Abstract
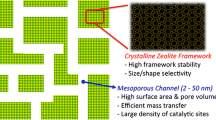
Application of a microwave technique to the conventional hydrothermal process is gaining importance, especially, in the synthesis of nanoporous materials. This microwave technique is regarded as a novel synthesis tool because it gives several beneficial advantages such as homogeneous nucleation, rapid synthesis, formation of uniform crystals, and small crystallites, facile morphology control, energy efficiency and so on. Recently, it was found that it offers an efficient way to control the crystal morphology, size and orientation, and even crystalline phase which are required for many emerging applications of nanoporous materials. This review summarizes recent work on the microwave effect, supramolecular interactions and control of crystal morphology upon microwave synthesis of nanoporous materials performed by the present authors. Synthesis and morphology control of nanoporous materials such as ZSM-5, zeolite beta, metallosilicates, AlPO, MCM-41, SBA-15, SBA-16, etc. have been accomplished with microwave irradiation. In particular, the rapid nucleation and crystallization of ZSM-5 zeolite under microwave irradiation made it possible to enable the continuous microwave synthesis, implying a great industrial and technological importance. The formation of nanoporous materials, especially, silicate or aluminosilicate molecular sieves was described on the basis of supramolecular interactions between organic template molecules and silicate species under microwave irradiation. Besides decreasing synthesis time, it was duly demonstrated that the microwave technique provides an effective way to control particle size distribution and macroscopic morphology in the synthesis. Moreover, for the application of these porous materials, microwave-induced nanofabrication of microporous and mesoporous materials is more important than that of simple porous materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M.P. Mingos, Res. Chem. Intermed. 20 (1994) 85.
A.R. Crosland and N. Bratchell, J. Assoc. Public Anal. 26 (1988) 89.
S.A. Matthes, In Introduction to Microwave Sample Preparation: Theory and practice, L.B. Jassie and H.M. Kingston (eds), (ACS, Washington DC, 1988) p. 33.
H.M. Kingston and S.J. Haswell (eds), Microwave-Enhanced Dhemistry, Fundamentals, Sample Preparation, and Application (ACS, Washington DC, 1997).
G. Roussy and P. Chenot, J. Phys. Chem. 85 (1981) 2199.
K.J. Rao, B. Vaidhyanathan, M. Ganguli and P.A. Ramakrishnan, Chem. Mater. 11 (1999) 882.
O. Tatsuo and W. Akiko, Phys. Chem. Commun. 3 (2001) 1.
G. Roussy, S. Hilaire, J.M. Thiebaut, G. Maire, F. Garin and S. Ringler, Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 156 (1997) 167.
G. Bond, R.B. Moyes and D.A. Whan, Catal. Today, 17 (1993) 427.
F.J. Berry, L.E. Smart, P.S. Sai Prasad, N. Lingaiah and P. Kanta Rao, Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 204 (2000) 191.
Y. Wang, J.H. Zhu, J.M. Cao, Y. Chun and Q.H. Xu, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 26 (1998) 175.
X. Zhang, D.O. Hayward and D.M.P. Mingos, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 40 (2001) 2810.
S.M. Margolis, L. Jasse and H.M. Kingston, J. Aut. Chem. 13 (1991) 93.
A. Sanders, H. Wetzel,M. Kunst,In Microwave Processing of Materials II, W. Snyder Jr., W.H. Sutton, M. Iskander and D.L. Johnson (eds), Vol. 189, (MRS, Pittsburgh, PA, 1990) p. 403.
W.H. Sutton, Ceramic Bull. 68 (1989) 376.
C.S. Cundy, R.J. Plaisted and J.P. Zhao, Chem. Commun. (1998) 1465.
P. Lidström, J. Tierney, B. Wathey and J. Westman, Tetrahedron 57 (2001) 9225.
C.S. Cundy, Collect. Czech, Chem. Commun. 63 (1998) 1699and references therein.
J. Zhu, O. Polchik, S. Chen and A. Gedanken, J. Phys. Chem. B 104 (2000) 7344.
G.A. Ozin, Adv. Mater. 4 (1992) 612.
M.E. Davis, Nature 417 (2002) 813.
C.T. Kresge, M.E. Leonowicz, W.J. Roth, J.C. Vartuli and J.S. Beck, Nature 359 (1992) 710.
C.B. Amphlett, Inorganic Ion Exchangers, (Elsevier, New York, 1964).
D.W. Breck and E.M. Flanigen (eds), Zeolite Molecular Sieves, (Society of Chemical Industry, London, 1968) p. 47.
A. Corma, Chem. Rev. 97 (1997) 2373.
A. Corma, J. Catal., in press.
C.S. Cundy and P.A. Cox, Chem. Rev. 103 (2003) 663.
