Abstract
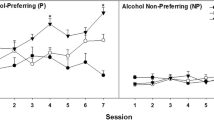
The Alcohol Tolerant (AT) and Alcohol Nontolerant (ANT) rats, selectively bred for ethanol-induced ataxia on the inclined plane at ALKO in Finland, were moved to the University of Colorado in 1998. The selection phenotype was tested on generation 60 animals in Colorado. In week one, ataxia was measured on the inclined plane 30 minutes after an intraperitoneal dose of 2 g/kg 15% w/v ethanol. Differences in ethanol-induced ataxia between the AT and ANT lines at the University of Colorado were similar to those in the original lines in Finland. In week two, ataxia was measured on the inclined plane at 5 and 30 minutes, and tolerance was measured as the time to regain the original angle of sliding. The AT rats rapidly developed tolerance to 2 g/kg ethanol on the inclined plane; tolerance development was significantly slower in the ANT rats. In week three, the animals were tested for the duration of loss of righting reflex (LORR) and blood ethanol concentration at regain of the righting reflex (BECRRR) following a dose of 3.5 g/kg. The AT rats had a significantly higher BECRRR than did the ANT rats, but did not differ in LORR. A separate experiment with previously untreated rats demonstrated that naïve animals of the two lines did not differ in BECRRR or LORR. AT and ANT rats were genotyped for the mutation that occurs in the gene for the α6 subunit of the GABAA receptor, a natural mutation that is known to affect benzodiazepine responses. All ANT animals tested carried the mutant allele, whereas some AT families carried the mutation and others were wild type. There was no effect of the mutation in AT rats for any of the phenotypes that were tested. After several generations of brother–sister mating, the AT and ANT lines were more than 90% inbred as determined by genotyping. One AT (wild-type) line and one ANT (mutant) line were selected for breeding an F2 intercross generation of 1200 animals. They were phenotyped for sensitivity and tolerance to ethanol on each of three consecutive weeks. Order of testing had a modest effect on some of the phenotypes: when tested during the third week as compared to weeks one or two, BECRRR was increased, 30-minute sensitivity was increased, and development of acute tolerance was increased. Statistically significant correlations were found between tolerance and sensitivity at both 5 and 30 minutes, and between LORR and BECRRR. The smaller (or absence of) significant correlations between others of the phenotypes indicate(s) that they are most likely controlled by different sets of genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deitrich, R. A., Bludeau, P., and Erwin, V. G. (2000). Phenotypic and genotypic relationships between ethanol tolerance and sensitivity in mice selectively bred for initial sensitivity to ethanol (SS and LS) or development of acute tolerance (HAFT and LAFT). Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 24:595-604.
Draski, L. J., Spuhler, K. P., Erwin, V. G., Baker, R. C., and Deitrich, R. A. (1992). Selective breeding of rats differing in sensitivity to the effects of acute ethanol administration. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 16:48-54.
Draski, L. J., Bice, P. J., and Deitrich, R. A. (2001). Developmental alterations of ethanol sensitivity in selectively bred high and low alcohol sensitive rats. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 70:387-396.
Eriksson, K., and Rusi, M. (1981). Finnish selection studies on alcohol-related behaviors: general outline. In G. E. McClearn, R. A. Deitrich, and V. G. Erwin (s.), Development of animal models as pharmacogenetic tools. Rockville, MD: NIAAA Research Monograph, pp. 87-117.
Eriksson, C. J. P., and Sarviharju, M. (1984). Motor impairment, narcosis and hypothermia: separate genetic mechanisms. Alcohol 1:59-62.
Hellevuo, K., and Korpi, E. R. (1988). Failure of Ro 15-4513 to antagonize ethanol in rat lines selected for differential sensitivity to ethanol and in Wistar rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 30:183-188.
Hellevuo, K., Kiianmaa, K., and Korpi, E. R. (1989). Effect of GABAergic drugs on motor impairment from ethanol, barbital and lorazepam in rat lines selected for differential sensitivity to ethanol. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 34:399-404.
Kaheinen, P., Korpi, E. R., Pyykko, I., Mantysalo, S., and Ignatius, J. (1988). Hippocampal rhythmic slow activity in rat lines selected for differences in ethanol-induced motor impairment. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 30:177-181.
Kiianmaa, K., Hellevuo, K., and Korpi, E. R. (1988). The AT (alcohol tolerant) and ANT (alcohol nontolerant) rat lines selected for differences in sensitivity to ethanol: an overview. In K. Kuriyama, A. Takada, and H. Ishii (s.), Biomedical and Social Aspects of Alcohol and Alcoholism. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers BV, pp. 415-418.
Korpi, E. R., and Uusi-Oukari, M. (1989). GABAA receptor-mediated chloride flux in brain homogenates from rat lines with differing innate alcohol sensitivities. Neuroscience 32:387-392.
