Abstract
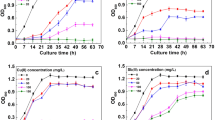
Free cyanide at 1 mm decreased the initial sulfate reduction rate of a batch culture of granular sludge from 0.3 to 0.14 mmol d−1 g−1 SS (suspended solid), whereas 0.5 mm cyanide had a minimal effect (0.25 mmol d−1 g−1 SS). The order of toxicity of metal-complexed cyanides to the sludge was as follows: zinc-complexed cyanide (most toxic) > free cyanide = nickel-complexed cyanide > copper-complexed cyanide (least toxic), which also corresponds well with the order of the stability (dissociation) constants of the metal-cyanide complexes. A consortium degrading cyanide was enriched using nickel cyanide as the sole nitrogen source. This consortium completely removed 0.5 mm of nickel-complexed cyanide under sulfate-reducing conditions in 11 d. Analysis of clone library of 16S rRNA genes shows that the consortium was composed of three major phylotypes including Desulfovibrio.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcil A, Mudder T (2003) Microbial destruction of cyanide wastes in gold mining: process review. Biotechnol. Lett. 25: 445–450.
Annachhatre AP, Amornkaew A (2001) Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket treatment of starch wastewater containing cyanide. Water Environ. Res. 73: 622–632.
Bose P, Bose MA, Kumar S (2002) Critical evaluation of treatment strategies involving adsorption and chelation for wastewater containing copper, zinc and cyanide. Adv. Environ. Res. 7: 179–195.
Dean JA (1985) Lang's Handbook of Chemistry, 13th edn. New York: McGraw Hill.
Delbès C, Moletta R, Godon JJ (2000) Monitoring of activity dynamics of an anaerobic digester bacterial community using 16S rRNA polymerase chain reaction-single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Environ. Microbiol. 2: 506–515.
Eckenfelder WW (1989) Industrial Water Pollution Control. New York: McGraw Hill.
Fallon RD, Cooper DA, Speece R, Henson M (1991) Anaerobic biodegradation of cyanide under methanogenic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 1656–1662.
Gerhartz W (1987) Ullman's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 5th edn. Florida: VCH.
Gijzen HJ, Bernal E, Ferrer H (2000) Cyanide toxicity and cyanide degradation in anaerobic wastewater treatment. Water Res. 34: 2447–2454.
Patil YB, Paknikar KM (1999) Removal and recovery of metal cyanides using a combination of biosorption and biodegradation processes. Biotechnol. Lett. 21: 913–919.
Richardson RE, Bhupathiraju VK, Song DL, Goulet TA, Alvarez-Cohen L (2002) Phylogenetic characterization of microbial communities that reductively dechlorinate TCE based upon a combination of molecular techniques. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36: 2652–2662.
Rollinson G, Jones R, Meadows MP, Harris RE, Knowles CJ (1987) The growth of a cyanide-utilising strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens in liquid culture on nickel cyanide as a source of nitrogen. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 40: 199–205.
Song YC, Piak BC, Shin HS, La SJ (1998) Influence of electron donor and toxic materials on the activity of sulfate reducing bacteria for the treatment of electroplating wastewater. Water Sci. Tech. 38: 187–194.
Tuttle JH, Dugan PR, Randles CI (1969) Microbial sulfate reduction and its potential utility as an acid mine water pollution abatement procedure. Appl. Microbiol. 17: 297–302.
Utgikar VP, Cehn BY, Chaudhary N, Tabak HH, Haines JR, Govind R (2001) Acute toxicity of heavy metals to acetate-utilizing mixed cultures of sulfate-reducing bacteria: EC100 and EC 50. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 20: 2662–2669.
Yoon JH, Cho YG, Kang SS, Kim SB, Lee ST, Park YH (2000) Rhodococcus koreensis sp. nov., a 2,4-dinitrophenol-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50: 1193–1201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quan, ZX., Bae, JW., Rhee, SK. et al. Toxicity and degradation of metal-complexed cyanide by a bacterial consortium under sulfate-reducing conditions. Biotechnology Letters 26, 1007–1011 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000030048.04282.da
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000030048.04282.da