Abstract
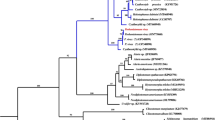
The subfamily Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) comprises hematophagous insects, most of which are actual or potential vectors of Trypanosoma cruzi, the protozoan agent of Chagas’ disease (American trypanosomiasis). DNA sequence comparisons of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) genes were used to infer phylogenetic relationships among 32 species of the subfamily Triatominae, 26 belonging to the genus Triatoma and six species of different genera. We analyzed mtDNA fragments of the 12S and 16S ribosomal RNA genes (totaling 848–851 bp) from each of the 32 species, as well as of the cytochrome oxidase I (COI, 1447 bp) gene from nine. The phylogenetic analyses unambiguously supported several clusters within the genus Triatoma. In the morphological classification, T. costalimai was placed tentatively within the infestans complex while T. guazu was not included in any Triatoma complex. The placement of these species in the molecular phylogeny indicated that both belong to the infestans complex. We confirmed with a strong support the inclusion of T. circummaculata, a member of a different complex based on morphology, within the infestans complex. On the other hand, the present phylogenetics analysis did not support the monophyly of the infestans complex species as it was suggested in our previous studies. While no strong inference of polyphyly of the genus Triatoma was provided by the bootstrap analyses, the other species belonging to Triatomini analyzed could not be distinguished from the species of Triatoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalos, J.W., 1948. Sobre híbridos naturales y experimentales de Triatoma. Anal. Inst. Med. Reg. 2: 209–223.
Abalos, J.W., 1974. Distribución e importancia epidemiológica de las Triatominae de la Argentina. Rev. Fac. Ci. Ex. Fís. Nat. Cba. Biol. 1: 5–16.
Bargues, M.D., A. Marcilla, J.P. Dujardin & S. Mas-Coma, 2002. Triatomine vectors of Trypanosoma cruzy: a molecular perspective based on nuclear ribosomal DNA markers. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 96: 159–164.
Carcavallo, R.U., J.A. Cichero, A. Martínez, A.F. Prosen & F. Ronderos, 1967. Una nueva especie del género TriatomaLaporte (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae). Seg. J. Entoepidemiol. Arg. 2: 43–48.
Carcavallo, R.U., J. Jurberg & H. Lent, 1998. Torrealbaia martinezi, gen. nov. sp. n, da tribo Cavernicolini (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae): Uma abordagem filogenética. Entomología y Vectores 5: 143–150.
Corrêa, R.R. & H.N. Espínola, 1964. Descriçao de Triatoma pseudomaculata, nova especie de triatomineo de Sobral, Geara (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Arg. Hig. Saúde Pública, São Paulo 29: 115–127.
Dias, J.C.P., 1965. Reinfestação do municipio de Bambui por triatomineos transmissores da doença de Chagas. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz Rio J. 63: 107–119.
Dias, J.C.P., 1987. Epidemiology of Chagas' disease in Brazil, pp. 57-84 in Chagas' Disease Vectors, edited by Z. Brener & A.M. Stoka. CRC, Boca Raton, FL.
Dias, J.C.P., 1988. Controle de vetores da doença de Chagas no Brasil e risco de reinvasão domiciliar por vetores secundários. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz Rio J. 83: 387–391.
Felsenstein, J., 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 17: 368–376.
Felsenstein, J., 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using bootstrap. Evolution 39: 783–791.
Felsenstein, J., 1995. PHYLIP, version 3.57c. University of Washington, Seattle.
Gajate, P.P., M.V. Bottazzi, S.M. Pietrokovsky & C. Wisnivesky-Colli, 1996. Potential colonization of the peridomicile by Triatoma guasayana (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) in Santiago del Estero, Argentina. J. Med. Entomol. 33: 635–639.
García, B.A., 1999. Molecular phylogenetic relationships among species of the genus Triatoma, pp. 971–980 in Atlas of Chagas' Disease Vectors in the Americas, Vol. III, edited by R.U. Carcavallo, I. Galíndez Girón, J. Jurberg & H. Lent. Editora Fiocruz, Rio de Janeiro.
García, B.A. & J.R. Powell, 1998. Phylogeny of species of Triatoma(Hemiptera: Reduviidae) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. J. Med. Entomol. 35: 232–238.
García, B.A., E.N. Moriyama & J.R. Powell, 2001. Mitochondrial DNA sequences of triatomines (Hemiptera: Reduviidae): phylogenetic relationships. J. Med. Entomol. 38: 675–683.
Gorla, D.E., J. Jurberg, S.S. Catalá & C.J. Schofield, 1993. Systematics of Triatoma sordida, Triatoma guasayanaand, Triatoma patagonica (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz Rio J. 88: 379–385.
Gyllensten, U.B. & H.A. Erlich, 1988. Generation of singlestranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 7652–7656.
Hypsa, V., D.F. Tietz, J. Zrzavy, R.O.M. Rego, C. Galvão & J. Jurberg, 2002. Phylogeny and biogeography of Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae): molecular evidence of a New World origin of the Asiatic clade. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 23: 447–457.
Jurberg, J. & C. Galvão, 1997. Hermanlentian. gen. da tribo Triatomini, com um rol de especies de Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz Rio J. 92: 181–185.
Jurberg, J., C. Galvão, H. Lent, F. Monteiro, C. Macedo Lopes, F. Panzera & R. Pérez, 1998. Revalidacão de Triatoma garciabesiCarcavallo, Cichero, Martínez, Prosen & Ronderos, 1967 (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Entomología y Vectores 5: 107–122.
