Abstract
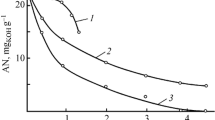
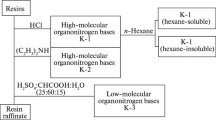
Resin–asphaltene concentrates were obtained by the redox reaction of acid tar and naphtha deasphalting residue and used for fabrication of sulfo–cation exchangers. The strongly acid powdered sulfo cation exchanger with a static exchange capacity of 3.8 meq/g and mechanical strength of 92% is characterized by elevated thermohydrolytic stability and radiation stability. Based on its properties, it can be used in metal–gauze–asbestos gravity filters at atomic power plants for preliminary treatment of water.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Yu. V. Pokonova, Khim. Tekhnol. Topl. Masel, No. 3, 44-49 (2002).
A. Ashirov and Yu. V. Pokonova, Zh. Prikl. Khim., 49, No. 1, 56-58 (1971).
E. V. Egorov and P. D. Novikov, Effect of Ionizing Radiation on Ion-Exchange Materials [in Russian], Atomizdat, Moscow (1965).
Yu. V. Pokonova and J. Speight, Atomic Power Plants [in Russian], Vysshaya Shkola, Moscow (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pokonova, Y.V. Oily Acid Tars as Feedstock for Manufacture of Cation Exchangers. Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils 40, 189–194 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CAFO.0000031903.77382.21
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CAFO.0000031903.77382.21