Abstract
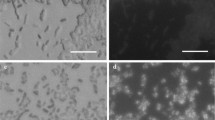
A new poly(l-lactide) (PLA)-degrading actinomycete, Kibdelosporangium aridum, degraded more than 97 mg out of 100 mg added high molecular weight PLA film (Mn: 3.4 × 105) within 14 d in liquid culture. l-Lactic acid, the monomeric degradation product of PLA, was totally assimilated by the strain. In solid culture, many distinct grooves formed by the morphology of filamentous microorganisms on the surface of a PLA film were observed by scanning electron microscopy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikura Y, Kudo T (1999) Isolation of a microorganism capable of degrading poly(L-lactide). J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 45: 247–251.
Jarerat A, Tokiwa Y (2001a) Degradation of poly(tetramethylene succinate) by thermophilic actinomycetes. Biotechnol. Lett. 23: 647–651.
Jarerat A, Tokiwa Y (2001b) Degradation of poly(L-lactide) by a fungus. Macromol. Biosci. 1: 136–140.
Jarerat A, Tokiwa Y (2003) Degradation of poly(L-lactide) by Saccharothrix waywayanensis. Biotechnol. Lett. 25: 401–404.
Jarerat A, Pranamuda H, Tokiwa Y (2002) Poly(L-lactide)-degrading activity in various actinomycetes. Macromol. Biosci. 2: 420–428.
Labeda DP, Hatano K, Kroppenstedt RM, Tamura T (2001) Revival of the genus Lentzea and proposal for Lechevalieria gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51: 1045–1050.
Lunt J (1997) Large-scale production, properties and commercial applications of polylactic acid polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 59: 145–152.
Nakamura K, Tomita T, Abe N, Kamio Y (2001) Purification and characterization of an extracellular poly(L-lactic acid) depolymerase from a soil isolate, Amycolatopsis sp. strain K104-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67: 345–353.
Pranamuda H, Tokiwa Y (1999) Degradation of poly(L-lactide) by strains belonging to genus Amycolatopsis. Biotechnol. Lett. 21: 901–905.
Pranamuda H, Tokiwa Y, Tanaka H (1997) Polylactide degradation by an Amycolatopsis sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 1637–1640.
Pranamuda H, Tsuchii A, Tokiwa Y (2001) Poly(L-lactide)-degrading enzyme produced by Amycolatopsis sp. Macromol. Biosci. 1: 25–29.
Tokiwa Y, Pranamuda H (2001) Microbial degradation of aliphatic polyesters. In: Doi Y, Steinbuchel A, eds. Biopolymers, Vol. 3. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, pp. 85–103.
Tokiwa Y, Konno M, Nishida H (1999) Isolation of silk degrading microorganisms and its poly(L-lactide) degradability. Chem. Lett. 1999: 355–356.
Vainionpaa S, Rokkanen P, Tormall P (1989) Surgical application of biodegradable polymers in human-tissues. Prog. Polym. Sci. 14: 679–716.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jarerat, A., Tokiwa, Y. & Tanaka, H. Poly(l-lactide) degradation by Kibdelosporangium aridum . Biotechnology Letters 25, 2035–2038 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000004398.38799.29
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000004398.38799.29