Abstract
Purpose. To develop an in vitro assay for studying the feasibility of specific targeting of ultrasound contrast agents (USCAs) for ultrasound diagnostics by employing the parallel plate flow chamber, which provides an environment that mimics some aspects of the in vivo conditions like shear rate and flow effects.
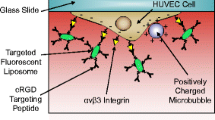
Methods. USCAs based on air-filled microparticles (MP) were functionalized with specific antibodies using carbodiimide coupling chemistry and characterized by fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS). The binding experiments were done by subjecting the MP to shear stress as they interact with the target-coated surface of the flow chamber.
Results. A successive modification of MP with antibody and the glass surface with antigen was achieved and quantified. The binding studies showed specific attachment of targeted MP to EDB-FN (EDB domain of fibronectin) surface. The binding of MP via nonspecific interactions was minimal. The binding efficiency of antibody-loaded MP is dependent on the applied shear stress. An increase in the wall shear stress resulted in a decrease in binding efficiency. Binding efficiency was found to be correlated with the antibody density and antigen density on the interacting surfaces.
Conclusions. The results indicate that the test system developed is reliable for characterizing targeted MP without any additional labeling and can be used as a functionality assay for studying the binding characteristic of USCA with respect to different parameters like density of targeting antibodies on the microparticle surface and of target protein. In addition, the microparticles can be studied in detail under different shear rates and flow conditions. Further studies concerning the in vitro-in vivo correlation will be necessary to further increase the value of this in vitro method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. L. Klibanov, M. S. Hughes, F. S. Villanueva, R. J. Jankowski, W. R. Wagner, J. K. Wojdyla, J. H. Wible, and G. H. Brandenburger. Targeting and ultrasound imaging of microbubble-based contrast agents, magnetic resonance materials in physics. Biol. Med. 8:177-184 (1999).
H. Leong-Poi, A. L. Klibanov, J. P. Christiansen, Y. Huo, and J. R. Lindner. Development of an angiogenesis-targeted microbubble ultrasound contrast agent. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 39: 360-364 (2002).
R. J. Lindner. Detection of inflamed plaques with contrast ultrasound. Am. J. Cardiol. 90:L32-L35 (2002).
M. Rudin and R. Weissleder. Molecular imaging in drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2:123-131 (2003).
S. Melkko, C. Halin, L. Borsi, L. Zardi, and D. Neri. An antibody-calmodulin fusion protein reveals a functional dependence between macromolecular isoelectric point and tumor targeting performance. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 54:1485-1490 (2002).
L. Zardi, B. Carnemolla, A. Siri, T. E. Petersen, G. Paolella, G. Sebastio, and F. E. Baralle. Transformed human cells produce a new fibronectin isoform by preferential alternative splicing of a previously unobserved exon. EMBO J. 6:2337-2342 (1987).
G. Theilmeier, T. Lenaerts, C. Remacle, D. Collen, J. Vermylen, and M. Hoylaerts. Circulating activated platelets assist THP-1 monocytoid/endothelial cell interaction under shear stress. Blood 94:2725-2734 (1999).
Z. J. Li, N. Mohamed, and J. M. Ross. Shear stress affects the kinetics of Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to collagen. Biotechnol. Prog. 16:1086-1090 (2000).
S. K. Bhatia and D. A. Hammer. Influence of receptor and ligand density on the shear threshold effect for carbohydrate-coated particles on L-selectin. Langmuir 18:5881-5885 (2002).
L. Klibanov. Targeted delivery of gas-filled microspheres contrast agents for ultrasound imaging. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 37:139-157 (1999).
G. E. R. Weller, E. Lu, M. M. Csikari, A. L. Klibanov, D. Fischer, W. R. Wagner, and F. S. Villanueva. Ultrasound imaging of acute cardiac transplant rejection with microbubbles targeted to intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Circulation 108:218-224 (2003).
D. A. Jones, C. W. Smith, and L. V. McIntire. Flow effects on leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelium. In P. Richardson and M. Steiner (eds.), Principles of Cell Adhesion, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1995, pp. 143-160.
G. Thoma, W. Kinzy, L. Bruns, J. T. Patton, J. L. Magnani, and R. Banteli. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a potent E-Selectin antagonist. Med. Chem. 42:4909-4913 (1999).
U. Bakowsky, G. Schumacher, C. Gege, R. R. Schmid, U. Rothe, and G. Bendas. Cooperation between lateral ligand mobility and accessibility for receptor recognition in selectin-induced cell rolling. Biochemistry 41:4704-4712 (2002).
L. D. McIntire and S. G. Eskin. Mechanical and biochemical aspects of leucocyte interactions with model vessel wall. In H. J. Meiselman, M. A. Lichtman, and P. L. La Celle (eds.), White Cell Mechanics: Basic Science and Clinical Aspects, Wiley Publishers, New York, 1984, pp. 209.
U. Budde, A. Briel, G. Roessling, K. Lovis, W. Schmidt, M. Gottfried, and J. P. Ingwersen. Multi-stage method for producing gas-filled microcapsules, EP1180043, 2002.
J. Piehler, A. Brecht, R. Valiokas, B. Liedberg, and G. Gauglitz. A high-density Poly (ethylene glycol) polymer brush for immobilization of glass-type surfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 15:473-481 (2000).
M. B. Lawrence and T. A. Springer. Neutrophils roll on E-selectin. J. Immunol. 151:6338-6346 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, S., Olbrich, C., Kirsch, J. et al. A Real-Time in Vitro Assay for Studying Functional Characteristics of Target-Specific Ultrasound Contrast Agents. Pharm Res 21, 920–926 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000029278.27038.5b
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000029278.27038.5b