Abstract
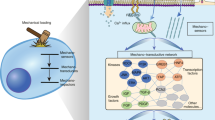
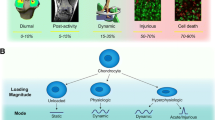
Mechanical forces influence chondrocyte metabolism and are critically important for maintenance of normal cartilage structure and integrity. In cells of the musculoskeletal system and mechanoresponsive cells in other tissues, integrins seem to be involved in the mechanotransduction process. Integrin activity is important in the early cellular responses to mechanical stimulation, regulating activation of a number of intracellular cascades that induce changes in gene expression and tissue remodeling. In normal human articular chondrocytes, integrin activation, consequent to mechanical stimulation in vitro, results in tyrosine phosphorylation of regulatory proteins and subsequent secretion of autocrine and paracrine acting soluble mediators including substance P and interleukin 4. Significant differences in signaling events and cellular responses are seen when normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes are mechanically stimulated. These differences may relate to differences in integrin expression and function. Improved comprehension of how integrins mediate chondrocyte responses to mechanical stimulation, and how cross talk between integrin signaling, extracellular matrix, and autocrine/paracrine signaling molecules regulate mechanotransduction and cellular reactions are necessary for further understanding of how load influences cartilage structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aplin, A. E., A. Howe, S. K. Alahari, and R. L. Juliano. Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol. Rev. 50:197-263, 1998.
Arner, E. C., and M. A. Pratta. Modulation of interleukin-1-induced alterations in cartilage proteoglycan metabolism by activation of protein kinase C. Arthritis Rheum. 34:1006-1013, 1991.
Arner, E. C., and M. C. Tortorella. Signal transduction through chondrocyte integrin receptors induces matrix metalloproteinase synthesis and synergises with interleukin-1. Arthritis Rheum. 38:1304-1314, 1995.
Attur, M. G., M. N. Dave, R. M. Clancy, I. R. Patel, S. B. Abramson, and A. R. Amin. Functional genomic analysis in arthritis-affected cartilage: Yin-yang regulation of inflammatory mediators by a5β1 and aVβ3 integrins. J. Immunol. 164:2684-2691, 2000.
Bjelle, A. O. Content and composition of glycosaminoglycans in human knee joint cartilage. Variation with site and age in adults. Connect. Tissue. Res. 3:141-147, 1975.
Bonassar, L. J., A. J. Grodzinsky, E. H. Frank, S. G. Davila, N. R. Bhaktav, and S. B. Trippel. The effect of dynamic compression on the response of articular cartilage to insulin-like growth factor-I. J. Orthop. Res. 19:11-17, 2001.
Bonassar, L. J., J. D. Sandy, M. W. Lark, A. H. Plaas, E. H. Frank, and A. J. Grodzinsky. Inhibition of cartilage degradation and changes in physical properties induced by IL-1beta and retinoic acid using matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 344:404-412, 1997.
Brandt, K. D., S. L. Myers, D. Burr, and M. Albrecht. Osteoarthritic changes in canine articular cartilage, subchondral bone, and synovium fifty-four months after transection of the anterior cruciate ligament. Arthritis Rheum. 34:1560-1570, 1991.
Buschmann, M. D., Y. J. Kim, M. Wong, E. Frank, E. B. Hunziker, and A. J. Grodzinsky. Stimulation of aggrecan synthesis in cartilage explants by cyclic loading is localized to regions of high interstitial fluid flow. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 366:1-7, 1999.
Chen, H.-C., and J.-L. Guan. Association of focal adhesion kinase with its potential substrate phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91:10148-10152, 1994.
Chikama, T., M. Nakamura, and T. Nishida. Upregulation of integrin alpha5 by a C-terminus four-amino-acid sequence of substance P (phenylalanine-glycine-leucine-methionine-amide) synergistically with insulin-like growth factor-1 in SV-40 transformed human corneal epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 255:692-697, 1999.
Chong, L. D., A. Traynor-Kaplan, G. M. Bokoch, and M. A. Schwartz. The small GTP-binding protein Rho regulates a phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase in mammalian cells. Cell 79:507-513, 1994.
Clancy, R. M., J. Rediske, X. Tang, N. Nijher, S. Frenkel, M. Philips, and S. B. Abramson. Outside-in signaling in the chondrocyte. Nitric oxide disrupts fibronectin-induced assembly of a subplasmalemmal actin/rho A/focal adhesion kinase signaling complex. J. Clin. Invest. 100:1789-1796, 1997.
