Abstract
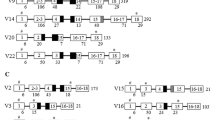
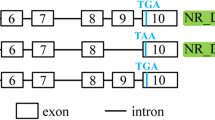
The Mx gene encodes an antiviral protein and is induced by type I interferons (IFNs). In this study, a new bovine Mx gene (designated Mx1B) was isolated from the endometrial cDNA library of the early pregnant cow. Although the Mx1B cDNA contained a single open reading frame (ORF) the same as the known Mx1, the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) and 5′ coding region of Mx1B were rather different from the corresponding regions of Mx1 Genomic structure analysis revealed that bovine Mx1B was an alternative splicing variant of Mx1 and had transcription regulatory sequences in the upstream region. RT-PCR and its sequencing identified another Mx1 splicing variant and demonstrated that these bovine Mx1 splicing variants were ubiquitously expressed in various tissues. Furthermore, it was found that all the bovine breeds investigated had identical splice sites of Mx1 and Mx1B. It is speculated that cattle have at least two functional Mx isoforms that might provide strong natural resistance to specific viruses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnheiter, H., & Meier, E. (1990). Mx proteins: Antiviral proteins by chance or by necessity? New Biolog. 2:851.
Bourne, H. R., Sanders, D. A., & McCormick, F. (1991). The GTPase superfamily; conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature 349:117.
Chang, K. C., Goldsink, G., & Lida, J. (1990). Studies in the vivo expression of the influenza resistance gene Mx by in-situ hybridization. Arch. Virol. 110:151.
Charleston, B., & Stewart, H. J. (1993). An interferon-induced Mx protein: cDNA sequence and high-level expression in the endometrium of pregnant sheep. Gene 137:327.
Chen, M. S., Obar, R. A., Schroeder, C. C., Austin, T. W., Poodry, C. A., Wadsworth, S. C., & Vallee, R. B. (1991). Multiple forms of dynamin are encoded by shibire, a Drosophila gene involved in endocytosis. Nature 351:583.
Dreiding, P., Staeheli, P., & Haller, O. (1985). Interferon-induced protein Mx accumulates in nuclei of mouse cells expressing resistance to inf1uenza viruses. Virology 140:192.
Ellinwood, N. M., Berryere, T. G., Fournier, B. P., Bowen, R. A., Buchanan, F. C., & Schumutz, S. M. (1999). MX1 maps to cattle chromosome 1. Anim. Genet. 30:164.
Ellinwood, N. M., McCue, J. M., Gordy, P. W., & Bowen, R. A. (1998). Cloning and characterization of cDNAs for a bovine (Bos taurus) Mx protein. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 18:745.
Horisberger, M. A. (1988). The action of recombinant bovine interferons on influenza virus replication correlates with the induction of two Mx-related proteins in bovine cells. Virology 162:181.
Horisberger, M. A. (1992). Interferon-induced protein MxA is a GTPase which binds transiently to cellular proteins. J. Virol. 66:4705.
Horisberger, M. A., & Gunst, M. C. (1991). Interferon-induced proteins: Identification of Mx proteins in various mammalian species. Virology 180:185.
Hug, H., Costas, M., Staeheli, P., Aebi, M., & Weissmann, C. (1988). Organization of the murine Mx gene and characterization of its interferon-and virus-inducible promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:3065.
Jin, H. K., Takada, A., Kon, Y., Haller, O., & Watanabe, T. (1999). Identification of the murine Mx2 gene: Interferon-induced expression of the Mx2 protein from the fetal mouse gene confers resistance to vesicular stomatitis virus. J. Virol. 73:4925.
Lopez, J. W., & Woods, G. T. (1984). Influenza virus in ruminants: A review. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 45:445.
Meier, E., Kunz, G., Haller, O., & Arnheiter, H. (1990). Activity of rat Mx proteins against a rhabdovirus. J. Virol. 64:6263.
Muller, M., & Brem, G. (1991). Disease resistance in farm animals. Experienta 47:923.
Obar, R. A., Collins, C. A., Hammarback, J. A., Shpetner, H. S., & Vallee, R. B. (1990). Molecular cloning of the microtubule-associated mechanochemical enzyme dynamin reveals homology with a new family of GTP-binding proteins. Nature 347:256.
Ott, T. L., Yin, J., Wiley, A. A., Kim, H.-T., Gerami-Naini, B., Spencer, T. E., Bartol, F. F., Burghardt, R. C., & Bazer, F. W. (1998). Effects of the estrous cycle and early pregnancy on uterine expression of Mx protein in sheep (Ovis aries). Biol. Reprod. 59:784.
Pavlovic, J., Zurcher, T., Haller, O., & Staeheli, P. (1990). Resistance to influenza virus and vesicular stomatitis virus conferred by expression of human MxA protein. J. Virol. 64:3370.
Pitossi, F., Blank, A., Schroder, A., Schwarz, A., Hussi, P., Schwemmle, M., Pavlovic, J., & Staeheli, P. (1993). A functional GTP-binding motif is necessary for antiviral activity of Mx proteins. J. Virol. 67:6726.
Puwaravutipanich, T., & Panyim, S. (1975). The nuclear basic proteins of human testes and ejaculated spermatozoa. Exp. Cell Res. 90:153.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (1989a). Extraction and purification of plasmid DNA. In Molecular Cloning. 1.21. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (1989b). Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. In Molecular Cloning. 9.14. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Staeheli, P. (1990). Interferon-induced proteins and the antiviral state. Adv. Virus Res. 38:147.
Staeheli, P., & Haller, O. (1987). Interferon-induced Mx protein: A mediator of cellular resistance to influenza virus. Interferon 8:1.
Staeheli, P., Haller, O., Boll, W., Lindenmann, J., & Weissmann, C. (1986).Mx protein: Constitutive expression in 3T3 cells transformed with cloned Mx cDNA confers selective resistance to influenza virus. Cell 44:147.
van der Bliek, A. M, and Meyerowitz, E. M. (1991). Dynamin-like protein encoded by the Drosophila shibire gene associated with vesicular traffic. Nature 351:411.
Wuethrich, R., Staeheli, P., & Haller, O. (1985). In Kirchner, H., and Schellekens, H. (eds.), The Biology of the Interferon System, Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, p. 317.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kojima, T., Oshima, K., Watanabe, H. et al. The Bovine Mx1 Gene: Characterization of the Gene Structure, Alternative Splicing, and Promoter Region. Biochem Genet 41, 375–390 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIGI.0000007773.15979.13
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIGI.0000007773.15979.13