Abstract
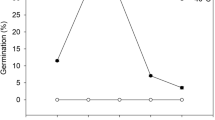
An effort has been made to assess the role of reactive oxygen species in germination and subsequent growth of Amaranthus lividus under elevated temperature. Transfer of A. lividus seeds from 25 to 45 °C for 4, 8 and 12 h, during early imbibitional period reduced percentage of germination, relative germination performance, relative growth index and seedling length. Heat shock during early germination decreased also the activities of free radical scavenging enzymes like catalase, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase, increased the accumulation of superoxide, hydrogen peroxide and induced lipoxygenase mediated membrane lipid peroxidation. Membrane injury index and relative leakage ratio revealed a rise with concomitant reduction in membrane protein thiol content in heat shock raised seedlings. The results indicate that heat shock in A. lividus seeds induced an excessive generation of ROS and led to an oxidative membrane damage, causing early growth impairment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alka, Khanna-Chopra, R.: Influence of temperature in germination and seedling growth and its relationship with amylase activity and respiration in wheat varieties differing in temperature tolerance.-Indian J. exp. Biol. 33: 775–779, 1995.
Bartoli, C.G. Simontacehi, M. Ambussi, E. Beltrano, J., Montaldi., Puntarulo S.: Drought and watering dependent oxidative stress: effect of antioxidant content in 7Titicu171 aestiviu L. leaves.-.1. exp. Bot. 50: 375–383. 1999.
Bewley, J.D., Black, M.: Physiology and Biochemistry of Seeds in Relation to Germination.-Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1982.
Bhaskar, 1., Balasubramanian, K.A.: Lipid peroxidation of coenocytic membranes.-Indian J. exp. Biol. 32: 89–93, 1995.
Bhattacharjec. S., Mukhcrjee, A.K.: Ethylene evolution and membrane lipid peroxidation as indicators of salt injury in leaf tissues of Amaranthus lividus seedlings.-Indian J. exp. Biol. 34: 279–281, 1996.
Bhattacharjee, S., Mukherjee, A.K.: T'he deleterious effects of high temperature during early germination on membrane integrity and subsequent germination of Amaranthus lividus.- Seed Sci. echnol. 26: 1–8. 1998.
Cakmak, I. Ilorst. W.J.: Effect of aluminium on lipid peroxidation. superoxide dismutase. catalasc and pcroxidase.-Physiol. Plant. 83: 463–471. 1991.
Chaitanya. K.S.K., Naithani. S.C.: Role of superoxide. lipid peroxidation and superoxide dismutase in membrane perturbation during loss of viability in seeds of Shorea rohbzsta Gaertn. F.-New Phytol. 126: 623–627. 1994.
Chan. T. Jr., Sanvcrter. S. Convey. HM.: Electrolytic leakage and ethylene production induced by chilling of papayas.-Iort. Sci. 20: 1070–1073, 1985.
Dekok. L.J., Kuiper, P.J.C: Effect of short term dark incubation with sulfate, chloride and selenate on the glutathione content of spinanch leaf discs.-Physiol. Plant. 68: 477–482. 1986.
Ellman, G.: Tissue sulfhydryl groups.-Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 82: 72–77, 1959.
Fadzillah, N.M., Gill, V., Finch, R.P., Burdon, R.H.: Chilling, oxidative stress and antioxidative responses in shoot cultivars of rice.-Planta 199: 552–556, 1996.
Fick, N.G., Qualset, C.D.: Genetic control of endosperm amylase activity and gibberellin response in standard height and short statured wheat.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 72: 892–895. 1975.
Fridovich, I.: Oxygen radicals, hydrogen peroxide and oxygen toxicity.-In: Pryor. W.A. (ed.): Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine. Pp. 239–277. Academic Press, New York 1976.
Gasper. C.L. Dhindsa, R.S.: Correlation between germination and activities of SOD peroxidase under salinity in rice (Orvza sativa).- Plant Physiol. 67(Suppl.): 19, 1981.
Giannopolitis. C.N. Ries. S.K.: Superoxide dismutase. I. Occurrence in higher plants-Plant Physiol. 59: 309–314. 1977.
Gixelberg. A. Horowitz. M. Poljakoff-NMlaber. A.: Solute leakage from Sol/nimul ngruti seeds exposed to high temperatures during imbibition.-J. exp. Bot. 35: 1754–1763. 1984.
Heath. R.L. Packer. L.: Photooxidation in isolated chloroplasts: kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid oxidation.-Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 125: 189–198. 1968.
Hildebrand. D. F.: Lipoxygenases.-PhFsiol. Plant. 76: 249–253. 1989.
Jiang. M. Zhang, J.: Effect of abscisic acid and active oxygen species. antioxidative defence system and oxidative damage in leaves of maize seedlings.-Plant Cell Physiol. 42: 1265–1273, 2001.
