Abstract
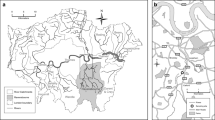
The objective of this study is to compare Anyang River bed sediments with water chemical composition and to assess the anthropogenic chemical inputs into the river system. Eight sampling locations were chosen along the river channel. Bed and suspended river sediments and water samples were collected, and analyzed for their chemical and physical composition. Data revealed that trace element concentrations in the river water were generally below world average, except for As, Mn, Ni and Cr. Among the three phases: water, bed and suspended sediment, more than 99% of the trace elements was associated with the bed sediment. Concentrations of trace elements in the sediment were a function a particle size distribution and organic content. The calculated degrees of enrichment based on the least influenced sample (ASD 1) indicated the river sediments were enriched with respect to background. The enrichment factors for Pb, Zn and As were relatively lower than for Cr, Co, Ni and Zn. The difference in the enrichment seems to reflect the human activities influence in the basin, and specially for Cd. Speciation of the elements in the five different chemical forms in the sediment by sequential extraction indicated that the reducible fraction was predominant for Fe, Zinc and Cu showed an irregular variation among the different fractions; whereas, Cd and Pb were more regular. Zinc and Cu highly existed mostly in exchangeable forms. Acid soluble and reducible forms were also important for most metals. The speciation implies that the metals associated with the sediment are subject to release into water bodies as goechemical variables (pH and Eh) change. Currently, the introduced metals are deposited near the source area and are mostly associated with the sediment, implying that the river bed sediment acts mainly as a sink, rather than a pool. The accumulated and enriched toxic trace elements can pose a potential pollution of river water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, J.D., Brown, D.S. and Novo-Grdac, K.J.: 1991, Minteqa2/Proefa2, A Geochemical Assessment Model for Environmental Systems: Version 3.0 User's Manual, USEPA Washington, DC.
Barbanti, A. and Bothner, M.H.: 1993, A procedure for partitioning bulk sediments into distinct grain-size fractions for geochemical analysis, Environmental Geology 21, 3-31.
Bilos, C., Colombo, J.C. and Rodriguez Presa, M.J.: 1998, Trace metals in suspended particles, sediments and Asiatic clams (Corbicula fluminea) of the Rio de la Plata Estuary, Argentina, Environmental Pollution 99, 1-11.
Chung, F.H.: 1974, Quantitative interpretation of X-ray diffraction patterns of mixtures. II. Adiabatic principle of X-ray diffraction analysis of mixture, Journal of Applied Crystallography 7, 526-531.
Dekov, V.M., Komy, Z., Araujo, F., van Put, A. and van Grieken, R.: 1997, Chemical composition of sediments, suspended matter, river water and groundwater of the Nile (Aswan-Sohag traverse), The Science of the Total Environment 20, 195-210.
Deutsch, W.J.: 1997, Water/rock interactions, in: Groundwater Geochemistry-Fundamentls and Application to Contamination, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp. 47-75.
Facetti, J., Dekov, V.M. and van Grieken, R.: 1998, Heavy metals in sediments from the paraguay River: a preliminary study, The Science of the Total Environment 209, 79-86.
Fetter, C.W.: 1993, Contaminant Hydrogeology, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliff, NJ, 458 pp.
Forstner, U. and Wittmann, G.T.W.: 1983, Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment, 2nd edn, Springer, Berlin, 486 pp.
Hem, J.D.: 1992, Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. U.S. Geol. Surv. Water-Supply Paper 2252.
Hounslow, A.W.: 1995, Water quality interpretation, in: Water Quality data-Analysis and Interpretation, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 71-128.
Martin, J.M. and Meyback, M.: 1979, Elemental mass-balance of material carried by major world rivers, Marine Chemistry 7, 173-206.
Ministry of Environment: 2000, Environmental White Book, Ministry of Environment, Seoul, 686 pp.
Ministry of Transport, Public Works and Water Management: 2000, Annexes, Circular on Target Values and Intervention Values for Soil Remediation, Netherlands, 51 pp.
Moon, J.-W., Moon, H.-S., Woo, N.-C., Hahn, J.-S., Won, J.-S., Song, Y., Lin, X. and Zhao, Y.: 2000, Evaluation of heavy metal contamination and implication of multiple sources from Hunchun Basin, northeastern China, Environmental Geology 39, 1039-1052.
Moore, D.M. and Reynolds Jr., R.C.: 1997, X-ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals, 2nd edn, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 378 pp.
Parkhurst, D.L.: 1995, User's Guide to Phreeqc-A Computer program for Speciation, Reaction-Path, Advective-Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations. U.S. Geological Survey, 143 pp.
Soares, H.M.V.M., Boaventura, R.A.R., Machado, A.A.S.C. and Esteves da Silva, J.C.G.: 1999, Sediments as monitors of heavy metal contamination in the Ave river basin (Portuga): multivariate analysis of data, Environmental Pollution 105, 311-323.
Song, Y., Wilson, M.J., Moon, H.-S., Bacon, J.R. and Bain, D.C.: 1999, Chemical and mineralogical forms of lead, zinc and cadmium in particle size fractions of some wastes, sediments and soils in Korea, Applied Geochemistry 14, 621-633.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P.G.C. and Bisson, M.: 1979, Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals, Analytical Chemistry 51, 844-851.
Zhang, J.: 1995, Geochemistry of trace metals from Chinese river/estuary systems: an overview, Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 41, 631-658.
Zoumins, T., Schmidt, A., Grigorova, L. and Calmano, W.: 2001, Contaminant in sediments: remobilization and demobilization, The Science of the Total Environment 266, 195-202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Moon, JW. & Moon, HS. Heavy Metals in the Bed and Suspended Sediments of Anyang River, Korea: Implications for Water Quality. Environmental Geochemistry and Health 25, 433–452 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EGAH.0000004567.80084.d1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EGAH.0000004567.80084.d1