Abstract
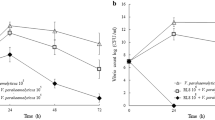
Enrichment of Artemia nauplii with a known probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii (SB) and its role in enhancing resistance against the pathogen Vibrio harveyi was investigated. SB was cultured, then fed to instar II Artemia nauplii in three different treatments; 102 (T1), 103 (T2) and 104 (T3) colony forming units (CFU) per ml in triplicate. The algae Nanochloropsis sp. was used as control diet. Survival and total count of CFU nauplii−1 was observed on different media (Sabouraud, for enumerating yeasts, thiosulphate citrate bile salts sucrose, for enumerating Vibrio and seawater agar, for enumerating total aerobic flora) for each replication. Enhanced survival of nauplii was observed in treatments as compared to control. Results indicated that enrichment of SB in Artemia nauplii proceeded in a linear fashion, and up to 3500 CFU of SB could be detected in one nauplii at 104 CFU ml−1 treatment. No conclusive trend could be observed in the count of Vibrio and total aerobic flora due to treatment. Enriched nauplii were then challenged with the pathogen V. harveyi for 24 and 48 h at a concentration of 6.1 × 106 CFU ml−1. The survival counts at 48 h showed that the resistance of the nauplii was significantly (P < 0.01) improved in those fed with 104 CFU ml−1 SB (90% survival rate after 48 h of challenge versus less than 40% for the infected control group without SB and treatments T1 and T2). This study shows that SB, which has been used for the first time in an aquatic live feed organism, has a profound beneficial effect on the nauplii by increasing its resistance to a pathogenic Vibrio infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguila A.A., Mansir A.T. and Manriquez A.R. 1994. Using brine shrimp as a drug carrier for therapeutic applications in aquaculture. Aquacult. Eng. 13: 301–309.
Buts J.-P., Corthier G. and Delmee M. 1993. Saccharomyces boulardii for Clostridium dicile – associated enteropathies in infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 16: 419–425.
Campbell R., Adams A., Tatner M.F., Chair M. and Sorgeloos P. 1993. Uptake of Vibrio anguillarum vaccine by Artemia salina as a potential oral delivery system to fish fry. Fish Shellfish Immun. 3: 451–459.
Czerucka D., Rouse I. and Rampal P. 1994. Saccharomyces boulardii inhibits secretagogue – mediated adenosive 3′–5′-cyclic monophosphate induction in intestinal cells. Gastroenterology 106: 65–72.
Dempsey A.C., Kitting C.L. and Rosson R.A. 1989. Bacterial variability among individual penaeid shrimp digestive tracts. Crustaceana 56: 267–278.
Dhert J., Lavens P. and Sorgeloos P. 1993. Preparation and use of Artemia as food for shrimp and prawn larvae. In: CRC Handbook in Mariculture, Vol. 1. Crustacean Aquaculture. McVey J. (ed) CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, pp. 61–63.
Dixon B.A., Van Pucke S.O., Chair M., Demasque M., Nelis H.J., Sorgeloos P. and De Leenheer A.P. 1995. Bioencapsulation of the antibacterial drug safrafloxacin in nauplii of the brine shrimp Artemia franciscana. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 7: 42–45.
Gatesoupe F.J. 1991. Managing the dietary value of Artemia in larval turbot, Scophthalmus maximus: the eect of enrichment and distribution techniques. Aquacult. Eng. 10: 111–119.
Gatesoupe F.J. 1993. Bacillus sp. spores as food additive for the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis: improvement of their bacterial environment and their dietary value for larval turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. In: Kaushik S.J. and Luque P. (eds) Fish Nutrition in Practice. Vol. 61. INRA, Paris, France, Les Colloques, pp. 561–568.
Gatesoupe F.J. 1994. Lactic acid bacteria increase the resistance of turbot larvae, Scophthalmus maximus, against pathogenic Vibrio. Aquat. Living Resour. 7: 277–282.
Gomez-Gil B., Roque A. and Turnbull J.F. 2000. The use and selection of probiotic bacteria for use in the culture of larval aquatic organisms. Aquaculture 191: 259–270.
Intriago P. and Jones D.A. 1993. Bacteria as food for Artemia. Aquaculture 113: 115–127.
Klein S.M., Elmer G.W., McFarland L.V., Surawicz C.M. and Levy R.H. 1993. Recovery and elimination of the biotherapeutic agent, Saccharomyces boulardii, in healthy human volunteers. Pharmaceut. Res. 10: 1615–1619.
Lavens P. and Sorgeloos P. 1986. Manual on the production and use of live food for aquaculture. FAO Fish. Tech. Pap. 361, 295 pp.
Lavilla-Pitogo C.R., Baticados M.C.L., Cruz-Lacierda E.R. and de la Pena L.D. 1990. Occurrence of luminous bacterial diseases of Penaeus monodon larvae in the Philippines. Aquaculture 87: 237–242.
Makridis P., Fjellheim A.J., Skjermo J. and Vadstein O. 2000. Control of the bacterial flora of Brachionus plicatilis and Artemia franciscana by incubation in bacterial suspension. Aquaculture 185: 207–218.
McFarland L.V. and Bernasconi P. 1993. Saccharomyces boulardii: a review of an innovative biotherapeutic agent. Microb. Ecol. Health D. 6: 157–171.
Mohamed K.S. 1995. Probiotics: an emerging concept in aquaculture nutrition and disease control. Seafood Export J. 26(7): 5–9.
Pothoulakis C., Kelly C.P., Joshi M.A., Gao N., O'Keane C.J., Castagliuolo I. and Lamout J.T. 1993. Saccharomyces boulardii inhibits Clostridium dicile toxin A binding and enterotoxicity in rat ileum. Gastroenterology 104: 1108–1115.
Rengpipat S., Phianphak W., Piyatiratitivorakul S. and Menasveta P. 1998. Eects of a probiotic bacterium on black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon survival and growth. Aquaculture 167: 301–313.
Ringo E., Sinclair P.D., Birkebeck H. and Barbour A. 1992. Production of ecosapentanoic acid (20:5 n-3) by Vibrio pelagius isolated from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus (L.) larvae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 3777–3778.
Strom E. and Ringo E. 1993. Changes in the bacterial composition of early developing cod, Gadus morhua (L). larvae following inoculation of Lactobacillus plantarum into the water. In: Wather B. and Fyhr H.J. (eds) Physiological and Biochemical Aspects of Fish Larval Development. University of Bergen, Norway, pp. 226–228.
Sugita H., Miyajima C. and Deguchi Y. 1991. The vitamin B12 producing ability of the intestinal microflora of freshwater fish. Aquaculture 92: 267–276.
Vidon N., Huchet B. and Rambaud J.C. 1986. Influence de Saccharomyces boulardii sur la secretion jejunale induite chez le rat par la toxine cholerique. Gasteroen. Clin. Biol. 10: 13–16.
Watanabe T., Kitajima C. and Fujita S. 1983. Nutritional values of live organisms used in Japan for mass propagation of fish: a review. Aquaculture 34: 115–143.
West P.A. and Colwell R.R. 1984. Identification and classification of Vibrionaceae – an overview. In: Colwell R.R. (ed) Vibrios in the Environment. John Wiley, New York, pp. 285–363.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patra, S., Mohamed, K. Enrichment of Artemia nauplii with the probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii and its resistance against a pathogenic Vibrio . Aquaculture International 11, 505–514 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AQUI.0000004193.40039.54
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AQUI.0000004193.40039.54