Abstract
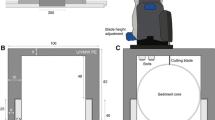
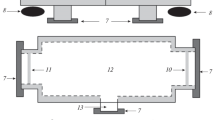
New, easy to use, liquid nitrogen-cooled equipment is described for sampling the upper layer (80–160 mm) of water sediment and associated benthic organisms in streams and lakes up to 1.2 m deep. The sediment sample has an area of 0.0531 m2 and retains its natural composition and spatial structure. The two sampler components weigh 15 kg in total, which enables sampler use by hand, even in rural areas that are not readily accessible. A successful 2-year testing period in several first and second order streams demonstrated the suitability of the apparatus for sampling sediment textures ranging from fine clay to cobbles and current velocities up to 1 m s−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bretschko, G., 1985. Quantitative sampling of the fauna of gravel streams (Project RITRODAT-LUNZ). Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 2049–2052.
Bretschko, G., 1990. The dynamic aspect of coarse particulate organic matter (CPOM) on the sediment surface of a second order stream free of debris dams (RITRODAT-LUNZ study area). Hydrobiologia 203: 15–28.
Fisher, S. G., N. B. Grimm, E. Marti, R. M. Holmes & J. B. Jones, 1998. Material spiralling in stream corridors: A telescoping ecosystem model. Ecosystems 1: 19–34.
Hess, A. D., 1941. New limnological sampling equipment. Limnol. Soc. Amer., Spec. Publ. 6: 5 pp.
Hill, M. T. R., 1999. A freeze-corer for simultaneous sampling of benthic macroinvertebrates and bed sediment from shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 412: 213–215.
Kajak, Z., 1971. Benthos of standing water. In Edmonson, W. T. & G. A. Winberg (eds), A Manual on Methods for the Assessment of Secondary Productivity in Fresh Waters. Blackwell Science Publications, Oxford: 25–65.
Niederreiter, R. & K.-H. Steiner, 1999. Der Freeze-Panel-Sampler (Frost-Platten-Sampler; FPS) – Ein neues korngrößenunabhängiges Verfahren zur Entnahme gefügeintakter oberflächennaher Urproben aus wassergesättigten Lockersedimenten. Hydrologie und Wasserbewirtschaftung 43: 30–32.
Shapiro, J., 1958. The core freezer – a new sampler for lake sediments. Ecology 39: 758.
Stocker, Z. S. J. & D. D. Williams, 1972. A freezing core method for describing the vertical distribution of sediment in a streambed. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17: 136–139.
Vannote, R. L., G. W. Minshall, K. W. Cummins, J. R. Sedell and C. E. Cushing, 1980. The river continuum concept. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37: 130–137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, F., Zimmermann-Timm, H. & Schönborn, W. The Bottom Sampler – a new technique for sampling bed sediments in streams and lakes. Hydrobiologia 505, 73–76 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000007286.70175.df
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000007286.70175.df