Abstract
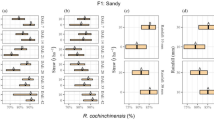
Soil loss and surface runoff patterns over a four-year period (1997–2000) were studied in erosion plots from three hillslopes under different vegetative covers (Rosmarinus officinalis, Triticum aestivum and natural-spontaneous vegetation) in Lanjaron (Alpujarras) on the south flank of the Sierra Nevada of southeast Spain. The erosion plots were located on the hillslopes at 35.5% incline, at 1,480 m in altitude and with 41.8 m2 (21 m×1.9 m) in area. The vegetative covers were tested for effectiveness in controlling the surface runoff and soil loss production. The highest runoff and erosion values, ranging from 114.1 to 1.7 mm yr−1 and from 14,564.3 to 6.6 kg ha−1 yr−1, respectively, over the entire study period, were measured under the Triticum aestivum. In the Rosmarinus officinalis, runoff ranged from 7.9 to 1.3 mm yr−1 and erosion from 156.4 to 2.3 kg ha−1 yr−1, while on the hillslope under natural-spontaneous vegetation, runoff ranged from 4.4 to 0.9 mm yr−1 and erosion from 322.3 to 2.2 kg ha−1 yr−1. According to the results the vegetative covers of Rosmarinus officinalis and natural-spontaneous vegetation reduced the soil losses by 99 and 98%, with respect to the Triticum aestivum, and the runoff losses by 94 and 96%, respectively. Also, the Rosmarinus officinalis and natural-spontaneous plants influenced infiltration by intercepting much of the rainfall water respect to the Triticum aestivum. Monitoring allowed more direct linkages to be made between management practices and their impacts on runoff and soil erosion, thereby enabling to identify problems and take appropriate preventive measures to improve the management practices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albadalejo, J., Stocking, M.A. and Díaz, E.: 1990, Soil Degradation and Rehabilitation in Mediterranean Environmental Conditions, C.S.I.C., Murcia, Spain, 235 pp.
Andreu, V., Rubio, J.L. and Cerni, R.: 1998, 'Effects of Mediterranean shrub cover on water erosion (Valencia-Spain),' J. Soil and Water. Cons. 53, 112-120.
Blackburn, W.H.: 1971, 'Factors Influencing Infiltration and Sediment Production of Semi-Arid Rangelands in Nevada,' Water Resour. Res. 11, 929-937.
Brandt, C.J.: 1988, 'The Transformation of Rainfall Energy by a Tropical Rain Forest Canopy in Relation to Soil Erosion,' J. Biogeogr. 15, 41-48.
Brandt, C.J.: 1990, 'Simulation of the Size Distribution and Erosivity of Raindrops and through Fall Drops,' Earth Surf. Processes Landforms 15, 687-698.
Brandt, C.J. and Thornes, J.B.: 1996, Mediterranean Desertification and Land Use, Wiley, Chichester, UK, 600 pp.
Cabezas, J., Vaquero, P. and Escudero, J.C.: 1991, 'Valoración de las Lluvias Interceptadas por Especies de Matorral Dotadas de Distintas Estrategias Estructurales,' Ecología 5, 163-171.
Carroll, C., Merton, L. and Burger, P.: 2000, 'Impact of Vegetative Cover and Slope on Runoff, Erosion, and Water Quality for Filed Plots on a Range of Soil and Spoil Materials on Central Queensland Coal Mines,' Aust. J. Soil Res. 38, 313-327.
Casermeiro, M.A., Molina, J.A., de la Cruz Caravaca, M.T., Costa, J.H., Massanet, M.I.H. and Moreno, P.S.: 2003, 'Influence of Scrubs on Runoff and Sediment Loss in Soils of Mediterranean Climate,' Catena(in press).
Cuadros, S. and Francia, J.R.: 1991, 'Caracterización del Sitio de Ensayo de Especies Forestales de Lanjarón, Vertiente sur de Sierra Nevada. Aspectos Climatológicos y Fitoclimáticos,' Sist. Rec. Fores. 1, 143-158.