IUPAC Manual of Symbols and Terminology, Appendix 2, Part 1, Colloid and Surface Chemistry, Pure Appl. Chem. 31 (1972) 578.
C. Gabriel, S. Gabriel, E.H. Grant B.S.J. Halsteed and D.P. Mingos, Chem. Soc. Rev. 27 (1998) 213.
G. Roussy and P. Chenot, J. Phys. Chem. 85 (1981) 2199.
P. Chu, F.G. Dwyer and J.C. Vartuli, US Patent 4778 666, 1998.
A. Arafat, J.C. Jansen, A.R. Ebaid and H. van Bekkum, In Synthesis of Microporous Materials, M.L. OccelliandH.E. Robson(eds), Vol. 1 (Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1992) p. 507.
A. Arafat, J.C. Jansen, A.R. Ebaid and H. van Bekkum, Zeolites 13 (1993) 162.
I. Girnus, K. Jancke, R. Vetter, J. Richter-Mendau and J. Caro, Zeolites 15 (1995) 33.
S.H. Jhung, J.-S. Chang, J.S. Hwang and S.-E. Park, Microporous Mesopor. Mater., in press.
J.G. Carmona, R.R. Clemente and J.G. Morales, Zeolite 18 (1997) 340.
C.G. Wu and T. Bein, Chem. Commun. (1996) 925.
S.-E. Park, D.S. Kim, J.-S. Chang and W.Y. Kim, Catal. Today 44 (1998) 301.
H.M. Sung-Suh, D.S. Kim and S.-E. Park, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 5 (1999) 191.
Y. Sun, W. Lin, J. Chen, Y. Yue and W. Pang, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 105A (1997) 77.
Y. Zhang, S. Zhao, G. Sun and Z. Wang, Cuihua Xuebao 21 (2000) 345.
B.L. Newalkar, S. Komarneni and H. Katsuki, Chem. Commun. (2000) 2389.
B.L. Newalkar and S. Komarneni, Chem. Mater. 13 (2001) 4573.
B.L. Newalkar, J. Olanrewaju and S. Komarneni, Chem. Mater. 13 (2001) 552.
B.L. Newalkar, J. Olanrewaju and S. Komarneni, Phys. Chem. B 105 (2001) 8356.
Y.K. Hwang, J.-S. Chang, Y.-U. Kwon and S.-E. Park, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 146 (2003) 101.
S.L. Burkett and M.E. Davis, In Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry, G. Alberti and T. Bein(eds), Vol. 7 (Pergamon, Exter, 1996) p.465.
A.R. von Hippel (eds), Dielectric Materials and Applications(MIT, Cambridge, 1954) p. 361.
D.E. Clark,In Microwave: Theory and Application in Materials Processing IV, D.E. Clark,W.H. SuttonandD.A. Lewis (eds), Ceram. Trans. 21 (Am. Ceram. Soc., Westerville, OH, 1991) p. 698.
D.M.P. Mingos and A.G. Whittaker, J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. (1992) 2751.
F. Smith, B. Cousins, J. Bozic and W. Flora, Anal. Chim. Acta. 177 (1985) 243.
E.H. Grant, R.J. Sheppard and G.P. South (eds), Dielectric Behaviour of Biological Molecules in Solution, (Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK, 1978).
D.M.P. Mingos and D.R. Baghurst, Chem. Soc. Rev. 20 (1991) 47.
D.S. KimPh.D. Thesis, A study on nanoporous materials synthesized by microwave, Korea University, 2000.
J.P. Zhao, C. Cundy and J. Dwyer, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 105 (1997) 181.
L. Gora and R.W. Thompson, Zeolites 18 (1997) 132.
D.S. Kim, J.M. Kim, J.-S. Chang and S.-E. Park, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 135 (2001) 333.
D. Zhao, Q. Huo, J. Feng, B.F. Chemlka and G.D. Stucky, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120 (1998) 6024.
S.A. Bagshaw, E. Prouzet and T.J. Pinnavaia, Science 269 (1995) 1242.
K.W. Gallis, J.T. Araujo, K.J. Duff, J.G. Moore and C.C. Landry, Adv. Mater. 11 (1999) 1452.
M. Grun, I. Lauer and K.K. Unger, Adv. Mater. 9 (1997) 254.
T. Bein, Chem. Mater. 5 (1993) 905.
D. Zhao, Q. Huo, J. Feng, B.F. Chemlka and G.D. Stucky, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120 (1998) 6024.
S.L. Burkett and M.E. Davis, J. Phys. Chem. 98 (1994) 4647.
A. Karlsson, M. Stöcker and R. Schmidt, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 27 (1999) 181.
D.S. Kim, S.-E. Park and S.A. Kang, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 129 (2000) 107.
