Abstract
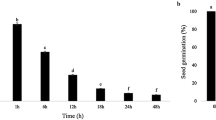
Following 16, 40 and 64 h exposure to 0.33 M NaCl given after 8 h water imbibition, lentil seeds showed a gradual decrease of germination upon their transfer to water. These salt related changes were accompanied by modifications in the protein patterns of embryo axes as revealed by two-dimensional electrophoresis separation and by the computer image analysis of protein spots. In comparison with 8 h water imbibed seeds, prominent proteins comprised between the 5.1 – 7.6 pH isoelectric point in the first dimension and 75 – 50 kDa molecular mass in the second dimension showed a significant increase in their abundance as salt exposure increased. On transfer to water to complete germination, the content of many of these proteins decreased at 24h in 2 – 3 cm length embryo axes in comparison with the corresponding embryo axes of seeds continuously imbibed in water for 24 h. Some groups of proteins ranging between 15.5 – 17.3 kDa, already present after 8 h water imbibition, were not detectable after 24 h but were expressed in seeds exposed to NaCl and transferred to water for 24 h. Up- and down-regulated proteins in lentil embryo axes, imbibed under non-lethal salt stress conditions, have been tentatively identified by comparison with the protein map of germinating seeds of the model plant Arabidopsis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bewley, J.D.: Seed germination and dormancy.-Plant Cell 9: 1055-1066, 1997.
Bliss, R.D., Platt-Aloia, K.A., Thomson, W.W.: Osmotic sensitivity in germinating barley seeds.-Plant Cell Environ. 9: 721-725, 1986.
Chen, R.D., Tabaeizadeh, Z.: Alteration of gene expression in tomato plants (Lycopersicon esculentum) by drought and salt stress.-Genome 35: 385-391, 1991.
Dell'Aquila, A.: Effect of combined salt and heat treatments on germination and heat-shock protein synthesis in lentil seeds.-Biol. Plant. 43: 591-594, 2000.
Dell'Aquila, A., Bewley, J.D.: Protein synthesis in the axes of polyethylene glycol treated pea seeds and during subsequent germination.-J. exp. Bot. 40: 1001-1007, 1989.
Dell'Aquila, A., Di Turi, M.: Amplification of ageing symptoms in two differently thermal-sensitive wheat (Triticum durum L.) genotypes by heat-shock: relationships between germination response and embryo protein patterns.-Seed Sci. Technol. 27: 467-476, 1999.
Dell'Aquila, A., Di Turi, M.: Two-dimensional electrophoresis and computer imaging analysis for the characterization of newly synthesized proteins in germinating durum wheat embryos.-Seed Sci. Technol. 30: 357-369, 2002.
Dell'Aquila, A., Spada, P.: Regulation of protein synthesis in germinating wheat embryos under polyethylene glycol and salt stress.-Seed Sci. Res. 2: 75-80, 1992.
Dell'Aquila, A., Spada, P.: The effect of salinity stress upon protein synthesis of germinating wheat embryos.-Ann. Bot. 72: 97-101, 1993.
Dell'Aquila, A., Corona, M.G., Di Turi, M.: Heat-shock proteins in monitoring aging and heat-induced toleance in germinating wheat and barley embryos.-Seed Sci. Res. 8: 91-98, 1998.
Dutta Gupta, S.: Protein profiles of somatic embryos and regenerated plants from NaCl selected and control cultures of orchardgrass.-Biol. Plant. 42: 297-302, 1999.
Elavumoottil, O.C., Martin, J.P., Moreno, M.L.: Changes in sugars, sucrose synthase activity and proteins in salinity tolerant callus and cell suspension cultures of Brassica oleracea L.-Biol. Plant. 46: 7-12, 2003.
Ellis, R.H., Roberts, E.H.: The quantification of ageing and survival in orthodox seeds.-Seed Sci. Technol. 101: 373-409, 1981.
Gallardo, K., Job, C., Groot, S.P.C., Puype, M., Demol, H., Vandekerckhove, J., Job, D.: Proteomic analysis of Arabidopsis seed germination and priming.-Plant Physiol. 126: 835-848, 2001.
Gulick, P.J., Dvorak, J.: Gene induction and repression by salt treatment in roots of the salinity-sensitive Chinese Spring wheat and the salinity-tolerant Chinese Spring x Elytrigia elongata amphiploid.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 99-103, 1987.
Kersten, B., Burkle, L., Kühn, E.J., Giavalisco, P., Konthur, Z., Lueking, A., Walter, G., Eickoff, H., Schneider, U.: Large-scale plant proteomics.-Plant. mol. Biol. 48: 133-141, 2002.
Ramagopal, S.: Differential mRNA transcription during salinity stress in barley.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 94-98, 1987.
Ramagopal, S.: Regulation of protein synthesis in root, shoot and embryonic tissues of germinating barley during salinity stress.-Plant Cell Environ. 11: 501-515, 1988.
Thiellement, H., Bahrman, N., Damerval, C., Plomion, C., Rossignol, M., Santoni, V., de Vienne, D., Zivy, M.: Proteomics for genetic and physiological studies in plants.-Electrophoresis 20: 2013-2026, 1999.
Waters, E.R., Garret, J.L., Vierling, E.: Evolution, structure and function of the small heat shock proteins in plants.-J. exp. Bot. 47: 325-338, 1996.
Zivy, M., de Vienne, D.: Proteomics: a link between genomics, genetics and physiology.-Plant mol. Biol. 44: 575-580, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dell'Aquila, A. Protein Patterns, Characterized by Computer Image Analysis, of Lentil Embryo Axes Germinating Under Salt Stress. Biologia Plantarum 48, 237–242 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOP.0000033450.16985.07
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOP.0000033450.16985.07