Abstract
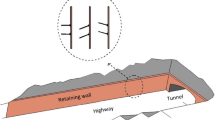
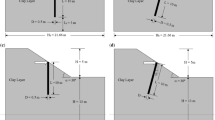
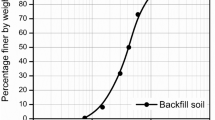
A series of highly instrumented dynamic centrifuge model tests were performed to investigate the potential of using sheet-pile walls for mitigating the adverse effects of foundation liquefaction on overlying highway embankments. The response of a prototype 4.5 m high cohesive highway embankment supported on a 6 m thick loose saturated sand layer was analyzed under dynamic base excitation conditions. In a series of four separate model tests, this embankment-foundation system was studied first without, and then with the following three different liquefaction countermeasure techniques, all involving sheet-piles: (a) sheet-pile extending to the foundation surface, (b) sheet-pile with toe area gravel surcharge berm, and (c) sheet-pile with toe area gravel surcharge berm extending into the foundation. Model response was monitored by numerous accelerometers, pore pressure transducers, and displacement gages. The underlying mechanism and effectiveness of each countermeasure is discussed based on the recorded dynamic response. All of the implemented countermeasures were found to significantly reduce embankment deformations. Particularly in the case of the sheet-pile with toe area gravel berm, cracking and lateral spreading of the embankment were practically eliminated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalier, K. (1996) Mitigation of earthquake induced liquefaction hazards, Ph.D. Thesis, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI), Troy, NY, USA, 659p.
Adalier, K. and Aydingun, O. (2000) Liquefaction during the June 27, 1998 Adana-Ceyhan (Turkey) Earthquake, J. Geotechnical and Geological Eng., 18(3), 155–174.
Adalier, K. and Elgamal, A.W. (2002) Seismic response of adjacent saturated dense and loose sand columns, Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 22(2), 115–127.
Adalier, K., Pamuk, A. and Zimmie, T.F. (2002) Seismic rehabilitation of cohesive earth embankments founded on saturated alluvial sandy deposits, Technical Report, Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, RPI, Troy, NY.
Adalier, K., Elgamal, A.W. and Martin, G.R. (1998) Foundation liquefaction countermeasures for earth embankments, J. Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE, 123(6), 500–517.
Arulanandan, K. and Scott, R.F., eds. (1993) Verification of numerical procedures for the analysis of soil liquefaction problems, Vol. 1, Balkema, Netherlands.
Arulmoli, K., Muraleetharan, K.K., Hossain, M.M. and Fruth, L.S. (1992) Verification of liquefaction analysis by centrifuge studies laboratory testing program soil data, Technical Report, EarthTech Corp., Irvine, CA.
Craig, W.H., James, R.G. and Schofield, A.N. (1988) Centrifuges in Soil Mechanics, Balkema, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 274p.
Elgamal, A.W., Zeghal, M., Taboada, V. and Dobry, R. (1996) Analysis of site liquefaction and lateral spreading using centrifuge testing records, Soils and Foundations, 36(2), 111–121.
Elgamal, A., Parra, E., Yang, Z. and Adalier, K. (2002) Numerical analysis of embankment foundation liquefaction countermeasures, J. Earthquake Engineering, 6(4), 447–471.
Finn, W.D.L. (2000) State-of-the-Art of geotechnical earthquake engineering practice, Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 20, 1–15.
JGS (1996) Japanese Geotechnical Society, Soils and Foundations Journal, Special Issue on Geotechnical Aspects of the January 17 1995 Hyogoken-Nambu Earthquake, January, Tokyo, Japan, 359p.
Laak, P.V., Adalier, K., Dobry, R. and Elgamal, A.W. (1998) RPI's large centrifuge shaker, In: Proceedings of the Intl. Conf. Centrifuge '98, Tokyo, Japan, pp. 105-110.
Lambe, T.W. and Whitman, R.V. (1969) Soil Mechanics. John Wiley, NY, 553p.
Marcuson, W.F., Hadala, P.F. and Ledbetter, R.H. (1996) Seismic rehabilitation of earth dams, J. of Geotech. Eng., ASCE, 122(1), 7–20.
Matsuo, O., Koga, Y., Koseki, T. and Washida, S. (1994) Study on cut-off sheet-pile method as a countermeasure against liquefaction of embankment foundation, In: Proceedings of the 4th US-Japan Workshop on Soil Liquefaction, Japan, pp. 203-222.
McCulloch, D.S. and Bonilla, M.G. (1967) Railroad damage in the Alaska Earthquake, J. Geotech. Eng. Div., ASCE, 93(5), 89–100.
Okamura, M. (2001) Personal communication, Head of the Japanese river dike seismic problem research group. Tsukuba-shi, Japan.
Park, Y.H., Kim, S.R., Kim, S.H. and Kim, M.M. (2000) Liquefaction of embankments on sandy soils and the optimum countermeasure against the liquefaction, In: Proceedings of the 12th World Conf. on Earthquake Engineering, Paper No. 1170.
Phillips, R., Guo, P.J. and Popescu, R., eds. (2002) Physical modeling in Geotechnics-ICPMG'02, Balkema, Rotterdam, Netherlands.
Schofield, A.N. (1981) Dynamic and earthquake geotechnical centrifuge modeling, In: Proceedings of the Int. Conf. on Recent Advances in Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering and Soil Dynamics, Rolla, Mo., 3, 1081–1100.
Taylor, R.N. ed. (1995) Geotechnical Centrifuge Technology. Blackie Academic & Professional Pub., Glasgow, UK, 296p.
TC4 (2001) Case histories of post-liquefaction remediation, Technical Committee for Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering-TC4, International Society of Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (ISSMGE), Tokyo, Japan.
Yamada, G. (1966) Damage to earth structures and foundations by the Niigata Earthquake, June 16, 1964, Soils and Foundations, 6(1), 1–13.
Yasuda, S., Iida, T., Kita, H., Saimura, Y. and Tanaka (1996) Countermeasures by sheet-piles with drain holes against the settlement of embankments due to liquefaction, In: Proceedings of the Int. Symp. on Seismic and Environmental Aspects of Dam Design: Concrete and Tailing Dams, pp. 486-496.
Zheng, J., Ohbo, N., Suzuki, K., Mishima, N. and Nagao, K. (1995) Analysis of results of centrifuge tests on seismic behavior of embankment, In: Proceedings of the 1st Int. Conf. Earthquake and Geotechnical Eng., 105-110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adalier, K., Pamuk, A. & Zimmie, T.F. Earthquake retrofit of highway/railway embankments by sheet-pile walls. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 22, 73–88 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GEGE.0000014000.27895.5d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GEGE.0000014000.27895.5d