Abstract
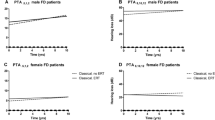
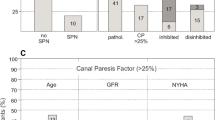
Summary: The aim of this study was to describe the nature and prevalence of hearing loss in Fabry disease (McKusick 301500), a rare X-linked lysosomal storage disorder, and its response to enzyme replacement therapy with agalsidase alfa. Fifteen hemizygous male Fabry patients (aged 25–49 years) were randomized to receive placebo or enzyme replacement therapy for 6 months; all have received open-label enzyme replacement therapy for an additional 24 months thus far. Pure-tone audiometry, impedance audiometry and otoacoustic emission testing were performed at 0 (baseline), 6, 18 and 30 months. Four patients (27%) had bilateral and 7 (47%) had unilateral high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL). Two (13%) had unilateral middle ear effusions with conductive losses persisting beyond 6 months. Only 3 (20%) had normal hearing. High-frequency SNHL deteriorated over the first 6 months in both placebo and active treatment groups by a median 4.3 dB (p=0.002, Wilcoxon matched pairs). This hearing loss subsequently improved above baseline by 2.1 dB at 18 months (p=0.02) and by 4.9 dB at 30 months (p=0.004). In conclusion, significant hearing loss, usually high-frequency SNHL, is a common manifestation of Fabry disease in adults. α-Galactosidase A replacement therapy with agalsidase alfa appears to reverse the hearing deterioration in these patients. This improvement is gradual, however, suggesting the need for long-term enzyme replacement therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
De Groot WP (1964) Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum Fabry. Dermatalogica 128: 321 349.
Eng CM, Guffon N, Wilcox WR, et al (2001) Safety and efficacy of recombinant human c-galactosidase A replacement in Fabry disease. N. Engl J Med 345: 9 16.
Germain DP, Avan P, Chassaing A, Bonfils P (2002) Patients affected with Fabry disease have an increased incidence of progressive hearing loss and sudden deafness: an investigation of twenty-two consecutive hemizygous male patients. BMC Med Genet 3: 10.
MacDermot KD, Holmes A, Miners AH (2001a) Anderson-Fabry disease: clinical manifes-tations and impact of disease in a cohort of 60 obligate carrier females. J Med Genet 38: 769–775.
MacDermot KD, Holmes A, Miners AH (2001b) Anderson-Fabry disease: clinical manifestations and impact of disease in a cohort of 98 hemizygous males. J. Med Genet 38: 750–760.
Mehta A (2002) New developments in the management of Anderson-Fabry disease. Q J Med 95: 647–653.
Meyerhoff WL, Liston S (1980) Metabolism and hearing loss. In Paparella MM, Schumrick DA, eds. The Ear, vol. 2., Otolaryngology, 3rd edn. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1828 1845.
Moore DF, Herscovitch P, Schiffmann R (2001a) Selective arterial distribution of cerebral hyperfusion in Fabry disease. J Neuroimaging 11: 303 307.
Moore DF, Scott LT, Gladwin MT, et al (2001b) Regional cerebral hyperperfusion and nitric oxide pathway deregulation in Fabry disease: reversal by enzyme replacement therapy. Circulation 104: 1506 1512.
Moore DF, Altarescu A, Ling GSF, et al (2002) Cerebrovascular hyperdynamicity in Fabry disease with reversal following enzyme replacement therapy. Stroke 33: 525–531.
Pastores GM, Thadhani R (2001) Enzyme replacement therapy for Anderson-Fabry disease. Lancet 358: 601–603.
Pastores GM, Thadhani R (2002) Advances in the management of Anderson-Fabry disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2: 325 333.
Quick CA (1976) Hearing loss in patients with dialysis and renal transplants Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 85: 776–790.
Schachern PA, Shea DA, Paparella MM, Yoon TH (1989) Otologic histopathology of Fabry's disease. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 98: 359 363.
Schiffmann R, Kopp JB, Austin HA III, et al (2001) Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 285: 2743 2749.
Whybra C, Kampmann C, Willers I, et al (2001) Anderson-Fabry disease: clinical manifestations of disease in female heterozygotes. J Inherit Metab Dis 24: 715 724.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajioff, D., Enever, Y., Quiney, R. et al. Hearing loss in Fabry disease: The effect of agalsidase alfa replacement therapy. J Inherit Metab Dis 26, 787–794 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOLI.0000009948.86528.72
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOLI.0000009948.86528.72