Abstract
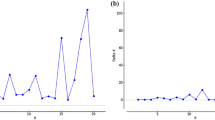
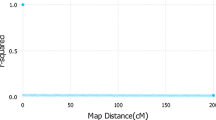
While extensive analyses have been conducted to test for, no formal analyses have been conducted to test against, the importance of candidate genes as putative QTLs using random population samples. Previously, we developed an LOD score exclusion mapping approach for candidate genes for complex diseases. Here, we extend this LOD score approach for exclusion analyses of candidate genes for quantitative traits. Under this approach, specific genetic effects (as reflected by heritability) and inheritance models at candidate QTLs can be analyzed and if an LOD score is ≤−2.0, the locus can be excluded from having a heritability larger than that specified. Simulations show that this approach has high power to exclude a candidate gene from having moderate genetic effects if it is not a QTL and is robust to population admixture. Our exclusion analysis complements association analysis for candidate genes as putative QTLs in random population samples. The approach is applied to test the importance of Vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene as a potential QTL underlying the variation of bone mass, an important determinant of osteoporosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amos, C.I., 1994. Robust variance-components approach for assessing genetic linkage in pedigrees. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 54: 535–543.
Boerwinkle, E., R. Chakraborty & C.F. Sing, 1986. The use of measured genotype information in the analysis of quantitative phenotypes in man. Ann. Hum. Genet. 50: 181–194.
Chakraborty, R. & P. Smouse, 1988. Recombination in haplotypes leads to biased estimates of admixture proportions in human populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 3071–3074.
Deng, H.-W., 2001. Population admixture may change, mask or reverse true genetic effects for complex traits. Genetics 159: 1319–1323.
Deng, H.-W. & W.-M. Chen, 2000a. Re: biased tests of association: comparison of allele frequencies when departing from Hardy-Weinberg proportions. Am. J. Epidemiol. 151: 335–357.
Deng, H.-W. & W.-M. Chen, 2000b. QTL fine mapping in extreme samples of finite populations for complex traits with familial correlation due to polygenes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67: 259–261.
Deng, H.-W. & J. Li, 2001. The effect of polygenes on transmission disequilibrium test of a QTL in nuclear families with multiple children. Genet. Epidemiol. 21: 243–256.
Deng, H.-W., J. Li, J.L. Li, M. Johnson, G. Gong & R.R. Recker, 1999. Association of VDR and estrogen receptor genotypes with bone mass in postmenopausal Caucasian women: different conclusions with different analyses and the implications. Osteoporosis Int. 9: 499–507.
Deng, H.-W., W.-M. Chen & R.R. Recker, 2000. QTL fine mapping by measuring and testing for Hardy-Weinberg and linkage disequilibrium at a series of linked marker loci in extreme samples of populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66: 1027–1045.
Deng, H.-W., W.-M. Chen, S. Recker, M.R. Stegman, J.L. Li, K.M. Davies, Y. Zhou, H.Y. Deng, R.R. Heaney & R.R. Recker, 2000a. Genetic determination of Colles' fractures and differential bone mass in women with and without Colles' fractures. J. Bone Miner. Res. 15: 1243–1252.
Deng, H.-W., W.-M. Chen, T. Conway, Y. Zhou, K.M. Davies, M.R. Stegman, H.Y. Deng & R.R. Recker, 2000b. Determination of bone mineral density of the hip and spine in human pedigrees by genetic and life-style factors. Genetic Epidemiol. 19: 160–177.
Deng, H.-W., W.-M. Chen & R.R. Recker, 2001. Population ad-mixture: detection by Hardy-Weinberg test and its quantitative effects on linkage-disequilibrium methods for localizing genes underlying complex traits.Genetics 157: 885–897.
Deng, H.-W., J. Li & R.R. Recker, 2001. LOD score exclusion analyses of candidate genes with random population samples. Ann. Hum. Genet. 65: 313–329.
Deng, H.-W., F.H. Xu, T. Conway, X.T. Deng, J.L. Li, K.M. Davies, H.Y. Deng, M. Johnson & R.R. Recker, 2001. Is population BMD variation linked to the marker D11s987 on chromosome 11q12–13? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolism 86: 3735–3741.
