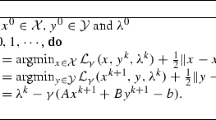Abstract
The problem discussed in this note is highly interesting. It is related to several dual iterative methods, such as the methods proposed by Kaczmarz, Hildreth, Agmon, Cryer, Mangasarian, Herman, Lent, Censor, and others. Cast as ‘row-action methods’ these algorithms have been proved as useful tools for solving large convex feasibility problems that arise in medical image reconstruction from projections, in inverse problems in radiation therapy, and in linear programming.
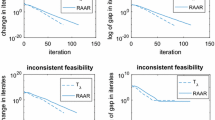
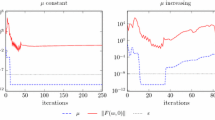
The question that we want to answer is how these algorithms behave when the feasible region is empty. It is shown that under certain conditions the primal sequence still converges while the dual sequence {y k } obeys the rule y k =u k +k v, where {u k } is a converging sequence and v is a fixed vector that satisfies A T v=0,v≥0,and,b T v>0. It is conjectured that these properties hold whenever the feasible region is empty. However, the validity of this claim remains an open question.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. Agmon, The relaxation method for linear inequalities, Canad. J. Math., 6 (1954), 382-392.
H. H. Bauschke, Projection algorithms: Results and open problems, in D. Butnariu, Y. Censor and S. Reich (eds.), Inherently Parallel Algorithms in Feasibility and Optimization and their Applications, Studies in Comput. Math., Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 2001, pp. 11-22.
H. H. Bauschke and J. M. Borwein, On projection algorithms for solving convex feasibility problems, SIAM Rev., 38 (1996), pp. 367-426.
H. H. Bauschke, J. M. Borwein, and A. S. Lewis, The method of cyclic projections for closed convex sets in Hilbert space, in Recent Developments in Optimization Theory and Nonlinear Analysis (Jerusalem,1995), Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, RI, 1997, pp. 1-38.
Y. Censor, Row-action methods for huge and sparse systems and their applications, SIAM Rev., 23 (1981), pp. 444-466.
Y. Censor, M. D. Altschuler, and W. D. Powlis, A computational solution of the inverse problem in radiation-therapy treatment planning, A ppl. Math. Comput., 25 (1988), pp. 57-87.
Y. Censor, P. O. B. Eggermont, and D. Gordon, Strong underrelaxation in Kaczmarz's method for inconsistent systems, Numer. Math., 41 (1983), pp. 83-92.
Y. Censor and T. Elfving, New methods for linear inequalities, Li near Algebra Appl.,42 (1982), pp. 199-211.
Y. Censor and S. A. Zenios, Parallel Optimization, Theory, Algorithms, and Applications, Oxford Univ. Press, 1997.
R. W. Cottle, G. H. Golub, and R. S. Sacher, On the solution of large, structured linear complementarity problems: The block partitioned case, Appl. Math. Optim., 4 (1978), pp. 348-363.
C. W. Cryer, The solution of a quadratic programming problem using systematic overrelaxation, SIA M J. Control, 9 (1971), pp. 385-392.
A. Dax, The convergence of linear stationary iterative processes for solving singular unstructured systems of linear equations, SIAM Rev., 32 (1990), pp. 611-635.
A. Dax, On theory and practice of row relaxation methods, in D. Butnariu, Y. Censor and S. Reich (eds.), Inherently Parallel Algorithms in Feasibility and Optimization and their Applications, Studies in Comput. Math., Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 2001, pp. 153-186.
A. Dax, The smallest correction of an inconsistent system of linear inequalities, Optimization and Engineering, 2 (2001), pp. 349-359.
A. Dax, The adventures of a simple algorithm, Linear Algebra Appl., 361 (2003), pp. 41-61.
A. Dax and V. P. Sreedharan, On theorems of the alternative and duality, J. Optim. Theory Appl., 94 (1997), pp. 561-590.
R. De Leone and O. L. Mangasarian, Serial and parallel solution of large scale linear programs by augmented Lagrangian successive overrelaxation, in A. Kurzhanski, K. Neuwmann and D. Pallaschke (eds.), Optimization, Parallel Processing and Applications, Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems 304, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1988, pp. 103-124.