Dedhar, S. Cell–substrate interactions and signaling through ILK. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12:250-256, 2000.
Duncan, R. L., and C. H. Turner. Mechanotransduction and the functional response of bone to mechanical strain. Calcif. Tissue Int. 57:344-358, 1995.
Enomoto-Iwamoto, M., M. Iwamoto, K. Nakashima, Y. Mukudai, D. Boettiger, M. Pacifici, K. Kurisu, and F. Suzuki. Involvement of alpha5beta1 integrin in matrix interactions and proliferation of chondrocytes. J. Bone Miner. Res. 12:1124-1132, 1997.
Fanning, P. J., G. Emkey, R. J. Smith, A. J. Grodzinsky, N. Szasz, and S. B. Tippel. Mechanical regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in articular cartilage. J. Biol. Chem. 278:50940-50948, 2003.
Giancotti, F. G., and E. Ruoslahti. Integrin signaling. Science 285:1028-1032, 1999.
Graff, R., S. Kelley, and G. Lee. Role of pericellular matrix in development of a mechanically functional neocartilage. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 82:457-464, 2003.
Guilak, F., W. R. Jones, H. P. Ting-Beall, and G. M. Lee. The deformation behavior and mechanical properties of chondrocytes in articular cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 7:59-70, 1999.
Guilak, F., R. A. Zell, G. R. Erickson, D. A. Grande, C. T. Rubin, K. J. McLeod, and H. J. Donahue. Mechanically induced calcium waves in articular chondrocytes are inhibited by gadolinium and amiloride. J. Orthop. Res. 17:421-429, 1999
Hamanishi, C., M. Hashima, H. Satsuma, and S. Tanaka. Protein kinase C activator inhibits progression of osteoarthritis induced in rabbit knee joints. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 127:540-544, 1996.
Han, O., T. Takei, M. Basson, and B. E. Sumpio. Translocation of PKC isoforms in bovine aortic smooth muscle cells exposed to strain. J. Cell. Biochem. 80:367-372, 2001.
Helminen, H. J., A. M. Saamanen, J. Jurvelin, I. Kiviranta, J. J. Parkkinen, M. J. Lammi, and M. Tammi. The effect of loading on articular cartilage. Duodecim 108:1097-1107, 1992.
Hildebrand, J. D., M. D. Schaller, and J. T. Parsons. Paxillin, a tyrosine-phosphorylated focal adhesion-associated protein binds to the carboxyl terminal domain of focal adhesion kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:637-647, 1995.
Holmvall, K., L. Camper, S. Johansson, J. H. Kimura, and E. Lundgren-Akerlund. Chondrocyte and chondrosarcoma cell integrins with affinity for collagen type II and their responses to mechanical stress. Exp. Cell Res. 221:496-503, 1995.
Horwitz, A., K. Duggan, C. Buck, M. Beckeri, and K. Burridge. Interactions of plasma membrane fibronectin receptor with talin—a transmembrane linkage. Nature 320:531-533, 1986.
Hynes, R. O. Integrins: Versatility, modulation and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69:11-25, 1992.
Ivaska, J., L. Bosca, and P. J. Parker. PKCɛ is a permissive link in integrin-dependent IFNγ signaling that facilitates JAK phosphorylation of STAT1. Nat. Cell Biol. 5:363-369, 2003.
Jalial, S., M. A. del Pozo, K.-D. Chen, H. Miao, Y.-S. Li, M. A. Schwartz, J. Y.-J. Shyy, and S. Chien. Integrin-mediated mechanotransduction requires its dynamic interaction with specific extracellular matrix (ECM) ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98:1042-1046, 2001.
Jin, M., E. H. Frank, T. M. Quinn, E. B. Hunziker, A. J. Grodzinsky. Tissue shear deformation stimulates proteoglycan and protein biosynthesis in bovine cartilage explants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 395:41-48, 2001.
Jobanputra, P., L. Hong, K. Jenkins, C. Bavington, F. R. Brennan, G. Nuki, J. L. Godolphin, and D. M. Salter. Modulation of human chondrocyte integrins by inflammatory synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 39:1430-1432, 1996.
Jones, K. L., M. Brown, S. Y. Ali, and R. A. Brown. An immunohistochemical study of fibronectin in human osteoarthritic and disease free articular cartilage. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 46:809-815, 1987.
Kiviranta, I., M. Tammi, J. Jurvelin, J. Arokoski, A.-M. Saamanen, and H. Helminen. Moderate running exercise augments glycosaminoglycans and thickness of articular cartilage in the knee joint of young beagle dogs. J. Orthop. Res. 6:188-195, 1988.
