Abstract
This paper analyzes the factors involved in successful implementation of innovative pedagogical practices using ICT in ten Israeli schools. The research questions addressed are:
1. What is the configuration and intensity level of the various factors involved in the implementation of innovative pedagogical practices using ICT in schools?
2. Can a connection be identified between the level of intensity of the different factors affecting the innovation and the level of change in various domains of innovation (e.g., teacher role, student role, curriculum, and time and space configurations)?
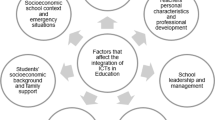
Data from ten case studies in Israeli schools were analyzed using the framework developed to measure the intensity of the factors involved in the innovation. Infrastructure, factors within the school, school climate and educational policy were found to be the most involved categories. These factors mostly affect aspects of the innovation related to teacher roles, instructional contents and teaching methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, P. and McLaughlin, M. (1974) Federal Programs Supporting Educational Change, Vol. I: A Model of Educational Change. Rand Corporation, Santa Monica, CA.
Berman, P. and McLaughlin, M. (1977) Federal Programs Supporting Educational Change. Rand Corporation, Santa Monica, CA.
Cuban, L. (1999) The lure of curricular reform and its pitiful history. Phi Delta Kappan, 75(5), 182–185.
Crofton, C. (1981) Planned Change in the Educational Environment. Unpublished report. Educational Testing Service, Evanston, IL.
ECS: Education Commission of the States (1999) Comprehensive School Reform: Five Lessons from the Field. Denver, Colorado.
Fullan, M. (1998) Leadership for the 21st century: Breaking the bonds of dependency. Educational Leadership, 55(7), 6–10.
Fullan, M. (2001) The New Meaning of Educational Change, 3rd edition. Teachers College, Columbia University, New York.
Gibton, D. (2001) Once the government provided education. Now it provides information on education: Insights from what UK headteachers think of Educational Law regarding decentralization policy, self-management and autonomy. In The Annual Conference of the British Educational Management and Administration Society (BEMAS), October 5–7, Newport-Pagnell, UK.
Goodlad, J. (1991) Why we need a complete redesign of teacher education. Educational Leadership, 49, 4–10.
Hall, G. E. and Hord, S. M. (1987) Changing in Schools. University of New York Press, Albany.
Kinsler, K. and Gamble, M. (2002) Reforming Schools. Continuum, New York.
Kozma, R. (2000) Qualitative Studies of Innovative Pedagogical Practices Using Technology. SITES M2 design document, IEA.
Kozma, R. (ed.) (2003) Technology, Innovation and Educational Change – A Global Perspective. ISTE Publications, Eugene, Oregon.
Lacey, C. (1977) The Socialization of Teachers. Methuen, London.
Lortie, D. (1975) Schoolteacher: A Sociological Study. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Malouf, D. and Schiller, E. (1995) Practice and research in special education. Exceptional Children, 61, 414–424.
Marsh, D. D. (2001) Educational leadership for the twenty-first century: Integrating three essential perspectives. In: Jossey-Bass Reader on Educational Leadership. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
McLaughlin, M. W. (1991) The rand change agent study: Ten years later. In Education Policy Implementation, A. R. Odden (ed.). State University of New York Press, Albany.
Meier, D. (1995) The Power of Their Ideas. Beacon Press, Boston.
Mioduser, D., Nachmias, R., Tubin, D., and Forkosh-Baruch, A. (2003) Analysis schema for the study of domains and levels of pedagogical innovation in schools using ICT. Education and Information Technologies, 8(1), 23–36.
OECD/CERI (2000) Schooling for Tomorrow, Methodology for Case Studies of Organizational Change. OECD.
Pelgrum, W. and Anderson, R. (eds.) (1999) ICT and the Emerging Paradigm for Life Long Learning: Worldeide Educational Assessment of Infrastructure, Coals and Practices. IEA and the University of Twente, Enshede, the Netherlands.
Rogers, E. M. (1995) Diffusion of Innovations. The Free Press, New York.
Rosenholtz, S. J. (1989) Teacher's Workplace: The Social Organization of Schools. Longman, White Plains, NY.
Sarason, S. (1993) The Case for Change: Rethinking the Preparation of Educators. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Scheurich, J. J. and Fuller, E. (1995) Is Systematic Reform the answer for schools and science education? Cautions from the fields. Theory into Practice, 34(1), 12–20.
Sizer, T. (1993) Horace's School: Redesigning the American High School. Houghton-Mifflin, Boston.
Tyack, D. and Cuban, L. (1995) Tinkering Toward Utopia. Harvard University Press, Cambridge.
Tubin, D. and Chen, D. (2002) School-based staff development for teaching within computerized learning envi-ronments. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 34(4), 517–528.
Tubin, D., Nachmias, R., Mioduser, D., and Forkosh-Baruch, A. (2003) Domains and levels of pedagogical innovation in schools using ICT: Ten innovative schools in Israel. Education and Information Technologies, 8(2), 127–145.
Underwood, J. and Underwood, G. (1990) Computers and Learning: Helping Children Acquire Thinking Skills. Blackwell, Oxford.
Venezky, R. L. (2001) Procedures for evaluation the impact of complex educational interventions. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 10(1), 17–30.
2649_33723_1_119832_1_1_1,00.html
Yin, R. K. (1984) Case Study Research: Design and Method. Sage Publication, Beverly Hills.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nachmias, R., Mioduser, D., Cohen, A. et al. Factors Involved in the Implementation of Pedagogical Innovations Using Technology. Education and Information Technologies 9, 291–308 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EAIT.0000042045.12692.49
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EAIT.0000042045.12692.49