Abstract
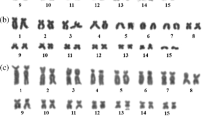
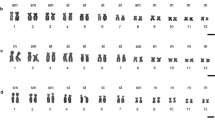
The karyotype, nucleolar organizer region (NOR) location and C-banding pattern of two species of Hylodes (H. phyllodes and H. asper) and two of Crossodactylus (Crossodactylus sp. n. and Crossodactylus cf. caramaschi) were studied. All species had a diploid number of 2n= 26, with differences in the chromosomal morphology of the Hylodes species while the two Crossodactylus species were cytogenetically indistinguishable. The NOR was located on pair 1 in both species of Hylodes, and on pair 8 in the Crossodactylus species. In the latter, the NOR was heteromorphic between the homologues. The NOR was coincident with a secondary constriction in the four species. Except to H. phyllodes, such secondary constrictions were clearly seen strongly stained after C-banding treatment. The C-banding pattern varied between the two species of Hylodes, but was identical in the Crossodactylus species. The results from conventionally stained karyotypes confirmed the uniformity within the genus Crossodactylus, and the relatively conserved karyotypes within Hylodes, in agreement with other literature reports. We conclude that the cytogenetic data do not provide further evidence which could be useful to corroborate the supposed relationships between the hylodines and dendrobatids since there are no unambiguous homeologies between the karyotypes of these groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar Jr., O., A.P. Lima, A.A. Giaretta & S.M. Recco-Pimentel, 2002. Cytogenetic analysis of four dart-poison frogs of the Epipedobates genus (Anura, Dendrobatidae). Herpetologica 58: 293–303.
Aguiar Jr., O., A.A. Garda, A.P. Lima, S.N. Báo, G.R. Colli & S.M. Recco-Pimentel, 2003. The biflagellate spermatozoon of the poison-dart frogs Epipedobates femoralis and Colostethus sp. (Anura, Dendrobatidae). J. Morphol. 255: 114–121.
Amaral, M.J.L.V., A.P. Fernades, S.N. Báo & S.M. Recco-Pimentel, 1999. An ultrastructural study of spermiogenesis in three species of Physalaemus (Anura, Leptodactylidae). Biocell 23: 211–221.
Amaral, M.J.L.V., A.J. Cardoso & S.M. Recco-Pimentel, 2000. Cytogenetic analysis of three Physalaemus species (Amphibia, Anura). Caryologia 53: 283–288.
Beç ak, M.L., 1968. Chromosomal analysis of eighteen species of Anura. Caryologia 21: 191–208.
Bogart, J.P., 1970. Systematic problems in the amphibian family Leptodactylidae (Anura) as indicated by karyotypic analysis. Cytogenetics 9: 369–383.
Bogart, J.P., 1991. The influence of life history on karyotypic evolution in frogs, pp. 233–258 in Amphibians Cytogenetics and 52 Evolution, edited by D.M. Green & S.K. Sessions. Academic Press, San Diego.
Brum-Zorrilla, N. & F.A. Saez, 1968. Chromosomes of Leptodactylidae (Amphibia-Anura). Experientia 27: 969.
Caldwell, J.P., 1996. The evolution of myrmecography and its correlates in poison frogs (Family Dendrobatidae). J. Zool. Lond. 240: 75–101.
De Lucca, E. & J. Jim, 1974. Os cromossomos de alguns Leptodactylidae (Amphibia, Anura). Rev. Bras. Biol. 34: 407–410.
Denaro, L., 1972. Karyotypes of Leptodactylidae anurans. J. Herpetol. 6: 71–74.
Duellman, W.E., 1967. Additional studies of chromosomes of anuran amphibians. Syst. Zool. 16: 38–43.
Ford, L.S., 1993. The phylogenetic position of the dart-poison frogs (Dendrobatidae) among anurans: an examination of the competing hypothesis and their characters. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 5: 219–231.