Knight, M. M., D. A. Lee, and D. L. Bader. The influence of elaborated pericellular matrix on the deformation of isolated articular chondrocytes cultured in agarose. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1405:67-77, 1998.
Knight, M. M., J. M. Ross, A. F. Sherwin, D. A. Lee, D. L. Bader, and C. A. Poole. Chondrocyte deformation within mechanically and enzymatically extracted chondrons compressed in agarose. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Gen. Subj. 1526:141-146, 2001.
Kolanus, W., and B. Seed. Integrins and inside-out signal transduction: converging signals from PKC and PIP3. Curr. Biol. 9:725-731, 1997.
Kuo, H.-P., H.-C. Lin, K.-H. Hwang, C.-H. Wang, and L.-C. Lu. Lipopolysaccharide enhances substance P-mediated neutrophil adherence to epithelial cells and cytokine release. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1891-1897, 2000.
Lapadula, G., F. Iannone, C. Zuccaro, V. Grattagliano, M. Covelli, V. Patella, G. Lo Bianco, and V. Pipitone. Chrondrocyte phenotyping in human osteoarthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 17:99-104, 1998.
Lee, D. A., T. Noguchi, S. P. Frean, P. Lees, and D. L. Bader. The influence of mechanical loading on isolated chondrocytes seeded in agarose constructs. Biorheology 37:149-161, 2000.
Lee, H.-S., S. J. Millward-Sadler, M. O. Wright, G. Nuki, R. Al-Jamal, and D. M. Salter. Activation of integrin—RACK1/PKC association in human articular chondrocyte mechanotransduction. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 10:890-897, 2002.
Lee, H.-S., S. J. Millward-Sadler, M. O. Wright, G. Nuki, and D. M. Salter. Integrin and mechanosensitive ion channel-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion proteins and-catenin in human articular chondrocytes after mechanical stimulation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 15:1501-1509, 2000.
Lin, T. H., A. E. Aplin, Y. Shen, Q. Chen, M. Schaller, L. Romer, I. Aukhil, and R. L. Juliano. Integrin-mediated activation of MAP kinase is independent of FAK: Evidence for dual integrin signaling pathways in fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 136:1385-1395, 1997.
Loeser, R. F. Chondrocyte integrin expression and function. Biorheology 37:109-116, 2000.
Loeser, R. F. Growth factor regulation of chondrocyte integrins. Arthritis Rheum. 40:270-276, 1997.
Loeser, R. F., C. S. Carlson, and M. P. McGee. Expression of beta 1 integrins by cultured articular chondrocytes and in osteoarthritic cartilage. Exp. Cell. Res. 217:248-257, 1995.
Lotz, M., J. H. Vaughan, and D. A. Crason. Effect of neuropeptides on production of inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Science 241:1218-1220, 1988.
Malek, A. M., and S. Izumo. Mechanism of endothelial cell shape change and cytoskeletal remodeling in response to fluid shear stress. J. Cell Sci. 109:713-726, 1996.
Mills, I., C. R. Cohen, K. Kamal, G. Li, T. Shin, W. Du, and B. E. Sumpio. Strain activation of bovine aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and alignment: Study of strain dependency and the role of protein kinase A and C signaling pathways. J. Cell Physiol. 170:228-234, 1997.
Millward-Sadler, S. J., A. Mackenzie, M. O. Wright, H.-S. Lee, K. Elliot, L. Gerrard, C. E. Fiskerstrand, D. M. Salter, and J. P. Quinn. Tachykinin expression in cartilage and function in human articular chondrocyte mechanotransduction. Arthritis Rheum. 48:146-156, 2003.
Millward-Sadler, S. J., M. O. Wright, L. W. Davies, G. Nuki, and D. M. Salter. Mechanotransduction via integrins and interleukin-4 results in altered aggrecan and matrix metalloproteinase 3 gene expression in normal, but not osteoarthritic, human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 43:2091-2099, 2000.
Millward-Sadler, S. J., M. O. Wright, H.-S. Lee, H. Caldwell, G. Nuki, and D. M. Salter. Altered electrophysiological responses to mechanical stimulation and abnormal signaling through 5 1 integrin in chondrocytes from osteoarthritic cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 8:272-278, 2000.
Millward-Sadler, S. J., M. O. Wright, H.-S. Lee, K. Nishida, H. Caldwell, G. Nuki, and D. M. Salter. Integrin-regulated secretion of interleukin 4: A novel pathway of mechanotransduction in human articular chondrocytes. J. Cell Biol. 145:183-189, 1999.
