Abstract
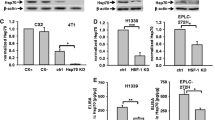
The confluence-dependent resistance of human larynx carcinoma HEp-2 cells to hydrogen peroxide and a new antitumor drug based on the combination of vitamins C and B12b was studied. It was found that this resistance in growing cells is suppressed by the disruption of intercellular contacts by EGTA and is related neither to the activity of P-glycoprotein nor to the content of intracellular glutathione and the activities of glutathione S-transferases, glutathione peroxidase and glutathionine reductase. Here we showed that the level of expression of the small heat shock protein hsp27, which is known to protect cells from a variety of stresses associated with apoptosis, in growing confluent cells both in the presence and absence of the vitamins B12b and C is much higher (about 20–25 times) than in nonconfluent cells. Taken together, the results suggest that the confluence-dependent resistance of cells to the combination of vitamins C and B12b and to hydrogen peroxide is mediated by hsp27 overexpression, which is activated via cell-cell adhesion.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Scheutz, J. D. and Schuetz, E. G. (1993) Extracellular matrix regulation of multidrug resistance in primary monolayer cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 4:31–40.
Dimanche-Boitrel, M. T., Genne, P., Duchamp, O., and Chauffert, B. (1994) Confluence dependent resistance (CDR) to doxorubicin and E-cadherin expression in murine mammary cells. Cancer Lett. 85:171-176.
Durand, R. E. and Sutherland, R. M. (1972) Effects of intercellular contact on repair of radiation damage. Exp. Cell Res. 71:75-80.
Meredith, J. E., Fazeli, B., and Schwartz, M. A. (1993) The extracellular matrix as a cell survival factor. Mol. Biol. Cell 4:953-961.
Muller, C. et al. (1992) High cell density-dependent resistance and P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in mitoxantrone-selected Chinese hamster cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 43:2091-2102.
Barhoumi, R. et al. (1995) Enhancement of melphalan toxicity by octanol in ovarian adenocarcinoma cell lines: effects of altered cell-cell communication, gluathione levels, and plasma membrane fluidity. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 25:70-79.
Fletcher, W. H. et al. (1987) Resistance to the cytolytic action of lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor coincides with the presence of gap junctions uniting target cells. J. Immunol. 139:956-962.
Garrido, D. et al. (1995) Circumvention of confluence-dependent resistance in a human multidrug-resistant colon-cancer cell line. Int. J. Cancer 61:873-879.
Garrido, C. et al. (1997) HSP27 as a mediator of confluence-dependent resistance to cell death induced by anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 57:2661-2667.
Mehlen, P., Kretz-Remy, C., Preville, X., and Arrigo, A.-P. (1996) Human hsp27, Drosophila hsp27, and αβ-crystallin expression-mediated increase in glutathione is essential for the protectivity activity of these proteins against TNF-α-induced cell death. MEBO J. 15:2965-2706.
Nocsik, E., Mihalik, R., Ali-Osman, F., and Aggarwal, B. B. (1994) Cell density-dependent regulation of cell surface expression of two types of human tumor necrosis factor receptors and its effect on cellular response. J. Cell Biochem. 54:453-464.
Vol'in, M. E. et al. (1998) Combinations of B12 vitamins with ascorbic acid as potential antitumor agents. Russ. Chem. J. 42:116-127. (Russian).
Akatov, V. S. et al. (2000) Combined vitamins B12 b and C induce the glutathione depletion and the death of epidermoid human larynx carcinoma cells HEp-2. Biosci. Reports 20:411-417.
Akatov, V. S. et al. (2000) DNA damage and tumor cell death due to combined vitamins B12 b and C action. Dokl. Rus. Acad. Sci. 373:838-840. (Russian).
Nomizu, M. et al. (1995) Identification of cell binding sites in the laminin a1 chain carboxyl-terminal globular domain by systematic screening of synthetic peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 270:20583-29590.
Akatov, V. S., Lavrovskaya, V. P., Grobova, M. E., and Lezhnev, E. I. (1990). Flow-diffusion chamber for cell-culture investigations. Tsitologia 32:399-404. (Russian).
Homolya, L. et al. (1993) Fluorescent cellular indicators are extruded by the multidrug resistance protein. J. Biol. Chem. 268:21493-21496.
Anderson, M. E. (1985) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in biological samples. Methods Enzymol. 113:548-555.
Calberg, I. and Mannervik, B. (1975) Purification and characterization of flavoenzyme glutathione reductase from rat liver. J. Biol. Chem. 250:5475-5480.
Paglia, D. E. and Valentine, W. N. (1967) Studies of the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 70:158-160.
Habig, W. H. and Jakoby, W. B. (1981) Glutathione S-transferases. Methods Enzymol. 77:398-405.
Dimanche-Boitrel, M. T. et al. (1992) Confluence-dependent resistance in human colon cancer cells: role of reduced drug accumulation and low intrinsic chemosensitivity of resting cells. Int. J. Cancer 50:677-682.
Mathieu, C., Jozan, S., and Mazars, P. (1995) Density-dependent induction of apoptosis by transforming growth factor-β1 in a human ovarian carcinoma cell line. Exp. Cell Res. 216:13-20.
Ziemann, C., Burkle, A., Kahl, G. F., and Hirsch-Ernst, K. I. (1999). Reactive oxygen species participate in mdr1b mRNA and P-glycoprotein overexpression in primary rat heptocyte cultures. Carcino-genesis 20:407-414.
Wartenberg, M., Fischer, K., Hescheler, J., and Sauer, H. (2000) Redox regulatin of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in multicellular prostate tumor spheroids. Int. J. Cancer 85:267-274.
Preville, X. et al. (1999) Mammalian small stress proteins protect against oxidative stress through their ability to increase glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and by maintaining optimal cellular detoxifying machinery. Exp. Cell Res. 247:61-78.
Mesdagh, N. et al. (1994) Chemoresistance to doxorubicin and cisplatin in a murine cell line. Analysis of P-glycoprotein, topoisomerase II activity, glutathione and related enzymes. Anticancer Res. 14:869-874.
Yu, D. S., Ma, C. P., and Chang, S. Y. (2000) Establishment and characterization of renal cell carcinoma cell lines with multidrug resistance. Urol. Res. 28:86-92.
Lee, F. Y., Sciandra, J., and Siemann, D. W. (1989) A study of the mechanism of resistance to Adriamycin in ûiûo. Glutathione metabolism, P-glycoprotein expression, and drug transport. Biochem. Pharmacol. 38:3697-705.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazurov, V.V., Solovieva, M.E., Leshchenko, V.V. et al. Small Heat Shock Protein hsp27 as a Possible Mediator of Intercellular Adhesion-Induced Drug Resistance in Human Larynx Carcinoma HEp-2 Cells. Biosci Rep 23, 187–197 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIRE.0000007692.59551.d8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIRE.0000007692.59551.d8