Abstract
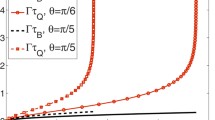
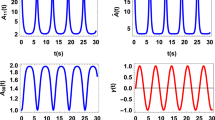
Using quantum theory operator method, we discuss the general reversible classical reactions A 1 + A 1 + ⋯ A r ↔ B 1 + B 2 + ⋯ + B s, where r and s are arbitrary natural positive numbers. We show that if either direction of the reaction is repeated a large number of times N in a finite total times T then in the limit of very large N, keeping T constant, one remains with the initial reacting particles only. We also show that if the reaction evolves through different possible paths of evolution, each of them beginning at the same side of the reaction, proceeds through different intermediate consecutive reactions and ends at the other side, then one may “realize” any such path by performing in a dense manner the set of reactions along it. the same results are also numerically demonstrated for the specific reversible reaction A + B ↔ A + C. We note that similar results have been shown to hold also in the quantum regime.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bar, D. The Effect of Increasing the Rate of Repetitions of Classical Reactions. International Journal of Theoretical Physics 43, 1169–1190 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:IJTP.0000048608.36649.62
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:IJTP.0000048608.36649.62