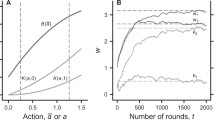
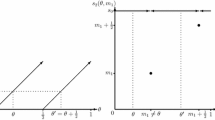
Abstract
We study an agency model, in which the principal has only incomplete information about the agent's preferences, in a dynamic setting. Through repeated interaction with the agent, the principal learns about the agent's preferences and can thus adjust the inventive system. In a dynamic computational model, we compare different learning strategies of the principal when facing different types of agents. The results indicate that better learning of preferences can improve the situation of both parties, but the learning process is rather sensitive to random disturbances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashlock, D., M.D. Smucker, E.A. Stanley and L. Tesfatsion (1995), “Preferential Partner Selection in an Evolutionary Study of Prisoner's Dilemma,” Economic Report Series 35, Iowa State University.
Axelrod, R. (1984), The Evolution of Cooperation. Basic Books, New York.
Axelrod, R. (1987), “The Evolution of Strategies in the Iterated Prisoner's Dilemma,” in L. Davis (Ed.), Genetic Algorithms and Simulated Annealing, Pitman, London, pp. 32–41.
Bower, A.G., S. Garber, and J.C. Watson (1996), “Learning About a Population of Agents and the Evolution of Trust and Cooperation,” International Journal of Industrial Organization, 15(2), 165–190.
Carley, K. (1999), “Learning Within and Among Organizations,” in A.S. Miner and P. Anderson (Eds.), Population—level Learning and Industry Change, Stamford, Conn., JAI Press, London, pp. 33–53.
Carley, K. and J.—S. Lee (1998), “Dynamic Organizations: Organizational Adaptation in a Changing Environment,” in J.A. Baum (Ed.) Disciplinary Roots of Strategic Management Research, Stamford, Conn., JAI Press, London, pp. 269–297.
Carley, K.M. and D.M. Svoboda (1996), “Modeling Organizational Adaptation as a Simulated Annealing Process,” Sociological Methods and Research, 25(1), 138–168.
Edmonds, B. (2001), “Towards a Descriptive Model of Agent Strategy Search,” Computational Economics, 18(1), 113–135.
Eisenhardt, K.M. (1989), “Agency Theory: An Assessment and Review,” Academy of Management Review, 14(1), 57–74.
Epstein, J.M. (2001), “Learning to Be Thoughtless: Social Norms and Individual Computation,” Computational Economics, 18(1), 9–24.
Flache, A. and M.W. Macy (2002), “Stochastic Collusion and the Power Law of Learning: A General Reinforcement Learning Model of Cooperation,” Journal of Conflict Resolution, 46(5), 629–653.
Grossmann, V. (2002), “Is it Rational to Internalize the Personal Norm that One Should Reciprocate?” Journal of Economic Psychology, 23(1), 27–48.
Harris, M. and A. Raviv (1979), “Optimal Incentive Contracts with Imperfect Information,” Journal of Economic Theory, 20(2), 231–259.
Hauk, E. (2001), “Leaving the Prison: Permitting Partner Choice and Refusal in Prisoner's Dilemma Games,” Computational Economics, 18(1), 65–87.
Hoffmann, R. (1999), “The Independent Localisations of Interaction and Learning in the Repeated Prisoner's Dilemma,” Theory and Decision, 47(1), 5772.
Hoffmann, R. (2001), “The Ecology of Cooperation,” Theory and Decision, 50(2), 101–118.
Kadane, J.B. and P.D. Larkey (1982), “Subjective Probability and the Theory of Games,” Management Science, 28(2), 113–120.
Kadane, J.B. and P.D. Larkey (1983), “The Confusion of Is and Ought in Game Theoretic Contexts,” Management Science, 29(12), 1365–1379.
Kirchkamp, O. (1999), “Simultaneous Evolution of Learning Rules and Strategies,” Journal of Economic Behaviour and Organization, 40(3), 295–312.
Klos, T.B. (1999), “Decentralized Interaction and Co—Adaptation in the Repeated Prisoner's Dilemma,” Computational and Mathematical Organization Theory, 5(2), 147–165.
Klos, T.B. and B. Nooteboom (2001), “Agent—Based Computational Transaction Cost Economics,” Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 25(3/4), 503–526.
Laslier, J.—F., R. Topol, and B. Walliser (2001), “A Behavioral Learning Process in Games,” Games and Economic Behavior, 37(2), 340–366.
Liebrand, W.B. and D.M. Messick (1996), “Computer Simulation of Cooperative Decision Making,” in W.B. Liebrand and D.M. Messick (Eds.), Frontiers in Social Dilemma Research, Springer, Berlin, pp. 215–234.
Macy, M.W. (1996), “Natural Selection and Social Learning in Prisoner's Dilemma: Co—adaptation with Genetic Algorithms and Artificial Neural Networks,” in W.B. Liebrand and D.M. Messick (Eds.), Frontiers in Social Dilemmas Research, Springer, Berlin, pp. 235–265.
Meng, C.—L. and R. Pakath (2001), “The Iterated Prisoner's Dilemma: Early Experiences with Learning Classifier System—Based Simple Agents,” Decision Support Systems, 31(4), 379–403.
Miller, J., C. Butts, and D. Rode (2002), “Communication and Cooperation,” Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, 47(2), 179–195.
Miller, J.H. (1996), “The Coevolution of Automata in the Repeated Prisoner's Dilemma,” Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, 29(1), 87–112.
Mirrlees, J.A. (1976), “The Optimal Structure of Incentives and Authority within an Organization,” The Bell Journal of Economics, 7(1), 105–131.
Rose, D. and T.R. Willemain (1996a), “The Principal—Agent Problem with Adaptive Players,” Computational and Mathematical Organization Theory, 1(2), 157–182.
Rose, D. and T.R. Willemain (1996b), “The Principal—Agent Problem with Evolutionary Learning,” Computational and Mathematical Organization Theory, 2(2), 139–162.
Rubinstein, A. (1986), “Finite Automata Play the Repeated Prisoner's Dilemma,” Journal of Economic Theory, 39(1), 83–96.
Schneeweiss, C. (1999), Hierarchies in Distributed Decision Making, Springer, Berlin.
Spremann, K. (1987), “Agent and Principal,” in G. Bamberg and K. Spremann (Eds.), Agency Theory, Information and Incentives, Springer, Berlin, pp. 3–37.
Vetschera, R. (2003), “Behavioral Uncertainty and Investments in Cooperative Relationships,” Managerial and Decision Economics, 24, in print.
Watanabe, Y. and T. Yamagishi (1999), “Emergence of Strategies in a Selective Play Environment with Geographic Mobility: A Computer Simulation,” in M. Foddy, M. Smithson, S. Schneider, and M. Hogg (Eds.), Resolving Social Dilemmas, Psychology Press, pp. 55–66.
Weber, M. (1987), “Decision Making with Incomplete Information,” European Journal of Operational Research, 28(1), 44–57.
Yamagishi, T. and N. Hayashi (1996), “Selective Play: Social Embeddedness of Social Dilemmas,” in W.B. Liebrand and D.M. Messick (Eds.), Frontiers of Social Dilemma Research, Springer, Berlin, pp. 363–384.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vetschera, R. Experimentation and Learning in Repeated Cooperation. Computational & Mathematical Organization Theory 9, 37–60 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CMOT.0000012308.48001.d9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CMOT.0000012308.48001.d9