Korpi, E. R., Uusi-Oukari, K., Wegelius, K., Casanova, M., Zito, M., and Kleinman, J. E. (1992a). Cerebellar and frontal cortical benzodiazepine receptors in human alcoholics and chronically alcohol-drinking rats. Biol. Psychiatry 31:774-786.
Korpi, E. R., Uusi-Oukari, K., Castren, E., Suzdak, P. D., Seppala, T., Sarviharju, M., and Tuominen, K. (1992b). Cerebellar GABAA receptors in two rat lines selected for high and low sensitivity to moderate alcohol doses: pharmacological and genetic studies. Alcohol 9:225-231.
Korpi, E. R., Uusi-Oukari, M., and Wegelius, K. (1992c). Substrate specificity of diazepam-insensitive cerebellar [3H] Ro 15-4513 binding sites. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 213:323-329.
Korpi, E. R., Keingoor, C., Kettenmann, H., and Seeburg, P. H. (1993). Benzodiazepine-induced motor impairment linked to point mutation in cerebellar GABAA receptor. Nature 361:356-359.
Korpi, E. R., and Seeburg, P. H. (1993). Natural mutation of GABAA receptor α6 subunit alters benzodiazepine affinity but not allosteric GABA effects. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 247:23-27.
Le, A. D., and Kiianmaa, K. (1989). Initial sensitivity and the development of acute and rapid tolerance to ethanol in the AT and ANT rats. In K. Kiianmaa, B. Tabakoff, and T. Saito (s.), Genetic aspects of alcoholism. The Finnish Foundation for Alcohol Studies 37:147-155.
Lewis, R. R., Kunz, A. L., and Bell, R. E. (1966). Error of intraperitoneal injections in rats. Lab. Anim. Care 16:505-509.
Malminen, O., and Korpi, E. R. (1988). GABA/benzodiazepine receptor/chloride ionophore complex in brains of rat lines selectively bred for differences in ethanol-induced motor impairment. Alcohol 5:239-249.
Malminiemi, O., and Korpi, E. R. (1989). Diazepam-insensitive [3H] Ro 15-4513 binding in intact cultured cerebellar granule cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 169:53-60.
Mäkelä, R., Wong, G., Lüddens, H., and Korpi, E. R. (1995). Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of rats with cerebellar GABAA receptors composed from mutant and wild-type α6 subunits. J. Neurochem. 65:2401-2408.
Näkki, R., Wong, G., and Korpi, E. R. (1995). [3H] MK-801 binding in various brain regions of rat lines selected for differential alcohol sensitivity. Alcohol 12:335-340.
Saba, L., Porcella, A., Congeddu, E., Colombo, G., Peris, M., Pistis, M., Gessa, G., and Pani, L. (2001). The R100Q mutation of the GABAA alpha 6 receptor subunit may contribute to voluntary aversion to ethanol in the sNP rat line. Mol. Brain Res. 87:263-270.
Sarviharju, M., and Korpi, E. R. (1993). Ethanol sensitivity and consumption in F2 hybrid crosses of ANT and AT rats. Alcohol 10:415-418.
Sellin, L. C., and Laakso, P. S. (1987). Effect of ethanol on motor performance and hippocampal population spikes in some standard and selectively outbred rat strains. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 11:502-505.
Tuominen, K., and Korpi, E. R. (1991). Diminished stress responses in the alcohol-sensitive ANT rat line. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 40:409-415.
Tuominen, K., Sarviharju, M., Honkanen, A., and Korpi, E. R. (1994). Phenotypic characterization of second generation offspring of alcohol-sensitive ANT and alcohol-insensitive AT rat lines. Alcohol 11:379-384.
Uusi-Oukari, M., and Korpi, E. R. (1989). Cerebellar GABAA receptor binding and function in vitro in two rat lines developed for high and low alcohol sensitivity. Neurochem. Res. 14:733-739.
Uusi-Oukari, M., and Korpi, E. R. (1990). Diazepam sensitivity of the binding of an imidazobenzodiazepine, [3H]R0 15-4513, in cerebellar membranes from two rat lines developed for high and low alcohol sensitivity. J. Neurochem. 54:1980-1987.
Uusi-Oukari, M., and Korpi, E. R. (1991). Specific alterations in the cerebellar GABAA receptors of an alcohol-sensitive ANT rat line. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 15:241-248.
Uusi-Oukari, M., and Korpi, E. R. (1992). Functional properties of GABAA receptors in two rat lines selected for high and low alcohol sensitivity. Alcohol 9:261-269.
Wong, G., Uusi-Oukari, M., Hansen, H. C., Suzdak, P. D., and Korpi, E. R. (1995). Characterization of novel ligands for wild-type and natural mutant diazepam-insensitive benzodiazepine receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 289:335-342.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radcliffe, R.A., Hoffmann, S.E., Deng, XS. et al. Behavioral Characterization of Alcohol-Tolerant and Alcohol-Nontolerant Rat Lines and an F2 Generation. Behav Genet 34, 453–463 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BEGE.0000023650.32243.39
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BEGE.0000023650.32243.39