Abstract
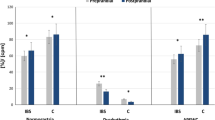
The aim was to assess the roles of gut hormones and immune dysfunction in irritable bowel. In Study I, rectal mucosal samples examined blindly showed no histological evidence of inflammation in 16 irritable bowel patients compared to 17 healthy controls. The proinflammatory mediators interleukin-1β and prostaglandin E2 also failed to show evidence of inflammation. Vasoactive intestinal peptide was elevated in irritable bowel (P=0.01), but substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and somatostatin levels were similar to control values. In Study II, 30 irritable bowel patients had elevated (P=0.002) plasma concentrations of vasoactive intestinal peptide compared to 30 controls, and peptide levels were unrelated to whether the patient's predominant bowel habit was constipation, diarrhea, or both in alternation. In conclusion, no evidence of inflammation was detected in irritable bowel patients, but elevated vasoactive intestinal peptide concentrations were observed in both studies and might represent a potential diagnostic tool for irritable bowel syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tompson WG, Longstreth GF, Drossman DA, Heaton KW, Irvine EJ, Muller-Lissner SA: Functional bowel disorders and functional abdominal pain. InThe Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, 2nd ed. Drossman DA, Corazziari E, Talley NJ, Thompson WG, Whitehead WE (eds). McLean, VA, Degnon Associates, 2000, pp 351–432
Kellow JE, Phillips SF, Miller LJ, Zinsmeister AR: Dysmotility of the small intestine in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 29:1236–1243, 1988
Whitehead WE, Engel BT, Schuster MM: Irritable bowel syndrome: Physiological and psychological differences between diarrheapredominant and constipation-predominant patients. Dig Dis Sci 25:404–413, 1980
Heaton KW, O'Donnell LJD, Braddon FEM, Mountbank RA, Hughes AO, Cripps PJ: Symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in a British urban community: Consulters and nonconsulters. Gastroenterology 102:1962–1967, 1992
Ritchie J: Pain from distension of the pelvic colon by inflating a balloon in the irritable colon syndrome. Gut 14:125–132, 1973
Whitehead WE, Holtkotter B, Enck P, Hoelzl R, Holmes KD, Anthony J, Shabsin HS, Schuster MM: Tolerance for rectosigmoid distension in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 98:1187–1192, 1990
Mertz H, Naliboff B, Munakata J, Niazi N, Mayer EA: Altered rectal perception is a biological marker of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 109:40–52, 1995
Whitehead WE, Palsson OS: Is rectal sensitivity a biological marker for irritable bowel syndrome: Psychological influences on pain perception in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 115(5):1263–1271, 1998
Collins SM: Is the irritable gut an inflamed gut? Scand J Gastroenterol 192:102–105, 1992
Collins SM, Barbara G, Vallance B: Stress, inflammation and the irritable bowel syndrome. Can J Gastroentrol 12(Suppl A):A47–A49, 1999
Weston AP, Biddle WL, Bhatia PS, Miner PB Jr: Terminal ileal mucosal mast cells in irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 38:1590–1595, 1993
Libel R, Biddle WL, Miner PB Jr: Evaluation of anorectal physiology in patients with increased mast cells. Dig Dis Sci 38:877–881, 1993
Khan I, Collins SM: Is there an in inflammatory basis for a subset of patients presenting with diarrhoea in the irritable bowel syndrome? Gastroenterology 106:A523, 1994
Barbara G, Stanghellini V, DeGiorgio R, Pasquinelli G, Cogliandro L, Cenacchi G, Santini D, Corradi F, Cremon C, Salvioli B, Cogliandro R, Corinaldesi R: Neuroimmune interactions in the colonic mucosa of irritable bowel syndrome patients. Gastroenterology 118:A138, 2000
Gwee KA, Graham JC, McKendrick MW, Collins SM, Marshall JS, Walters SJ, Read NW: Psychometric scores and persistence of irritable bowel after infectious diarrhoea. Lancet 347:150–153, 1996
