Abstract
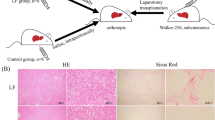
Gadolinium chloride (5 mg/kg) administered to mice 24 h before intravenous transplantation of HA-1 hepatoma cells decreased the volume density of tumor implants in the liver, reduced the intensity of degenerative and necrotic changes developing under the effect of growing tumor metastases, and prolonged the life span of tumor-bearing mice. Development of metastases was not associated with changes in cathepsin B activity in the liver, while activity of cathepsin L decreased only during the early period (4 days) after injection of gadolinium chloride. Injection of gadolinium chloride led to labilization of liver cell lysosomes because of overload with gadolinium chloride particles. The positive effect of gadolinium chloride was probably associated with depression of liver macrophages at the stage of tumor cell invasion and with subsequent migration of monocytes/macrophages preventing the growth of formed metastatic nodes in the liver.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
G. G. Avtandilov, Medical Morphometry [in Russian], Moscow (1990).
D. L. Morton and A. Bart, Biological Methods for Treatment of Oncological Diseases [in Russian], Moscow (2002), pp. 710-724.
V. B. Okulov, Vopr. Onkol., 43, No. 1, 102-106 (1998).
T. A. Usova, O. N. Poteryaeva, S. Ya. Zhanaeva, et al., Byull. Eksp. Biol. Med., 135, No. 1, 95-98 (2003).
O. V. Falameeva, O. N. Poteryaeva, S. Ya. Zhanaeva, et al., Ibid., 132, No. 8, 205-208 (2001).
M. J. Hardonk, F. W. J. Dijkhuis, and A. M. Joker, Cells of the Hepatic Sinusoid. Kupffer Cell Foundation, Eds. E. Wisse et al., Vol. 5, pp. 29-32 (1995).
N. Katunuma, A. Matsui, T. Kakegawa, et al., Adv. Enzyme Regul., 39, 247-260 (1999).
N. Katunuma, H. Tsuge, M. Nikatsuka, et al., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 397, 305-311 (2002).
G. Kogan, J. Sandula, T. Korolenko, et al., Intern. Immunopharmacol., 2, 775-781 (2002).
T. Korolenko, I. G. Svechnikova, K. Urazgaliyev, et al., Cellular Peptidases in Immune Functions and Diseases, Eds. S. Ansorge et al., New York (1997), pp. 315-321.
T. Meyer and I R. Hart, Eur. J. Cancer, 34, 214-221 (1998).
I. G. Svechnikova, T.A. Korolenko, Ju. F. Stashko, et al., Drugs Exp. Clin. Res., 24, 261-269 (1998).
B. Turk, D. Turk, and G. S. Salvesen, Curr. Pharm. Res., 8, 1623-1637 (2002).
B. Turk, D. Turk, and V. Turk, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1477, 98-111 (2000).
M. Yi and E. Ruoslahti, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 620-624 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhanaeva, S.Y., Korolenko, T.A., Nikitenko, E.V. et al. Effect of Liver Macrophage Depression on the Development of Liver Metastases of HA-1 Tumor in Mice. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 137, 581–584 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BEBM.0000042718.76183.40
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BEBM.0000042718.76183.40