Kocher, T.D., W.K. Thomas, A. Meyer, S.V. Edwards, S. Pääbo, F.X. Villablanca & A.C. Wilson, 1989. Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 6196–6200.
Lent, H. & P. Wygodzinsky, 1979. Revision of the Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae), and their significance as vectors of Chagas' disease. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 163: 123–520.
Lent, H., J. Jurberg & C. Galvão, 1994a. Revalidação do Gênero Mepraia, Mazza, Gajardo and Jörg, 1940 (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz Rio J. 89: 347–352.
Lent, H.,J. Jurberg, C. Galvão & R.U. Carcavallo, 1994b. Triatoma melanosoma, Novo status para Triatoma infestans melanosomaMartinez, Olmedo and Carcavallo, 1987 (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz Rio J. 89: 353–358.
Lyman, D.F., F.A. Monteiro, A.A. Escalante, C. Cordon-Rosales, D.M. Wesson, J.P. Dujardin & C.B. Beard, 1999. Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation among triatomine vectors of Chagas' disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 60: 377–386.
Marcilla, A., M.D. Bargues, J.M. Ramsey, E. Magallon-Gastelum, P.M. Salazar-Schettino, F. Abad-Franch, J.P. Dujardin, C.J. Schofield & S. Mas-Coma, 2001. The ITS-2 of the nuclear rDNA as a molecular marker for populations, species, and phylogenetic relationships in Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae), vectors of Chagas' disease. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 18: 136–142.
Martinez, A., R.A. Olmedo & R.U. Carcavallo, 1987. Una nueva subespecie argentina de Triatoma infestans. Chagas 4: 479–480.
Monteiro, F.A., R. Pérez, F. Panzera, J.P. Dujardin, C. Galvão, D. Rocha, F. Noireau, C. Schofield & C.B. Beard, 1999. Mitochondrial DNA variation of Triatoma infestanspopulations and its implication on the specific status of T. melanosoma. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz Rio J. 94: 229–238.
Monteiro, F.A., D.M. Wesson, E.M. Dotson, C.J. Schofield & C.B. Beard, 2000. Phylogeny and molecular taxonomy of the Rhodniini derived from mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 62: 460–465.
Noireau, F., S. Menezes dos Santos, M. Gumiel, J.P. Dujardin, M. dos Santos Soares, R.U. Carcavallo, C. Galvão & J. Jurberg, 2002. Phylogenetic relationships within the oliveiraicomplex (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae). Inf. Genet. Evol. 2: 11–17.
Palumbi, S., A. Martin, S. Romano, W.O. McMillan, L. Stice & G. Grabowski, 1991. The simple fool's guide to PCR, version 2.0. University of Hawaii, Honolulu.
Panzera, F., R. Pérez, Y. Panzera, F. Alvarez, E. Scvortzoff & R. Salvatella, 1995. Karyotype evolution in holocentric chromosomes of three related species of triatomines (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Chrom. Res. 3: 143–150.
Pereira, J., J.P. Dujardin, R. Salvatella & M. Tibayrenc, 1996. Enzymatic variability and phylogenetic relatedness among Triatoma infestans, T. platensis, T. delponteiand T. rubrovaria. Heredity 77: 47–54.
Rocha e Silva, E.O., J. Dias & O.F. Guarita, 1969. Suspensão do rociado no combate ao Triatoma infestansem áreas do Estado de São Paulo, Brasil. Rev. Saúde Pública 3: 173–181.
Saitou, N. & M. Nei, 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4: 406–425.
Sanger, F., S. Nicklen & A.R. Coulson, 1977. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74: 5463–5467.
Salvatella, R., 1993. Triatoma rubrovaria(Blanchard, 1843) (Hemiptera: Triatominae), vector secundario con potencial de intradomiciliación. Rev. da Soc. Bras. de Med. Tropicale 26: 43–45.
Schmunis, G.A., 1999. Iniciativa del Cono Sur, pp. 26–31 in Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on Population Biology and Control of Triatominae, Santo Domingo de los Colorados, Ecuador. INDRE, Mexico City.
Schofield, C.J., 1985. Control of Chagas' disease vectors. Br. Med. Bull. 41: 187–194.
Schofield, C.J., 1988. Biosystematics of the Triatominae, pp. 285–312 in Biosystematics of Haematophagous Insects, Systematics Association Special Vol. 37, edited by M.W. Service. Clarendon, Oxford.
Simon, C., F. Frati, A. Beckenbach, B. Crespi, H. Liu & P. Flook, 1994. Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 87: 651–701.
Swofford, D.L., 1999. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4.0b8. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts.
Tonn, R.J., 1988. Review of recent publications on the ecology, biology and control vectors of Chagas' disease. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 20: 4–24.
Usinger, R.L., P. Wygodzinsky & R.E. Ryckman, 1966. The biosystematics of Triatominae. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 11: 309–330.
Werman, S.D., E.H. Davidson & R.J. Britten, 1990. Rapid evolution in a fraction of the Drosophilanuclear genome. J. Mol. Evol. 30: 281–289.
Zeledón, R., 1974. Epidemiology, modes of transmission and reservoir hosts of Chagas' disease, pp. 51–85. in Associated Scientific Publishers, Trypanosomiasis and Leishmaniasis with special reference to Chagas' didease.Ciba Foundation Symposium No. 20, Amsterdam.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sainz, A.C., Mauro, L.V., Moriyama, E.N. et al. Phylogeny of Triatomine Vectors of Trypanosoma cruzi Suggested by Mitochondrial DNA Sequences. Genetica 121, 229–240 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000039842.82574.02
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000039842.82574.02