Abstract
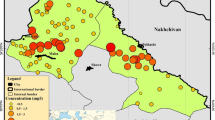
The west plain region of Jilin province of northeast China is one of the typical endemic fluorosis areas caused by drinking water for many years. Investigations of hydrogeological and eco-environmental conditions as well as endemic fluorosis were conducted in 1998. Results show that the ground water, especially, the water in the unconfined aquifer is the main source of drinking water for local residents. The fluoride concentration in groundwater in the unconfined aquifers is higher than that in the confined aquifer in the west plain of Jilin province. The fluoride concentration in the unconfined aquifer can be used to classify the plain into fluoride deficient area, optimum area and excess area, which trend from west to east. High fluoride (>1.0 mg L−1) in drinking water resulted in dental and skeletal fluorosis in local residents (children and pregnant women). There exists a positive correlation between fluoride concentration in the drinking water and the morbidities of endemic fluorosis disease (r 1 = 0.781, r 2 = 0.872). Health risks associated with fluoride concentration in drinking water are assessed. It has been determined that fluoride concentration in excess of 1.0 mg L−1 exposes residents to high health risks based on risk identification. The study area is classified into five health risk classes as shown in Figure 4. The risk indexes of this area more than 1.0 are accounted for 68% of the total west plain region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Endemic Disease Control Office in Jilin Province: 1996, The Present Status Fluorosis and Kaschin-Beek Disease in Jilin Province, Jilin People's Press, Jilin City (in Chinese).
Environment Protection Agent of China: 1987, Water quality-Analytical methods (GB7466~7494-87), National Standard of People's Republic of China.
Fang Ruikong: 1993, Chinese Medical Geography [M], Southeastern Chinese Normal University Press, Shanghai, pp. 102-108 (in Chinese).
Feng Bowen: 1996, Epidemiological characteristic of endemic fluorosis in Qianan county, Chinese Journal of Control Endemic Disease, China 16(Suppl. 6), 62-364.
Linthurst, R.A., Bourdeau, P. and Tardiff, R.G.: 1995, Methods to Assess the Effect of Chemicals on Ecosystems [M], SCOPE, John Wiley and Sons Ltd. New York, pp. 307-335.
Li He and Xu Guozhong: 1987, Effect of environmental factors on endemic fluorosis prevalence in lower plain area of west Jilin province, China, in: Proceedings of the Environment Geochemistry and Health, Geological Press, Beijing, pp. 112-115 (in Chinese).
Luo Hongbin: 1996, Investigation of dental caries of children in Changchun city, Chinese Journal of Control Endemic Disease, China 16(Suppl. 6), 326-327.
Meng Xianxi, Zhang Liping, Wang Zhongyi and Shi Chang Xiu: 1987, Fluoride in ecological environment of western Jilin province, China, in: Proceedings of the Environmental Geochemistry and Health, Geological Press, Beijing, pp. 336-338 (in Chinese).
Wang Wenjun and Zhang Xuelin: 1998, Study on fluoride level in water environment of west Songnen plain region, China, Journal of Environment Science 19(6), 662-666 (in Chinese).
Whiteford, G.M.: 1991, Fluoride, calcium and phosphorus metabolism in rats: Comparison of natural in gradients with semi-purified diets, Archives of Oral Biology 36(4), 291-297.
WHO: 1991, Fluoride and Fluoride (Environmental Health Criteria) 36, 274.
Zhang Bo, Hong Mei, Zhao Yongsheng: 2001, On GIS support distribution characteristics of the main components in the groundwater of the west plain region of Jilin province of China, World Geology 20, 175-182 (in Chinese).
Zhang Xuelin, Ren shufen and Rex, T.: 1996, Hydro-geochemical characteristics in ecotone zone of eco-environment in west region of northeast China, in: Proceedings of the Study on Ecotone Zone of Eco-environment in West Region of Northeast China, Huangxichou (ed), Science Press, Beijing, pp. 58-65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bo, Z., Mei, H., Yongsheng, Z. et al. Distribution and Risk Assessment of Fluoride in Drinking Water in the West Plain Region of Jilin Province, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health 25, 421–431 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EGAH.0000004560.47697.91
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EGAH.0000004560.47697.91