267–277). Proc. of the 5th International Drainage Workshop, Lahore, Pakistan, ICID & CHD II.
Sarwar A. & Feddes R.A. 2000. Evaluating drainage design parameters for the Fourth Drainage Project, Pakistan by using SWAP model: Part II-modelling results. Irrigation and Drainage Systems 14: 281–299.
Satyanarayana T.V., Hema Kumar H.V., Raghu Babu M. & Srinivasulu A. (Eds). 2000. Design and construction of drainage systems at Konanki and Uppugunduru. Technical Bulletin No. 3. Indo-Dutch Network Project, Bapatla, India. 30 pp.
Singh Man, Bhattacharya A.K., Singh A.K. & Singh A. 2002. Application of SALTMOD in coastal clay soil in India. Irrigation and Drainage Systems 16: 213–231.
Singh O.P. 1993. Drainage Problems and Design Criteria for Land Drainage Systems (pp 204–218). Procs. of the National Workshop on 'Sustainable Irrigation in Saline environment' Feb. 17-19, CSSRI, Karnal, India.
Srinivasulu, A. 2002. Salt and water balance modelling of the data from Konanki pilot area. Deputation Report on Collaborative research carried out at ILRI, Wageningen, The Netherlands submitted to the Government of India, New Delhi, India. 23 pp.
Vanegas Chacon E.A. 1993. Using SALTMOD to predict desalinization in the Leziria Grande Polder, Portugal (pp 11–74). MSc. thesis. Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
WAPCOS. 1999. Study of water logging in five canal commands. Report. Volume VI. Nagarjunasagar right canal command area. Water and Power Consultancy Service Limited, New Delhi, India. pp. 75–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasulu, A., Sujani Rao, C., Lakshmi, G. et al. Model Studies on Salt and Water Balances at Konanki Pilot Area, Andhra Pradesh, India. Irrigation and Drainage Systems 18, 1–17 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:IRRI.0000019405.64105.c9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:IRRI.0000019405.64105.c9