Durán, Z.V.H., Martínez, R.A. and Aguilar, R.J.: 2004, 'Nutrient Losses by Runoff and Sediment from the Taluses of Orchard Terraces,' Water, Air and Soil Pollut. 153, 355-373.
FAO: 1976, A Framework for Land Evaluation, Soil Bulletin 32 FAO, Rome, Italy.
Francis, C.F. and Thornes, J.B.: 1990, 'Runoff Hydrographs from Three Mediterranean Vegetations Cover Types,' in J.B. Thornes (ed.), Vegetation and Erosion, Processes and Environments,Wiley, Chichester, UK, pp. 363-384.
ICONA: 1988, Agresividad de las Lluvias en España, Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. Madrid, España, 33 pp.
ICONA: 1991, La Erosión en España. Síntesis, Madrid, España, 25 pp.
Imeson, A.C.: 1990, Climate Fluctuations and Soil Erosion under Mediterranean Conditions, Technical Report, International University, Méndez Pelayo, Valencia, Spain.
Imeson, A.C.: 1995, 'The Physical, Chemical and Biological Degradation of the Soil,' in R. Fantechi, D. Peter, P. Balabanis and J.L. Rubio (eds.), Desertification in a European Context: Physical and Socio-Economic Aspects, The European School of Climatology and Natural Hazards Course, Alicante, Spain, pp. 153-168.
Kosmas, C., Danalatos, N., Cammeraat, L.H., Chabart, M., Diamantopoulos, J., Farand, L., Gutierrez, L., Jacob, A., Marques, H., Tomasi, N., Usai, D. and Vaca, A.: 1997, 'The Effect of Land Use on Runoff and Soil Erosion Rates under Mediterranean Conditions,' Catena 29, 45-59.
Kumar, K., Deep, P., Panda, Y.S. and Satial, G.S.: 2002, 'Runoff and Soil Loss from Steep Slopes Treated with Low Cost Bioengineering Measures,' The Environmentalist 22, 133-141.
Lal, R., Hall, G.F. and Miller, F.P.: 1989, 'Soil Degradation: I Basic Processes,' Land Degrad. Rehab. 1, 51-69.
López, B.F., Romero, D.A. and Martínez, J.F.: 1991, 'Soil Erosion in a Semi-Arid Mediterranean Environment. El Ardal Experimental Field (Murcia, Spain),' in M. Sala, J.L. Rubio and R.J.M. García (eds.), Soil Erosion Studies in Spain, Geoforma, Logroño, Spain, pp. 137-152.
López, B.F., Romero, D.A., Martínez, J.F. and Martínez, J.F.: 1998, 'Vegetation and Soil Erosion under Semi-Arid Mediterranean Climate: A Case Study from Murcia (Spain),' Geomorphology 24, 51-58.
Martínez, R.A., Cuadros, S. and Francia, J.R.: 1993, 'Plantas Aromáticas, Melíferas y Medicinales: Caracterización y Selección Enfocada a la Lucha Contra la Erosión,' in: Actas del Congreso Vol. III, Congreso Forestal Español, Lourizan-Pontevedra, Spain, pp. 103-107.
Martínez, F.J., López, B.F., Martínez, F.J. and Romero, D.A.: 1995, 'Land Use and Soil-Vegetation Relationships in a Mediterranean Ecosystem: El Ardal, Murcia, Spain,' Catena 25, 153-167.
Martínez, R.A., Francia, J.R., Martínez, V.A., Ruiz, S. and Aguilar, J.R.: 2001, 'Evaluation of Protection Soil with Different Plant Covers,' in: T.L. García, J. Benítez and V.A. Martínez (eds.), Conservation Agriculture, a World Challenge, ECAF-FAO, Vol. 2, Madrid, Spain, pp. 431-434.