Kar. M. Mishra. D.: Catalase, peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase activities during rice leaf senescence.-Plant Phlsiol. 57: 315–320. 1976.
King. M. Ludford. P.M.: Chilling injury and electrolyte leakage in fruit of different tomato cultivars.-J. amer. Soc. hort. Sci. 111:201–210. 1983.
Krishnamlurth. K.S. Ankegoxda. S.J. Saji. KV.: Water stress effects on membrane damage and activities of catalase, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase enzymes in black pepper (Pipel igttto L.).-J. Plant Biol. 27 39–42. 2000.
Iex itt..: Responses of the Plants to Enx ironmental Stresses.-Chilling. Freezing and Temperature Stress. 2 Ed.-Academic Press. NewYork 1980.
MacNevin. W.M. Uron. P.F.: Spectrum of hydrogen peroxide fiom organic hydroperoxide.-Anal. Chem. 25: 1760–1761. 1953.
Marbach.. Mayer. A.M.: The effect of temperature change on leakage from pea seeds.-J. exp. Bot. 36: 353–358, 1985.
Neill. S. Deshikan. R. Clarke, A., Hankok, J.: H2,O signalling in plant cells.-In: Smallwood, MF. Calvert. C.M., Bowles. D.J. (ed.): Plant Responses to Environmental Stress. Pp. 59–64. BioScience Publ. Oxford 1999.
O'Kane. D. Gill, V., Boyd. P. Burdon, R.: Chilling oxidative stress and antioxidant rersponses in.rabidopsis thaliana callus.-Planta 198: 371–377. 1996.
Peterman, T.K., Siedow, J.N.: Behavior of lipoxygenase during establishment, rejuvenescence and senescence of soybean cotyledons.-Plant Physiol. 74: 367–368, 1985.
Robert, R., Stewart, C., Bewley, J.D.: Lipid peroxidation associated with accelerated ageing of soyabean axis.-Plant Physiol. 65: 245–248, 1980.
Shalata, A., Tal, M.: The effect of salt stress on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in the leaf of cultivated tomato and its wild salt tolerant relative Lycopersicon pennellii.- Physiol. Plant. 104: 169–174, 1998.
Short, G.E., Lacy, M.L.: Carbohydrate exudation from pea seed: effect of cultivar, seed age, seed color and temperature.-Phytopathology 66: 182–187, 1976.
Simon, E.W., Rajaharun, R.M.: Leakage during seed imbibition.-J. exp. Bot. 23: 1076–1085, 1972.
Singh, V.P.: Interaction of temperature and microsomal peroxidase in aflatoxin degradation by Aspergillus flavus 102566.-Curr. Sci. 72: 529–532, 1997.
Smirnoff, N.: Plant resistance to environmental stress.-Curr. Opinion Biotechnol. 9: 214–219, 1998.
Snell, F.D., Snell, C.T.: Colorimetric Methods of Analysis.-Van Nostrad Reinhold Co., New York 1971.
Steponkus, P.L.: Role of plasma membrane in freezing injury and cold acclimation.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 35: 543–548, 1984.
Stewart, R.B.C., Bewley, J.D.: Lipid peroxidation associated with accelerated ageing of soyabean axes.-Plant Physiol. 65: 245–248, 1980.
Sullivan, C.Y.: Mechanisms of heat and drought resistance in grain sorghum and methods of measurements.-In: Rao, N.G.P., House, L.R. (ed.): Sorghum in Seventies. Pp. 247–278. Oxford & IBH Publ. Co., New Delhi 1972.
Winston, G.W.: Physiological basis for free radical formation in cells: production and defenses.-In: Alscher, R., Cummings, J. (ed.): Stress Responses in Plants-Adaptation and Acclimation Mechanisms. Pp. 57–58, Wiley Liss, New York 1990.
Wismer, W.V., Worthing, W.M., Yada, R.Y., Marangoni, A.G.: Membrane lipid dynamics and lipid peroxidation in the early stages of low temperature sweetening in tubers of Solanum tuberosum.- Physiol. Plant. 102: 396–410, 1998.
Woodstock, L.W., Maxon, S., Faul, K., Bass, L.: Use of freeze drying and acetone impregnation with natural and synthetic antioxidants to improve storability of onion, pepper and parsley seeds.-J. amer. Soc. hort. Sci. 108: 692–696, 1983.
Zhao, S., Blumwald, E.: Changes in oxidation-reduction state and antioxidant enzymes in roots of jack pine seedlings during cold acclimation.-Physiol. Plant. 104: 134–142, 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharjee, S., Mukherjee, A. Implications of Reactive Oxygen Species in Heat Shock Induced Germination and Early Growth Impairment in Amaranthus lividus L.. Biologia Plantarum 47, 517–522 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOP.0000041055.77873.db
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOP.0000041055.77873.db