Ford, L.S. & D.C. Cannatella, 1993. The major clades of frogs. Herpetol. Monogr. 7: 94–117.
Frost, D.R., 2002. Amphibian species of the world: an on line reference. V2.2. American. http://research.amnh.org/herpetology/amphibia/index./html.
Giaretta, A.A. & O. Aguiar Jr., 1998. A new species of Megaelosia from the Mantiqueira Range, Southeastern Brazil. J. Herpetol. 32: 80–83.
Giaretta, A.A., W.C.A. Bokermann & C.B.F. Haddad, 1993. A review of the genus Megaelosia (Anura: Leptodactylidae) with description of a new species. J. Herpetol. 27: 276–285.
Green, D.M., 1986. Systematics and evolution of western North American frogs allied to Rana aurora and Rana boylii: karyological evidence. Syst. Zool. 35: 273–282.
Green, D.M. & S.K. Sessions, 1991. Nomenclature for chromosomes, pp. 431–432 in Amphibian Cytogenetics and Evolution, edited by D.M. Green & S.K. Sessions. Academic Press, San Diego.
Griffths, I., 1959. The phylogeny of Sminthillus limbatus and the status of the Brachycephalidae (Amphibia). Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 132: 457–489 (apud Ford, 1993).
Griffths, I., 1963. The phylogeny of Salientia. Biol. Rev. 38: 241–292 (apud Ford, 1993).
Heyer, W.R., 1975. A preliminary analysis of intergeneric relationships of the frog family Leptodactylidae. Smith. Contrib. Zool. 199: 1–55.
Heyer, W.R. & M.J. Diment, 1974. The karyotype of Vanzolinus discodactylus and comments on usefulness of karyotypes in determining relationships in the Leptodactylus complex (Amphibia, Leptodactylidae). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 87: 327–336.
Howell, W.M. & D.A. Black, 1980. Controlled silver staining of nucleolar organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a one step method. Experientia 36: 1014–1015.
John, B., 1988. The biology of heterochromatin, pp. 1–128 in Heterochromatin: Molecular and Structural Aspects, edited by R.S. Verma. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Kasahara, S., A.P.Z. Silva & C.F.B. Haddad, 1996. Chromosome banding in three species of Brazilian toads (Amphibia-Bufonidae). Braz. J. Genet. 19: 237–242.
King, A., 1990. Animal Cytogenetics. Vol. 4. Chordata 2, Amphibia. Gerbruder Borntraeger, Stuttgart and Berlin.
King, A., 1991. The evolution of heterochromatin in the amphibian genome, pp. 233–258 in Amphibian Cytogenetics and Evolution, edited by D.M. Green & S.K. Sessions. Academic Press, San Diego.
Kwon, A.S. & Y.H. Lee, 1995. Comparative spermatology of anuran with special references to phylogeny, pp. 321-332 in Advances in Spermatozoal Phylogeny and Taxonomy, edited by B.G.M. Jamieson, J. Ausió & J.L. Justine. Mém. Mus. Natn. Hist. Nat., Paris, Vol. 166.
Lourenço, L.B., A.J. Cardoso & S.M. Recco-Pimentel, 2000. Cytogenetics of Edalorhina perezi (Anura, Leptodactylidae). Cytologia 65: 359–363.
Lynch, J.D., 1971. Evolutionary relationships, osteology and zoogeography of Leptodactylidae frogs. Univ. Kansas Mus. Nat. Hist. Misc. Publ. 53: 1–238.
Lynch, J.D., 1973. The transition from archaic to advanced frogs, pp. 133–182 in Evolutionary Biology of Anurans: Contemporary Research on Major Problems edited by J.L. Vial. University of Missouri Press, Columbia.
Melo, A.S., S.M. Recco-Pimentel & A.A. Giaretta, 1995. The karyotype of the stream dwelling frog Megaelosia massarti (Anura, Leptodactylidae, Hylodinae). Cytologia 60: 49–52.