Gwee KA, Leog YL, Graham C, McKendrick MW, Collins SM, Walters SJ, Underwood JE, Path FRC, Read NW: The role of psychological and biological factors in post-infective gut dysfunction. Gut 44:400–406, 1999
Collins SM, McHugh K, Jacobson K, Khan I, Riddell R, Murase K, Weingarten HP: Previous inflammation alters the response of the rat colon to stress. Gastroenterology 111:1509–1515, 1996
Isaacs KL, Sartor RB, Haskill S: Cytokine messenger RNA pro-files in inflammatory bowel disease mucosa deteted by polymerase chain reaction amplifiation. Gastroenterology 103:1587–1595, 1992
Schreiber S, Nikolaus S, Hampe J, Hamling J, Koop I, Groessner B, Lochs H, Raedler A: Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 beta in relapse of Crohn's disease. Lancet 353:459–461, 1999
McAlindon ME, Hawkey CJ, Mahida YR: Expression of interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 1 beta converting enzyme by intestinal macrophages in health and inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 42:214–219, 1998
Sharon P, Liqumsky M, Rachmilewitz D, Zor U: Role of prostaglandins in ulcerative colitis. Enhanced production during active disease and inhibition by sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology 75:638–640, 1978
Chan J, Gonsalkorale WM, Perrey C, Previca V, Hajeer AH, Whorwell PJ, Hutchinson IV: IL-10 and TGF-B genotypes in irritable bowel syndrome: evidence to support an inflammatory component? Gastroenterology 118:A184, 2000
Mayer EA, Raybould HE: Role of visceral afferent mechanisms in functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 99:1688–1704, 1990
Dockray GJ: Vasocative intestinal polypeptide and related peptides. InGut Peptides: Biochemistry and Physiology. Nalsh JH, Dockray GJ (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1994
Krejs GJ, Fordtran JS, Bloom SR, Fahrenkrug J, Schaffalitzky de Muckarell OB, Fischer JE, Humphrey CS, O'Dorisio TM, Said SI, Walsh JH, Shulkes AA: Effect of VIP infusion on water and ion transport in the human jejunum. Gastroenterology 78:722–727, 1980
Love JA, Szurszewski JH: The electrophysiological effects of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the guinea-pig inferior mesenteric ganglion. J Physiol 394:67–84, 1987
Grider JR, Cable MB, Said SI, Makhlouf GM: Vasoactive intestinal peptide as a neural mediator of gastric relaxation. Am J Physiol 248:G73–G78, 1985
Hooshmand H: Chronic pain: reflex sympathetic dystrophy prevention and management. Ann Arbor, MI, CRC Press
Brown DR (ed). Gastrointestinal Regulatory Peptides. New York, Springer-Verlag, 1993
Newman JB, Lluis F, Townsend CM Jr: Somatostatin. InGastrointestinal Endocrinology. Thompson JC, Greely GH Jr, Rayford PL, Townsend CM Jr (eds). New York, McGraw-Hill, p 286
Whitehead WE, Delvaux M, Working Team: Standardization of barostat procedures for testing smooth muscle tone and sensory thresholds in the gastrointestinal tract. Dig Dis Sci 42:223–241, 1997
Gracely RH, McGrath PA, Dubner R: Ratio scales of sensory and affective verbal pain descriptors. Pain 5:5–18, 1978
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–681, 1970
Besterman HS, Sarson DL, Rambaud JC, Stewart JS, Guerin S, Bloom SR: Gut hormone responses in the irritable bowel syndrome. Digestion 21:219–224, 1981
Simren M, Stotzer PO, Sjovall H, Abrahamsson H, Bjornsson ES: Abnormal levels of neuropeptide Y and peptide YY in the colon in irritable bowel syndrome. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:55–62, 2003
Morise K, Furusawa A, Yamamoto H, Saito H: [Role of gut hormones in irritable bowel syndrome.] Nippon Rinsho Jap J Clin Med 50:2697–2702, 1992
Shinomura Y, Himeno S, Kurokawa M, Takashashi S, Kuroshima T, Okuno M, Kanayama S, Tsuji K, Higashimoto Y, Tarui S: Release of vasoactive intestinal peptide by intraduodenal infusion of HCl or fat and intramuscular injection of neostigmine in man. Hepatogastroenterology 32:129–132, 1985