Martínez, R.A., Francia, J.R., Martínez, V.A. and Ruiz, S.: 2002, 'Soil Conservation Techniques in the Cultivation of Perennials on Steep Slopes in Semi-Arid Ecosystems,' in J.L. Rubio, R.P.C. Morgan, A. Sins and V. Andreu (eds.), Proceedings of.48 Zuazo, Martínez and Raya the 3rd International Congress Man and Soil at the 3rd Millennium, Logroño, Spain, pp. 779-786.
Mota, J.F. and Valle, F.: 1996, 'Nuevos Datos para la Flora de Sierra Nevada (Andalucía, España),' Webbia 40, 323-334.
Ramos, M.C. and Porta, J.: 1993, 'Modelos de Distribución Espacio-Temporal de las Lluvias en la Zona Mediterránea del Anoia, Penedes. Influencia de la Sostenibilidad de los Cultivos en la Zona,' Ecología 7, 47-56.
Ramos, M.C. and Porta, J.: 1994, 'Rainfall Intensity and Erosive Potentiality in the NE Spain Mediterranean Area: Results on Sustainability of Vineyards,' Nuovo Cimento 17, 291-299.
Rivas, M.S.: 1961, 'Los Pisos de la Vegetación de Sierra Nevada, Andalucía, España,' Bol. R. Soc. Esp. Hist. Nat. 59, 55-64.
Rojo, L.: 1990, Plan Nacional de Restauración Hidrológico-Forestal y Control de la Erosión, Memoria, Tomo I: Mapas Tomo II, ICONA. Madrid, Spain.
Rosewell, C.J.: 1986, 'Rainfall Kinetic Energy in Eastern Australia,' J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 25, 1695-1701.
Rostagno, C.M.: 1989, 'Infiltration and Sediment Production as Affected by Soil Surface Conditions in Shrubland of Patagonia, Argentina,' J. Range. Manage. 42, 382-385.
Rubio, J.L., Andreu, V. and Cerni, R.: 1990, 'Degradación del Suelo por la Erosión Hídrica: Diseño Experimental y Resultados Preliminares, ' in: J. Alvadalejo, M.A. Stocking and E. Díaz (eds.), Degradación y Regeneración del Suelo en Condiciones Ambientales Mediterráneas, CSIC, Murcia, Spain, pp. 215-235.
Sanchez, L.A., Ataroff, M. and Lopez, R.: 2002, 'Soil Erosion under Different Vegetation Covers in the Venezuelan Andes,' The Environmentalist 22, 161-172.
Soil Survey Staff: 1999, Soil Taxonomy. A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, Agric. Handbook N 436, USDA-US, 778 pp.
Tromble, J.M.: 1987, 'Water Interception by Two Arid Land Shrubs,' J. Arid Environ. 15, 65-70.
UNEP: 1991, World Atlas of Desertification, United Nations Environmental Programme. Edward Arnold, London, UK, 69 pp.
Wiersum, K.F.: 1983, 'Effects of Various Vegetation Layers of an Acacia auriculiformisForest Plantations on Surface Erosion at Java, Indonesia,' in: S.A. El-Swaify, W.C. Moldenhauer and A. Lo (eds.), Soil Erosion and Conservation, Soil Conservation Society of America, Ankeny, IA, US, pp. 79-89.
Wischmeier, W.H. and Smith, D.D.: 1958, 'Rainfall Energy and Its Relationship to Soil Loss,' Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 39, 285-291.
Wischmeier, W.H. and Smith, D.D.: 1978, Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning, Agric. Handbook, 537, USDA-ARS, Washington, US, 59 pp.
Wu, H.I., Sharpe, P.J.H., Walker, J. and Penridge, L.K.: 1985, 'Ecological Field Theory: A Spatial Analysis of Resource Interference Among Plants,' Ecol. Model. 29, 215-243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuazo, V.D., Martínez, J.F. & Raya, A.M. Impact of Vegetative Cover on Runoff and Soil Erosion at Hillslope Scale in Lanjaron, Spain. The Environmentalist 24, 39–48 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ENVR.0000046345.44569.35
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ENVR.0000046345.44569.35