Abstract
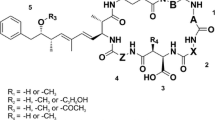
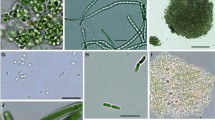
To learn more whether toxin formation by cyanobacteria is controlled by quorum sensing, the concentrations of microcystins and of homoserine lactones have been followed during a summer period in the deep mesotrophic Lake Zürich and in the shallow eutrophic Lake Muzzano. Specific cyanobacterial populations are present in both lakes, Planktothrix rubescens dominates in Lake Zürich, Microcystis wesenbergii in Lake Muzzano. Both organisms produced microcystins, and homoserine-lactones were detected as well in most of the samples. However, no clear relation between the concentrations of the two compounds was observed with sampling intervals of 2 weeks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachofen, R. & A. Schenk, 1998. Quorum sensing autoinducers: Do they play a role in natural microbial habitats?. Microbiol. Res. 153: 61–63.
Beattie, K. A. & G. A. Codd, 1995. Action of ultraviolet irradiation on microcystin-LR. In: Kaas, H. (ed.), 1st Int. Congr. Toxic Cyanobacteria. Rönne, Denmark, p. 5.
Bell, S. G. & G. A. Codd, 1994. Cyanobacterial toxins and human health. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 5: 256–264.
Berg, K., W. W. Carmichael, O. M. Skulberg, C. Benestad & B. Underdal, 1987. Investigation of a toxic water-bloom of Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanophyceae) in lake Akersvatn, Norway. Hydrobiologia 144: 97–103.
Blom, J. F., J. A. Robinson & F. Jüttner, 2001. High grazer toxicity of [D-Asp3, (E)-Dhb7]microcystin-RR of Planktotrix rubescens as compared to different microcystins. Toxicon 39: 1923–1932.
Carmichael, W. W., 1992. Cyanobacteria secondary metabolites-the cyanotoxins. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 72: 445–459.
Carmichael, W. W., 1996. Toxic Microcystis and the environment. In Watanabe, M.F., K. I. Harada, W. W. Carmichael & H. Fujiki (eds), Toxic Microcystis. CRC Press, Boca Raton, N.Y.: 1–11.
Christoffersen, K., S. Lyck & A. Winding, 2002. Microbial activity and bacterial community structure during degradation of microcystins. Aquat. Microbial. Ecol. 27: 125–136.
Dittmann, E., M. Erhard, M. Kaebernick, Ch. Scheler. B. A. Neilan. H. von Döhren & T. Borner, 2001. Altered expression of two light-dependent genes in a microcystin-lacking mutant of Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806. Microbiology-SGM 147: 3113–3119.
Dong, Y. H., J. L. Xu, X. Z. Li & L. H. Zhang, 2000. AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorumsensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proc. Natn. Acad. Sci. 97: 3526–3531.
Dong, Y. H., L. H. Wang, J. L. Xu, H. B. Zhang, X. F. Zhang & L. H. Zhang, 2001. Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserine lactonase. Nature 411: 813–817.
Fastner, J., M. Erhard, W.W. Carmichael, F. Sun, K. L. Rinehart, H. Rönicke & I. Chorus, 1999. Characterization and diversity of microcystins in natural blooms and strains of the genera Microcystis and Planktothrix from German freshwaters. Arch. Hydrobiol. 145: 147–163.
Harada K. I., K. Tsuji, M. F. Watanabe & F. Kondo, 1996. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria: III. Effect of pH and temperature. Phycologia. 35: 83–88.
Isenburg, C., M. Bottinelli, M. Tonolla & R. Peduzzi, 2000. Aspetti limnologici e microbiologici des laghetto di Muzzano (Ti). Bollettino Societa Scienze naturali 88: 41–51.
Jones, G. J. & P. T. Orr, 1994. Release and degradation of microcystin following algicide treatment of a Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in a recreational lake, as determined by HPLC and protein phosphatase inhibition assay. Wat. Res. 28: 871–876.
Kaebernick, M., B. A. Neilan, T. Börner & E. Dittmann, 2000. Light and the transcriptional response of the Microcystin biosynthesis gene cluster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 3387–3392.
Kiviranta, J., K. Sivonen, K. Lahti, R. Luukkainen & S. I. Niemela, 1991. Production and biodegradation of cyanobacterial toxins-a laboratory study. Arch. Hydrobiol. 121: 281–294.
Kotak, B. G, A. K. Lam, E. E. Prepas & S. E. Hrudey, 2000. Role of chemical and physical variables in regulating microcystin-LR concentration in phytoplankton of eutrophic lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 57: 1584–1593.
Lahti, K., J. Rapala, M. Färdig, M. Niemelä, & K. Sivonen, 1997. Persistence of cyanobacterial hepatotoxin, microcystin-LR in particulate material and dissolved in lake water. Wat. Res. 31: 1005–1012.
Lam, A. K. Y., E. E. Prepas, D. Spinach, & S. E. Hrudey, 1995. Chemical control of hepatotoxic phytoplankton blooms: implications for human health. Water Res. 29: 1845–1854.
Lawton, L. A., C. Edwards & G. A. Codd, 1994. Extraction and high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of microcystins in raw and treated waters. Analyst 119: 1525–1530.
Leadbetter, J. R. & E. P. Greenberg, 2000. Metabolism of acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals by Variovorax paradoxus. J. Bacteriol. 182: 6921–6926.
