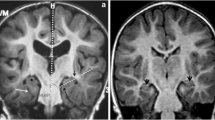
Abstract
Summary: This article summarizes the magnetic resonance imaging features of glutaric aciduria type I (GA I) based on the cases presented at the 3rd International Workshop on Glutaryl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency together with a review of previously reported neuroimaging characteristics of GA I. Previous reports have focused on characteristic findings, such as basal ganglia injury and frontotemporal atrophy or hypoplasia, subdural effusions and white-matter disease. Most of these findings have been demonstrated in symptomatic children, i.e. after manifestation of acute encephalopathic crises. In contrast, prospective investigations in presymptomatically diagnosed children are rare. Since more recent investigations have highlighted CNS changes in patients without encephalopathic crises, systematic prospective investigations of neuroradiological findings in this disease are indispensable for a better understanding of this disease. Based on these findings a suggestion for a MRI protocol is presented, supporting a standardized evaluation of patients with GA I.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Altman NR, Rovira MJ, Bauer M(1991)Glutaric aciduria type I:MR findings in two cases.Am J Neuroradiol 12:966-968.
Brismar J, Ozand PT (1995)CT and MR of the brain in glutaric aciduria type I:a review of 59 published cases and a report of 5 new patients.Am J Neuroradiol 16:675-683.
Desai NK, Runge VM, Crisp DE, Crisp MB, Naul LG (2003)Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in glutaric acidemia type I.Invest Radiol 38:489-496.
Elster AW (2004)Glutaric aciduria type I.Value of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing acute striatal necrosis.J Comput Assist Tomogr 28:98-100.
Eastwood JD, Engelter ST, MacFall JF, Delong DM, Provenzale JM (2003)Quantitative assessment of the time course of infarct signal intensity on diffusion-weighted images.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680-687.
Kölker S, Burgard P, Okun JG, et al (2004)Looking forward an evidence-based approach to glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 27:921-926.
Lansberg MG, Thijs VN, O'Brien MW, et al (2001)Evolution of apparent diffusion coe cient, diffusion-weighted,and T2-weighted signal intensity of acute stroke.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:637-644.
Möller HE, Koch HG,Weglage J, Freudenberg F, UllrichK (2003)Investigation of the cerebral energy status in patients withglutaric aciduria type I by 31 P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuropediatrics 34:57-60.
Strauss KA, Puffenberger EG, Robinson DL, Morton DH (2003)Type I glutaric aciduria,part 1:Natural history of 77 patients.Am J Me Genet 121C:38-52.
Twomey EL, Naughten ER, Donogue VB, Ryan S (2003)Neuroimaging findings in glutaric aciduria type 1.Pediatr Radiol 33:823-830.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neumaier-Probst, E., Harting, I., Seitz, A. et al. Neuroradiological findings in glutaric aciduria type I (glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency). J Inherit Metab Dis 27, 869–876 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOLI.0000045771.66300.2a
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOLI.0000045771.66300.2a