Devlin, B., K. Roeder & S.-A. Bacanu, 2001. Unbiased methods for population-based association studies. Genetic Epidemiol. 21: 273–284.
Edwards, J.H., 1980. Exclusion mapping. J. Med. Genet. 24: 539–543.
Eisman, J.A., 1995. Vitamin D receptor gene alleles and osteoporosis: An affirmative view. J. Bone Miner. Res. 10: 1289–1293.
Feder, J.N., A. Gnirke, W. Thomas & Z. Tsuchihasi, 1996. A novel MHC class I-like gene is mutated in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Nat. Genet. 13: 399–408.
Gong, G., S. Stern, S.C. Cheng, F. Fong, N. Mordeson, H.-W. Deng & R.R. Recker, 1999. On the association of bone mass density and Vitamin-D genotype polymorphisms. Osteoporosis Int. 9: 55–64.
Hanis, C.L., E. Boerwinkle, R. Chakraborty, D.L. Ellsworth & G.I. Bell, 1996. A genome-wide search for human non-insulin-dependent (type 2) diabetes genes reveals a major susceptibility locus on chromosome 2. Nat. Genet. 13: 161–166.
Kruglyak, L. & E.S. Lander, 1995. Complete multipoint sib-pair analysis of qualitative and quantitative traits. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 57: 439–454.
Lander, E. & L. Kruglyak, 1995. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting the reporting results. Nat. Genet. 11: 241–247.
Liu, Y.-Z., Y.-J. Liu, R.R. Recker & H.-W. Deng, 2003. Molecular genetic studies of gene identification for osteoporosis: the 2002 update. J. Endocrinol. 177: 147–196.
Morton, N.E. & A. Collins, 1999. Tests and estimates of allelic association in complex inheritance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 11389–11393.
Nielsen, D.M., M.G. Ehm & B.S. Weir, 1998. Detecting marker-disease association by testing for Hardy-Weinberg disequilibrium at a marker locus. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 63: 1531–1540.
Ott, J., 1999. Analysis of Human Genetic Linkage. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, MD, 3rd edn.
Page, G.P. & C.I. Amos, 1999. Comparison of linkage-disequilibrium methods for localization of genes influencing quantitative traits in humans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64: 1194–1205.
Page, G.P., C.I. Amos & E. Boerwinkle, 1998. The quantitative LOD score: test statistic and sample size for exclusion and linkage of quantitative traits in human sibships. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 62: 962–968.
Recker, R.R. & H.-W. Deng, 2002. Role of genetics in osteoporosis. Endocrine 17: 55–66.
Risch, N. & J. Teng, 1998. The relative power of family-based and case-control designs for linkage disequilibrium studies of complex human diseases. I. DNA polling. Genome Res. 8: 1273–1288.
Salamone, L.M., R. Ferrell, D.M. Black, L. Palermo, R.S. Epstein, N. Petro, N. Steadman, L.H. Kuller & J.A. Cauley, 1996. The association between Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and bone mineral density at the spine, hip and whole-body in premenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 6: 63–68.
Spielman, R.S., R.E. Mcginnis & W.J. Ewens, 1993. Transmission test for linkage disequilibrium: the insulin gene region and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Am. J. Hum. Genet. 52: 506–516.
Tsai, K.S., S.H. Hsu, W.C. Cheng, C.K. Chen, P.U. Chieng & W.H. Pan, 1996. Bone mineral density and bone markers in relation to Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in Chinese men and women. Bone 19: 513–518.
Weir, B.S., 1996. Genetic Data Analysis II. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA.
Yamagata, Z., T. Miyamura, S. Iijima, A. Asaka, M. Sasaki, J. Kato & K. Koizumi, 1994. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism and bone mineral density in healthy Japanese women. Lancet 344: 1027 (letter).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, HW. LOD Score Exclusion Analyses for Candidate QTLs using Random Population Samples. Genetica 119, 303–315 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000003827.86624.ac
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000003827.86624.ac