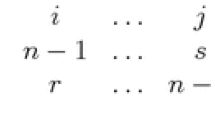Abstract
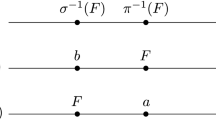
A permutation array (or code) of length n and distance d is a set Γ of permutations from some fixed set of n symbols such that the Hamming distance between each distinct x, y ∈ Γ is at least d. One motivation for coding with permutations is powerline communication. After summarizing known results, it is shown here that certain families of polynomials over finite fields give rise to permutation arrays. Additionally, several new computational constructions are given, often making use of automorphism groups. Finally, a recursive construction for permutation arrays is presented, using and motivating the more general notion of codes with constant weight composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Battiti and M. Protasi, Reactive local search for the maximum clique problem, Algorithmica, Vol. 29 (2001) pp. 610–637.
A. Bonisoli and P. Quattrocchi, Each invertible sharply d-transitive finite permutation set with d ≤ 4 is a group, J. Algebraic Combin., Vol. 12 (2000) pp. 241–250.
A. E. Brouwer, James B. Shearer, N. J. A. Sloane and Warren D. Smith, A new table of constant weight codes, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, Vol. 36 (1990) pp. 1334–1380.
C. J. Colbourn, T. Kløve and A. C. H. Ling, Permutation arrays for powerline communication and mutually orthogonal Latin squares, IEEE Trans. Information Theory (to appear).
P. Das, The number of permutation polynomials of a given degree over a finite field, Finite Fields and Their Applications, Vol. 8 (2002) pp. 478–490.
D. R. de la Torre, C. J. Colbourn and A. C. H. Ling, An application of permutation arrays to block ciphers. Proceedings of the Thirty-first Southeastern International Conference on Combinatorics, Graph Theory and Computing (Boca Raton, FL, 2000). Congr. Numer., Vol. 145 (2000) pp. 5–7.
M. Deza and S. A. Vanstone, Bounds for permutation arrays, J. Statist. Plann. Inference, Vol. 2 (1978) pp. 197–209.
H. C. Ferreira and A. J. H. Vinck, Interference cancellation with permutation trellis codes, Proc. IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, Vol. 5 (2000) pp. 2401–2407.
P. Frankl and M. Deza, On the maximum number of permutations with given maximal or minimal distance, J. Combin. Theory Ser. A, Vol. 22 (1977) pp. 352–360.
R. Lidl and H. Niederreiter, Finite Fields, second edition, Cambridge University Press (1997).
N. Pavlidou, A. J. H. Vinck, J. Yazdani and B. Honary, Power line communications: State of the art and future trends, IEEE Communications Magazine, (2003) pp. 34–40.
F. Ruskey, C. R. Miers and J. Sawada, The number of irreducible polynomials and Lyndon words with given trace, SIAM J. Discrete Math., Vol. 14 (2001) pp. 240–245.
M. Svanström, P. R. J. Östergard and G. T. Rumelova, Bounds and constructions for ternary constant-composition codes, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, Vol. 48 (2002) pp. 101–111.
H. Tarnanen, Upper bounds on permutation codes via linear programming, European J. Combin., Vol. 20 (1999) pp. 101–114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, W., Colbourn, C.J. & Dukes, P. Constructions for Permutation Codes in Powerline Communications. Designs, Codes and Cryptography 32, 51–64 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DESI.0000029212.52214.71
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DESI.0000029212.52214.71