Miyamoto, M.M., 1983. Frogs of the Eleutherodactylus rugulosus group: a cladistic study of allozyme, morphological, and karyological data. Syst. Zool. 32: 109–124.
Morescalchi, A., 1973. Amphibia, pp. 233–348 in Cytotaxonomy and Vertebrate Evolution, edited by A.B. Chiarelli and E. Capana. Academic Press, New York.
Myers, C.W., O.A. Paolillo & J.W. Daly, 1991. Discovery of a defensively malodorous and nocturnal frog in the family Dendrobatidae: phylogenetic significance of a new genus and species from Venezuelan Andes. Am. Mus. Novit. 3002: 1–33.
Noble, G.K., 1931. The Biology of the Amphibia. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Odierna, G., F. Andreone, G. Aprea, O. Arribas, T. Capriglione & M. Vences, 2000. Cytological and molecular analysis in the rare discoglossid species, Alytes muletensis (Sanchiz & Adrover, 1977) and its bearing on archeobatrachian phylogeny. Chrom. Res. 8: 435–442.
Rasotto, M.B., P. Cardellini & M. Sala, 1987. Karyotypes of five Dendrobatidae (Anura, Amphibia). Herpetologica 43: 177–182.
Rosa, C., O. Aguiar Jr., A.A. Giaretta & S.M. Recco-Pimentel, 2003. Karyotypic variation in the genus Megaelosia (Anura, Leptodactylidae) with the first description of a B chromosome in leptodactylid frogs. Copeia 2003(1): 166–174.
Savage, J.M., 1973. The geographic distribution of frogs: patterns and predictions, pp. 341–355 in Evolutionary Biology of the Anurans, edited by J.L. Vial. University of Missouri Press, Columbia.
Schmid, M., 1978. Chromosome banding in Amphibia II. Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolus organizer regions in Ranidae, Microhylidae and Racophoridae. Chromosoma 68: 131–148.
Schmid, M., 1982. Chromosome banding in Amphibia VII. Analysis of the structure and variability of NORs in Anura. Chromosoma 87: 327–344.
Schmid, M., J. Orlet & C. Klett, 1979. Chromosome banding in Amphibia III. Sex chromosomes in Triturus. Chromosoma 71: 29–55.
Schmid, M., C. Steinley, I. Nanda & J.T. Epplen, 1990. Chromosome banding in Amphibia, pp. 21–45 in Cytogenetics of Amphibians and Reptiles, edited by E. Olmo. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel.
Silva, A.P.Z., C.F.B. Haddad & S. Kasahara, 2000. Chromosomal studies on five species of the genus Leptodactylus Fitzinger, 1826 (Amphibia, Anura) using differential staining. Cytobios 103: 25–38.
Sumner, A.T., 1972. A simple technique demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 75: 304–306.
Toft, C.A., 1995. Evolution of diet specialization in poison dart frogs (Dendrobatidae). Herpetologica 51: 202–216.
Veiga-Menoncello, A.C.P., A.P. Lima & S.M. Recco-Pimentel, 2001. Cytogenetics of five Colostethus species (Anura-Dendrobatidae), with description of a new chromosome number. Chromosome Res. 9 (Suppl. 1): 82.
Vences, M., J. Kosuch, S. Lötters, A. Widmer, K.H. Jungfer, J. Köhler & M. Veith, 2000. Phylogeny and classification of poison frogs (Amphibia: Dendrobatidae), based on mitochondrial 16S and 12S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 15: 34–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguiar, O., Carvalho, K.A., Giaretta, A.A. et al. Cytogenetics of Hylodes and Crossodactylus Species (Anura, Leptodactylidae) with Comments on Hylodinae/Dendrobatidae Relationships. Genetica 121, 43–53 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000019926.50310.26
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000019926.50310.26