H.M. Sung-Suh, D.S. Kim, Y.K. Park and S.-E. Park, Res. Chem. Intermed. 26(2000) 283.
S.-E. Park, D.S. Kim, J.-S. Chang and W.Y. Kim, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 117 (1998) 265.
J.K. Thomas, Chem. Rev. 80 (1980) 283.
M. Almgreen, F. Grieser and J.K. Thomas, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102 (1980) 3188.
K. Kalyanasundaram and J.K. Thomas, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 99 (1977) 2039.
A. Galarneau, D. Lerner, M.F. Ottariani, F.D. Renzo and F. Fajular, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 117 (1998) 405.
H. Itoh, S. Ishido, M. Nomura, T. Hayakawa and S. Mitaku, J. Phys. Chem. 100 (1996) 9047.
A. Firouzi, D. Kumar, L.M. Bull, T. Besier, P. Sieger, Q. Huo, S.A. Walker, J.A. Zasadzinski, C. Glinka, J. Nicol, D. Margolese, G.D. Stucky and B.F. Chmelka, Science 267 (1995) 1138.
A. Monnirer, F. Schüth, Q. Huo, D. Kumar, D. Margolese, R.S. Maxwel, G.D. Stucky, M. Krishnamurty, P. Petroff, A. Firouzi, M. Janicke and B.F. Chmelka, Science 261 (1993) 1299.
D. Calabro, E.W. Valyocsik and F.X. Ryan, Micropor. Mater. 7 (1996) 243.
S.L. Burkett and M.E. Davis, In Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry, G. Alberti and T. Bein (eds), Vol. 7 (Pergamon, Exter, 1996) p. 465.
H. Gies and B. Marler, Zeolites 12 (1992) 42.
A.V. Goretsky, L.W. Beck, S.I. Zones and M.E. Davis, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 28 (1999) 387.
M.E. Davis, Cattech 1 (1997) 19.
M.A. Camblor, A. Corma and S.J. Valencia, Mater. Chem. 8 (1998) 2137.
C.J. Brinker and G.W. Scherer, In Sol-gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing (Academic Press, New York, 1990) p. 644.
E.D. Neas and M.J. Collins, In Introduction to Microwave Sample Preparation, H.M. Kinston and L.B. Jassie (eds), (ACS, Washington, DC, 1988) p. 7
A. Kuperman, S.and Nadimi, S.G.A. Ozin, J.M. Garces and M.M. Olken, Nature 365 (1993) 239.
S. Feng and T. Bein, Science 265 (1994) 1839.
P. Yang, T. Deng, D. Zhao, P. Feng, D. Pine, B.F. Chmelka, G.M. Whitesides and G.D. Stucky, Science 282 (1998) 2244.
D.A. Doshi, N.K. Huesing, M. Lu, H. Fan, Y. Lu, K. Simmons-Potter Jr., B.G. Potter, A.J. Hurd and C.J. Brinker, Science 209 (2000) 107.
L. Huang, Z. Wang, J. Sun, L. Miao, Q. Li, Y. Yan and D. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122 (2000) 3530.
M.Z. Yates, K.C. Ott, E.R. Birnbaum and T.M. McCleeskey, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41 (2002) 476.
M. Ganschow, G. Schulz-Ekloff, M. Wark, M. Wendschuh-Josties and D. Wöhrle, J. Mater. Chem., 11 (2001) 1823.
H. Du, M. Fang, W. Xu, X. Meng and W.J. Pang, Mater. Chem. 7 (1997) 551.
S. Mintova, S. Mo and T. Bein, Chem. Mater. 10 (1998) 4030.
S.-E. Park, D.S. Kim and Y.K. Hwang, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 145 (2003) 91.
Y.K. Hwang, Ph. D. Thesis, Synthesis and Nanofabrication of Nanoporous Materials, SungKyunKwan Univeristy, 2002.
J.M. Kim, D.S. Kim, J.S. Hwang, J.-S. Chang and S.-E. Park, Abstr. Pap. 221st, Am. Chem. Soc. (2001) San Diego CA, United States, April 1-5, 2001.
S.-E. Park, D.S. Kim, Y.K. Hwang, J.-S. Chang, J.S. Hwang and S.H. Jhung, Abstr. Pap. 224th, Am. Chem. Soc. Boston, MA, United States, August 18-22, 2002.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, SE., Chang, JS., Hwang, Y.K. et al. Supramolecular Interactions and Morphology Control in Microwave Synthesis of Nanoporous Materials. Catalysis Surveys from Asia 8, 91–110 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CATS.0000026990.25778.a8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CATS.0000026990.25778.a8