Simren M, Abrahamsson H, Bjornsson ES: An exaggerated sensory component of the gastrocolonic response in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 48:20–27, 2001
Waldman DB, Gardner JD, Zfass AM, Makhlouf GM: Effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide, secretin, and related peptides on rat colonic transport and adenylate cyclase activity. Gastroenterology 73:518–523, 1977
Barbezat GO, Grossman MI: Intestinal secretion: Stimulation by peptides. Science 174:422–424, 1971
Krejs GJ, Fordtran JS, Bloom SR, Fahrenkrug J, Schaffalitzky de Muckarell OB, Fisher JE, Humphrey CS, O'Dorisio TM, Said SI, Walsh JH, Shulkes AA: Effect of VIP infusion on water and ion transport in the human jejunum. Gastroenterology 78:722–727, 1980
Biancani P, Walsh JH, Behar J: Vasoactive intestinal-polypeptide: A neurotransmitter for relaxation of the rabbit internal anal sphincter. Gastroenterology 89:867–874, 1985
De Beurme FA, Lefebvre RA: Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide as possible mediator of relaxation in the rat gastric fundus. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:711–715, 1988
Goyal RK, Rattan S, Said SI: VIP as a possible neurotransmitter of non-cholinergic non-adrenergic inhibitory neurons. Nature 288:378–380, 1980
Grider JR, Rivier JR: Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) as transmitter of inhibitory motor neurons of the gut: Evidence from the use of selective VIP antagonists and VIP antiserum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:738–742, 1990
Love JA, Szurszewski JH: The electrophysiological effects of vasocative intestinal polypeptide in the guinea-pig inferior mesenteric ganglion. J Physiol 384:67–84, 1987
Grider JR: Identification of neurotransmitters regulating intestinal peristaltic reflex in humans. Gastroenterology 97:1414–1419, 1989
Koch TR, Carney JA, Go L, Go VL: Idiopathic chronic constipation is associated with decreased colonic vasoactive intestinal peptide. Gastroenterology 94:300–310, 1988
Milner P, Crowe R, Kamm MA, Lennard-Jones JE, Burnstock G:Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide levels in sigmoid colon in idiopathic constipation and diverticular disease. Gastroenterology 99:666–675 1990
Koch TR, Mitchener SR, Go VL: Plasma vasoactive intestinal polypeptide concentration determined in patients with diarrhea. Gastroenterology 100:99–106, 1991
Bloom SR: Vasoactive intestinal peptide, the major mediator of the WDHA (pancreatic cholera) syndrome: Value of measurement in diagnosis and treatment. Am J Dig Dis 23:373–376, 1978
Dawson J, Bryant MG, Bloom SR, Peters JJ: Gastrointestinal regulatory peptide storage granule abnormalities in jejunal mucosal diseases. Gut 25:636–643, 1984
Lembo T, Fullerton S, Diehl D, Raeen H, Munakata J, Naliboff B, Mayer EA: Symptom duration in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol 91:898–905, 1996
Munakata J, Naliboff B, Harraf F, Kodner A, Lembo T, Chang L, Silverman DHS, Mayer EA: Repetitive sigmoid colon stimulation induces rectal hyperalgesia in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 112:55–63, 1997
Lembo T, Munakata J, Mertz H, Niazi N, Kodner A, Nikas V, Mayer EA: Evidence for the hypersensitivity of lumbar splanchnic afferents in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 107:1686–1696, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palsson, O.S., Morteau, O., Bozymski, E.M. et al. Elevated Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Concentrations in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 49, 1236–1243 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DDAS.0000037818.64577.ef
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DDAS.0000037818.64577.ef