Miyamoto, S., H. Teramoto, J. S. Gutkind, and K. M. Yamada. Integrins can collaborate with growth factors for phosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinases and MAP kinase activation: Roles of integrin aggregation and occupancy of receptors. J. Cell Biol. 135:1633-1645, 1996.
Moro, L., M. Venturino, C. Bozzo, L. Silengo, F. Altruda, L. Beguinot, G. Tarone, and P. Defilippi. Integrins induce activation of the EGF receptor: Role in MAP kinase induction and adhesion dependent cell survival. EMBO J. 17:6622-6632, 1998.
Nakamura, M., T. Nagano, T. Chikama, and T. Nishida. Upregulation of phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase and paxillin by combination of substance P and IGF-1 in SV-40 transformed human corneal epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 242:16-20, 1998.
Naruse, K., T. Yamada, X. R. Sai, M. Hamaguchi, and M. Sokabe. pp125FAK is required for stretch dependent morphological response of endothelial cells. Oncogene 17:455-463, 1998.
Osborn, K., S. Trippel, and H. Mankin. Growth factor stimulation of adult articular cartilage. J. Orthop. Res. 7:35-42, 1989.
Ostergaard, K., D. M. Salter, C. B. Andersen, J. Petersen, and K. Bendtzen. CD44 expression is up-regulated in the deep zone of osteoarthritic cartilage from human femoral heads. Histopathology 31:451-459, 1997.
Ostergaard, K., D. M. Salter, J. Petersen, K. Bendtzen, J. Hvolris, and C. B. Andersen. Expression of α-and β-subunits of the integrin superfamily in articular cartilage from macroscopically normal and osteoarthritic human femoral heads. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 57:303-308, 1998.
Otey, C. A., and K. Burridge. Patterning of the membrane cytoskeleton by the extracellular matrix. Sem in. Cell Biol. 1:391-399, 1990.
Paukkonen, K., K. Selkainaho, J. Jurvelin, and H. J. Helminen. Cells and nuclei of articular cartilage chondrocytes in young rabbits enlarged after nonstrenuous physical exercise. J. Anat. 142:13-20, 1985.
Pavasant, P., T. Shizari, and C. Underhill. Hyaluronan synthesis by epiphysial chondrocytes is regulated by growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-1, parathyroid hormone and transforming growth factor-beta 1. Matrix Biol. 15:423-432, 1996.
Ren, X. D., G. M. Bokoch, A. Traynor-Kaplan, G. H. Jenkins, R. A. Anderson, and M. A. Schwartz. Physical association of the small GTPase Rho with a 68 kDa phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase in Swiss 3T3 cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7:435-442, 1996.
Roberts, S., B. Weightman, J. P. G. Urban, and D. Chapell. Mechanical and biochemical properties of human articular cartilage in osteoarthritic femoral heads and in autopsy specimens. J. Bone Joint Surg. 68:278-288, 1986.
Ruwhof, C., and A. van der Laarse. Mechanical stress-induced cardiac hypertrophy: Mechanisms and signal transduction pathways. Cardiovasc. Res. 47:23-37, 2000.
Sadoshima, J., and S. Izumo. Mechanical stretch rapidly activates multiple signal transduction pathways in cardiac myocytes: Potential involvement of an autocrine/paracrine mechanism. EMBO J. 12:1681-1692, 1993.
Salter, D. M., J. E. Robb, and M. O. Wright. Electrophysiological responses of human bone cells to mechanical stimulation: Evidence for specific integrin function in mechanotransduction. J. Bone Miner. Res. 12:1133-1141, 1997.
Santala, P., and J. Heino. Regulation of integrin-type cell adhesion receptors by cytokines. J. Biol. Chem. 266:23505-23509, 1991.
Sauerland, K., R. X. Raiss, and J. Steinmeyer. Proteoglycan metabolism and viability of articular cartilage explants as modulated by the frequency of intermittent loading. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 11:343-350, 2003.
Schaller, M. D., J. D. Hildebrand, J. D. Shannon, J. W. Fox, R. R. Vines, and J. T. Parsons. Autophosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK, directs SH2-dependent binding of pp60src. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:1680-1688, 1994.
Schlaepfer, D. D., M. A. Broome, and T. Hunter. Fibronectin-stimulated signaling from a focal adhesion kinase-c-Src complex: Involvement of the Grb2, p130cas, and Nck adaptor proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:1702-1713, 1997.