A. R. De Pierro and A. N. Iusem, A simultaneous projection method for linear inequalities, Linear Algebra Appl., 64 (1985), pp. 243-253.
A. R. De Pierro and A. N. Iusem, On the asymptotic behaviour of some alternate smoothing series expansion iterative methods, Linear Algebra Appl., 130 (1990), pp. 3-24.
L. G. Gubin, B. T. Polyak, and E. V. Raik, The method of projections for finding the common point of convex sets, USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys., 7 (1967), pp. 1-24.
S. P. Han, Least-squares solution of linear inequalities, Technical Report 2141, Math. Res. Center, Univ. of Wisconsin-Madison, 1980.
M. Hanke and W. Niethammer, On the acceleration of Kaczmarz's method for inconsistent linear systems, Linear Algebra Appl., 130 (1990), pp. 83-98.
M. Hanke and W. Niethammer, On the use of small relaxation parameters in Kaczmarz's method, Z. Angew. Math. Mech., 70 (1990), pp. 575-576.
G. T. Herman, A relaxation method for reconstructing object from noisy x-rays, Math. Prog., 8 (1975), pp. 1-19.
G. T. Herman, Image Reconstruction from Projections: The Fundamentals of Computerized Tomography, Academic Press, New York, 1980.
G. T. Herman and A. Lent, A family of iterative quadratic optimization algorithms for pairs of inequalities with applications in diagnostic radiology, Math. Programming Study, 9 (1978), pp. 15-29.
C. Hildreth, A quadratic programming procedure, Naval Res. Logist. Quart., 4 (1957), pp. 79-85; Erratum, Ibid., p. 361.
A. N. Iusem and A. R. De Pierro, A simultaneous iterative method for computing projections on polyhedra, SIAM J. Control, 25 (1987), pp. 231-243.
A. N. Iusem and A. De Pierro, On convergence properties of Hildreth's quadratic programming algorithm, Math. Programming, 47 (1990), pp. 37-51.
S. Kaczmarz, Angenäherte Auflösung von Systemen linearer Gleichungen, Bull. Acad. Polon. Sci. Lett. A, 35 (1937), pp. 355-357.
A. Lent and Y. Censor, Extensions of Hildreth's row-action method for quadratic programming, SIAM J. Control Optim., 18 (1980), pp. 444-454.
D. G. Luenberger, Optimization by Vector Space Methods, Wiley, New York,1969.
O. L. Mangasarian, Nonlinear Programming, Mc Graw-Hill, New York, 1969.
O. L. Mangasarian, Solution of symmetric linear complementarity problems by iterative methods, J. Optim. Theory Appl., 22 (1977), pp. 465-485.
O. L. Mangasarian, Iterative solution of linear programs, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 18 (1981), pp. 606-614.
O. L. Mangasarian, Sparsity-preserving SOR algorithms for separable quadratic and linear program, Comput. Oper. Res., 11 (1984), pp. 105-112.
O. L. Mangasarian and R. De Leone, Parallel successive overrelaxation methods for symmetric linear complementarity problems and linear programs, J. Optim. Theory Appl., 54 (1987), pp. 437-446.
T. S. Motzkin and I. J. Schoenberg, The relaxation method for linear inequalities, Canad. J. Math., 6 (1954), pp. 393-404.
F. Natterer, The Mathematics of Computerized Tomography, Wiley, New York, 1986.
K. Tanabe, Projection method for solving a singular system of linear equations and its applications, Numer. Math., 17 (1971), pp. 203-214.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dax, A. An Open Question on Cyclic Relaxation. BIT Numerical Mathematics 43, 929–943 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BITN.0000014544.99142.62
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BITN.0000014544.99142.62