Abstract
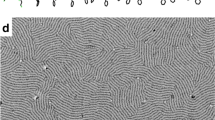
Synthesis of lamellar self-assemblies symmetric polystyrene–polybutylmethacrylate (PS–PBMA) copolymers, doped by magnetic nanoparticles was described. Self-assembly is a spontaneous process by which molecules and nanophase entities may materialize into organized aggregates or networks. As soon as particles are coated by a grafted PS layer, they can be confined in the PS layer of the polymeric smectic. The lamellar order was maintained up to volume fractions of particles of 25% as determined by transmission electron microscopy. This volume fraction may be increased by addition of the PS homopolymer to the structure or by increasing the molecular weight of the diblock copolymer.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Stix, G., Little Big Science, Sci. Am., 2001, vol. 285, no. 3, pp. 26–32.
Hamley, I.W., Nanostructure Fabrication Using Block Copolymers, Nanotechnology, 2003, vol. 14, pp. R3--R54.
Bates, F.S. and Fredrickson, G.H., Block Copolymer Thermodynamics: Theory and Experiment, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 1990, vol. 41, pp. 525–557.
Hamley, I.W., Physics of Block Copolymers, Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press, 1999.
Hadjichristidis, N., Pispas, S., and Floudas, G., Block Copolymers: Synthetic Strategies, Physical Properties, and Applications, New York: Wiley, 2003.
Hamley, I.W., Developments in Block Copolymer Science and Technology, Chichester: Wiley, 2003.
Matsen, M.W., The Standard Gaussian Model for Block Copolymers Melts, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2002, vol. 14, pp. R21–R47.
Hamley, I.W., Structure and Flow Behavior of Block Copolymers, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2001, vol. 13, pp. R643–R671.
Bates, F.S. and Fredrickson, G.H., Block Copolymers-Designer Soft Materials, Phys. Today, 1999, vol. 52, pp. 32–38.
Drolet, F. and Fredrickson, G.H., Optimizing Chain Bridging in Complex Block Copolymers, Macromole-cules, 2001, vol. 34, pp. 5317–5324.
Bohbot-Raviv, Y. and Wang, Z.G., Discovering New Ordered Phases of Block Copolymers, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2001, vol. 85, pp. 3428–3431.
Fabre, P., Casagrande, C., Veyssie, M., et al., Ferrosmectics: A New Magnetic and Mesoscopic Phase, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1990, vol. 64, no. 5, pp. 539–542.
Menager, C., Belloni, L., Cabuil, V., et al., Osmotic Equilibrium between an Ionic Magnetic Fluid and an Electrostatic Lamellar Phase, Langmuir, 1996, vol. 12, no. 14, pp. 3516–3522.
Rosensweig, R., Ferrohydrodynamics, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1985.
Mansky, P., Russell, T.P., Hawker, C.J., et al., Ordered Diblock Copolymer Films on Random Copolymer Brushes, Macromolecules, 1997, vol. 30, pp. 681--6813.
Coulon, G., Collin, B., Ausserre, D., et al., Islands and Holes on the Free Surface of Thin Diblock Copolymers Films: 1. Characteristics of Formation and Growth, J. Phys., 1990, vol. 51, pp. 2801–2809.
Coulon, G., Ausserre, D., and Russell, T.P., Interference Microscopy on Thin Diblock Copolymers Films, J. Phys., 1990, vol. 51, pp. 777–783.
Hamdoun, B., Ausserre, D., Joly, S., et al., New Nano-composite Materials, J. Phys. II, 1996, vol. 6, pp. 49--501.
Cabuil, V., Hochart, H., Perzynski, R., and Lutz, P.J., Synthesis of Cyclohexane Magnetic Fluids through Adsorption of End-Functionalized Polymers on Mag-netic Particles, Prog. Colloid. Polym. Sci., 1994, vol. 97, pp. 75–79.
Massart, R., Preparation of Aqueous Magnetic Liquid in Alkaline and Acidic Media, IEEE Trans. Magn., 1981, vol. 17, no. 2, p. 1247.
Bacri, J.C., Perzynski, R., Salin, D., et al., Magnetic Colloidal Properties of Ionic Ferrofluids, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1986, vol. 62, pp. 36–46.
Dubois, E., Cabuil, V., Massart, R., et al., Preparation and Properties of Monodisperse Magnetic Fluids, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1995, vol. 149, pp. 1–5.
Trent, J.S., Scheinbeim, J.I., and Couchman, P.R., Ruthenium Tetraoxide Staining of Polymers, Macromolecules, 1983, vol. 16, pp. 589–598.
Lauter-Pasyuk, V., Lauter, H.J., Ausserre, D., et al., Effect of Nanoparticle Size on the Internal Structure of Copolymer–Nanoparticles Composite Thin Films Stud-ied by Neutron Reflection, Physica B (Amsterdam), 1998, vol. 241, pp. 1092–1094.
Hamboun, B., Ausserre, D., Cabuil, V., and Joly, S., Composites copolymères–nanoparticule: I. Période-lamellaire dans le régime des “petites nanoparticules,” J. Phys. II, 1996, vol. 6, pp. 503–510.
Lauter-Pasyuk, V., Lauter, H.J., Ausserre, D., et al., Neutron Reflectivity Studies of Composite Nanoparticle Copolymer Thin Films, Physica B (Amsterdam), 1998, vol. 248, pp. 243–245.
Lefebure, S., Cabuil, V., Ausserre, D., et al., Lamellar Composite Magnetic Materials, Prog. Colloid. Polym. Sci., 1998, vol. 110, pp. 94–98.
Hamdoun, B., Ausserre, D., and Joly, S., Composites Copolymères–Nanoparticule: courbure, J. Phys. II, 1996, vol. 6, pp. 1–10.
Edrington, A.C., Urbas, A.M., DeRege, P., et al., Poly-mer-Based Photonic Crystals, Adv. Mater., 2001, vol. 13, pp. 421–425.
Fink, Y., Urbas, A.M., Bawendi, M.G., et al., Block Copolymers as Photonic Bandgap Materials, J. Light-wave Technol., 1999, vol. 17, no. 11, pp. 1963–1969.
Fink, Y., Thomas, E.L., Urbas, A., et al., Self Assembly Block Copolymer Structures as Photonic Crystals, Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, vol. 221, PHYS part 2, p. 36.
Fink, Y., Winn, J.N., Fan, S., et al., Dielectric Omnidirectional Reflector, Science, 1998, vol. 282, pp. 1679–1682.
Urbas, A., Sharp, R., Fink, Y., et al., Tunable Block Copolymer/Homopolymer Photonic Crystals, Adv. Mater., 2000, vol. 12, no. 11, pp. 812–814.
Bockstaller, M.R., Kolb, R., and Thomas, E.L., Metallodielectric Photonic Crystals Based on Diblock Copolymers, Adv. Mater., 2001, vol. 13, no. 23, pp. 1783–1786.
Hamboun, B., Composites Copolymères/Nanoparticules, PhD Thesis, Maine Univ., 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdoun, B. Lamellar Self-Assembly Nanostructured Magnetic Materials. Inorganic Materials 40, 949–954 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:INMA.0000041327.72483.ab
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:INMA.0000041327.72483.ab