Schlaepfer, D. D., S. Hanks, T. Hunter, and P. van der Greer. Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature 372:786-791, 1994.
Schneller, M., K. Vuori, and E. Ruoslahti. αVβ3 integrin associates with activated insulin and PDGFb receptors and potentiates the biological activity of PDGF. EMBO J. 16:5600-5607, 1997.
Schwartz, M. A. Integrin signaling revisited. Trends Cell Biol. 11:466-470, 2001.
Schwartz, M. A., and V. Baron. Interactions between mitogenic stimuli, or a thousand and one connections. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11:197-202, 1999.
Short, S. M., J. L. Boyer, and R. L. Juliano. Integrins regulate the linkage between upstream and downstream events in G-protein-coupled receptor signaling to mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 275:12970-12977, 2000.
Short, S. M., G. A. Talbott, and R. L. Juliano. Integrin-mediated signaling events in human endothelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 9:1969-1980, 1998.
Shyy, J. Y.-J., and S. Chien. Role of integrins in cellular responses to mechanical stress and adhesion. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9:707-713, 1997.
Slowman, S. D., and K. D. Brandt. Composition and glycosaminoglycan metabolism of articular cartilage from habitually loaded and habitually unloaded sites. Arthritis Rheum. 29:88-94, 1986.
Stefanovic-Ravic, M. J., J. Stadler, and C. H. Evans. Nitric oxide and arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 36:1036-1044, 1993.
Takei, T., O. Han, M. Ikeda, P. Male, I. Mills, and B. E. Sumpio. Cyclic strain stimulates isoform-specific PKC activation and translocation in cultured human keratinocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 67:327-337, 1997.
Taskiran, D., M. J. Stefanovic-Ravic, H. Georgescu, and C. H. Evans. Nitric oxice mediates suppression of cartilage proteoglycan synthesis by interleukin-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 200:142-148, 1994.
Urban, J. P. G. The chondrocyte: A cell under pressure. Br. J. Rheumatol. 33:901-908, 1994.
Valhmu, W. B., E. J. Stazzone, N. M. Bachrach, F. Saed-Nejad, S. G. Fischer, V. C. Mow, and A. Ratcliffe. Load-controlled compression of articular cartilage induces a transient stimulation of aggrecan gene expression. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 353:29-36, 1998.
Veldhuijzen, J. P., L. A. Bourret, and G. A. Rodan. In vitro studies of the effect of intermittent compressive forces on cartilage cell proliferation. J. Cell. Physiol. 98:299-306, 1979.
Vuori, K., H. Hirai, S. Aizawa, and E. Ruoslahti. Introduction of p130cas signaling complex formation upon integrin-mediated cell adhesion: A role for Src family kinases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:2606-2613, 1996.
Waldman, S. D., C. G. Spiteri, M. D. Grynpas, R. M. Pilliar, J. Hong, and R. A. Kandel. Effect of biomechanical conditioning on cartilaginous tissue formation in vitro. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 85:101-105, 2003.
Wang, N., J. P. Butler, and D. E. Ingber. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science 260:1124-1127, 1993.
Wright, M. O., J. L. Godolphin, E. Dunne, C. Bavington, P. Jobanputra, G. Nuki, and D. M. Salter. Hyperpolarisation of cultured human chondrocytes following cyclical pressurisation involves α5β1 integrin and integrin-associated intracellular pathways. J. Orthop. Res. 15:742-747, 1997.
Wright, M. O., P. Jobanputra, C. Bavington, D. M. Salter, and G. Nuki. The effects of intermittent pressurisation on the electrophysiology of cultured human articular chondrocytes: Evidence for the presence of stretch-activated membrane ion channels. Clin. Sci. 90:61-71, 1996.
Wright, M. O., R. Stockwell, and G. Nuki. Response of plasma membrane to applied hydrostatic pressure in chondrocytes and fibroblasts. Connect. Tissue Res. 28:49-70, 1992.
Wu, Q. Q., and Q. Chen. Mechanoregulation of chondrocyte proliferation, maturation, and hypertrophy: Ion-channel dependent transduction of matrix deformation signals. Exp. Cell Res. 156:383-391, 2000
Yonezawa, Y., K. Kato, H. Yagita, Y. Yamauchi, and K. Okumura. VLA-5-mediated interaction with fibronectin induces cytokine production by human chondrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 219:261-265, 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Millward-Sadler, S.J., Salter, D.M. Integrin-Dependent Signal Cascades in Chondrocyte Mechanotransduction. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 32, 435–446 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ABME.0000017538.72511.48
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ABME.0000017538.72511.48