Long, B. M., G. J. Jones & P. T. Orr, 2001. Cellular microcystin content in N-limited Microcystis aeruginosa can be predicted from growth rate. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 67: 278–283.
McClean, K. H., M. K. Winson, L. Fish, A. Taylor, S. R. Chhabra, M. Camara, M. Daykin, J. H. Lamb, S. Swift, B. W. Bycroft, G. S. A. Stewart, & P. Williams, 1997. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acyl homoserine-lactones. Microbiology-SGM 143: 3703–3711.
McLean, R. L. C., M. Whiteley, D. J. Stickler & W. C. Fuqua, 1997. Evidence of autoinducer activity in naturally occurring biofilms. FEMS Microbiol. Letters 154: 259–263.
Micheletti, S., F. Schanz & A. E. Walsby, 1998. The daily integral of photosynthesis by Planktothrix rubescens during summer stratification and autumnal mixing in Lake Zürich. New Phytol. 139: 233–246.
Miller, M. B. & B. L. Bassler, 2001. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55: 165–199.
Oh, H. M., S. J. Lee, M. H. Jang & B. D. Yoon, 2000. Microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa in a phosphorus-limited chemostat. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 66: 176–179.
Orr, P. T. & G. J. Jones, 1998. Relationship between microcystin production and cell division rates in nitrogen-limited Microcystis aeruginosa cultures. Limnol. & Oceanogr. 43: 1604–1614.
Ostensvik, O., O. M. Skulberg, B. Underdal & V. Hormazabal, 1998. Antibacterial properties of extracts from selected planktonic freshwater cyanobacteria-a comparative study of bacterial bioassays. J. Appl. Microbiol. 84: 1117–1124.
Park, H. D., M. F. Watanabe, K. I. Harada, H. Nagai, M. Suzuki, M. Watanabe & H. Hayashi, 1993. Hepatotoxin (microcystin) and neurotoxin (anatoxin-a) contained in natural blooms and strains of cyanobacteria from Japanese freshwaters. Natural Toxins 1: 353–360.
Paerl, H. W. & D. F. Millie, 1996. Physiological ecology of toxic aquatic cyanobacteria. Phycologia 35: 160–167.
Prepas, E. E. & F. H. Rigler, 1982. Improvements in quantifying the phosphorus concentration in lakes water. Can. J. Aquat. Sci. 39: 822–829.
Schanz, F., 1985. Vertical light attenuation and phytoplankton development in Lake Zürich. Limnol. & Oceanogr. 30: 299–310.
Swift, S., J. A. Downie, N.A. Whitehead, A. M. L. Barnard, G. P. C. Salmond & P. Williams, 2001. Quorum sensing as a population-density-dependent determinant of bacterial physiology. Adv. Microbial Physiol. 45: 199–270.
Tsuji, K., S. Nalto, F. Kondo, N. Ishiwaka, M. F. Watanabe, M. Suzuki & K. I. Harada, 1994. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria I: Effect of light on decomposition and isomerization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 28: 173–177.
Tsuji, K., T. Watanuki, F. Kondo, N. Ishiwaka, M. F. Watanabe, S. Suzuki, H. Nakazawa, M. Suzuki, & K. I. Harada, 1995. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria II: Effect of UV light on decomposition and isomerization. Toxicon 33: 1619–1631.
Utkilen, H. & N. Gjølme, 1992. Toxin production by Microcystis aeruginosa as a function of light in continuous cultures and its ecological significance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 1321–1325.
Vezie, C., L. Brient, K. Sivonen, G. Bertru. J. C. Lefeuvre & M. Salkinoja-Salonen, 1997. Occurrence of microcystin-containing cyanobacterial blooms in freshwaters of Brittany. Arch. Hydrobiol. 139: 401–413.
Vining, L. C., 1990. Functions of secondary metabolites. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 44: 395–427.
Watanabe, M. F., K. I. Harada, K. Matsuura, M. Watanabe, & M. Suzuki, 1989. Heptapeptide toxin production during the batch culture of two Microcystis species (Cyanobacteria). J. Appl. Phycol. 1: 161–165.
Wiedner, C., P. M. Visser, J. Fastner, J. S. Metcalf, G. A. Codd & L. R. Mur, 2003. Effects of light on the microcystin content of Microcystis Strain PCC 7806. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 69: 1475–1481.
Whitehead, N. A., A. M. L. Barnard, H. Slater, N. J. L. Simpson & G. P. C. Salmond. 2001. Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Revs. 25: 365–404.
Williams, P., T. J. Baldwin, & J. A. Downie. 1999. Bacterial crosstalk-communication between bacteria, plant, and animal cell. In England, R., G. Hobbs, N. Baiton & D. Mcl Roberts (eds), Microbial Signaling and Communication. Society for General Microbiology Symp. 57: 1–32.
Winson, M. K., S. Swift, L. Fish, J. P. Throup, F. Jørgensen, S. R. Chhabra, B. W. Bycroft, P. Williams & G. S. A. B. Stewart, 1998. Construction and analysis of lux CDABE-based plasmids sensors for investigating N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 163: 185–192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braun, E., Bachofen, R. Homoserine-lactones and microcystin in cyanobacterial assemblages in Swiss lakes. Hydrobiologia 522, 271–280 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000029968.70297.c3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000029968.70297.c3