Abstract
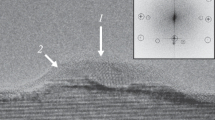
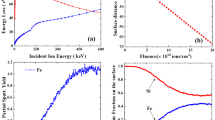
The phase formation and crystallization processes of metastable [CsCl]Fe1−x Si phases were investigated by irradiatingɛ-FeSi/Si(111) thin films with a pulsed excimer laser in the energy density range 300–900 mJ/cm2. The samples were analysed by Rutherford backscattering and channeling spectrometry (RBS/C), cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and conversion electron Mössbauer spectroscopy (CEMS). Laser irradiation results in mixing of the FeSi with the Si substrate, with the final concentration depending on the laser energy density. Due to the extremely rapid quench of the melt, a non-uniform Fe concentration is obtained. Analysis by cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy confirmed that this phase, which exhibits epitaxial ordering, corresponds to the metastable [CsCl]Fe1−x Si phase, which converts into the semiconductingβ-FeSi2 upon annealing at 600°C. CEMS indicates that no stable Fe-silicide phase nor a combination of stable phases have been formed. The CEM spectra consist of a distribution of quadrupole doublets and isomer shifts, in agreement with a [CsCl]Fe1−x Si phase that exhibits a (i) composition gradient and (ii) a random number of Fe vacancies in the neighbouring shells. These distributions make the CEM spectra hard to interpret. Full-Potential Linearized Augmented Plane Wave (FLAPW) calculations were performed to gain more insight in the hyperfine interaction parameters of the metastable [CsCl]Fe1−x Si phase and their dependence on a concentration variation. These calculations confirm the decreasing trend of the isomer shift with increasing number of laser pulses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bost, M. C. and Mahan, J. E.,J. Appl. Phys. 58 (1985), 2696.
Leong, D., Harry, M., Reeson, K. J. and Homewood, K. P.,Nature 387 (1997), 686.
Proceedings of the 46th Spring Meeting of the Japan Society of Applied Physics and Related Societies on “Silicide semiconductors and their applications to Si-based optoelectronics”,Thin Solid Films 381 (2001) 171.
Von Känel, H., Mäder, K. A., Müller, E., Onda, N. and Sirringhaus, H.,Phys. Rev. B 45 (1992), 13807.
Von Känel, H., Stalder, R., Sirringhaus, H., Onda, N. and Henz, J.,Appl. Surf. Sci. 53 (1991), 196.
Vazquez de Parga, A. L., De la Figuera, J., Ocal, C. and Miranda, R.,Europhys. Lett. 18 (1992), 595.
Le Thanh, V., Chevrier, J. and Derrien, J.,Phys. Rev. B 46 (1992), 15946.
Degroote, S., Kobayashi, T., Dekoster, J., Vantomme, A. and Langouche, G.,Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 337 (1994), 685.
Degroote, S., Vantomme, A., Dekoster, J. and Langouche, G.,Appl. Surf. Sci. 91 (1995), 72.
Desimoni, J., Bernas, H., Behar, M., Lin, X. W., Washburn, J. and Liliental-Weber, Z.,Appl. Phys. Lett. 62 (1993), 306.
Maltez, R. L., Amaral, L., Behar, M., Vantomme, A., Langouche, G. and Lin, X. W.,Phys. Rev. B 54 (1996), 11659.
Grimaldi, M., Baeri, P., Spinella, C. and Langomarsino, S.,Appl. Phys. Lett. 60 (1992), 1132.
Wagner, S., Carpene, E., Schaaf, P. and Weisheit, M.,Appl. Surf. Sci. 186 (2002), 156.
Comrie, C. M., Falepin, A., Richard, O., Bender, H. and Vantomme, A., to be published inJ. Appl. Phys. 95 (2004).
Falepin, A., Comrie, C. M., Cottenier, S. and Vantomme, A.,Mater. Sci. Eng. B 89 (2002), 386.
Falepin, A., Comrie, C. M., Vantomme, A. and Langouche, G.,Hyp. Interact. 134 (2001), 153.
Fanciulli, M., Roosenblad, C., Weyer, G., Von Känel, H. and Onda, N.,Thin Solid Films 275 (1996), 8.
Desimoni, J., Sánchez, F. H., Fernádez van Raap, M. B., Bernas, H., Clere, C. and Lin, X. W.,Phys. Rev. B 51 (1995), 86.
Falepin, A., Cottenier, S., Comrie, C. and Vantomme, A., to be published.
Blaha, B., Schwarz, K. and Luitz, J., WIEN 97, A full potential linearized augmented plane wave package for calculating crystal properties, Karlheinz Schwarz, Tech. Univ. Wien, Vienna, 1999; Updated version of Blaha, B., Schwarz, K., Sorantin, S. and Trickey, S. B.,Comp. Phys. Commun. 59 (1990), 399. In this work, version 97.10 was used.
Radermacher, K., Mantl, S., Dieker, Ch. and Lüth, H.,Appl. Phys. Lett. 59 (1991), 2145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
On the occasion of the 80th birthday of Hendrik de Waard
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falepin, A., Cottenier, S., Comrie, C.M. et al. Formation and microstructure of cubic metastable iron silicides synthesized during pulsed laser annealing. Hyperfine Interact 151, 131–144 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYPE.0000020412.84450.6c
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYPE.0000020412.84450.6c