Abstract
1. Spatio-temporal changes in phosphorylated (pNFP) and nonphosphorylated (npNFP) neurofilament proteins were assessed immunocytochemicaly in adult rat cerebe- llum, 2–30 days following unilateral injection of kainic acid (KA) or physiological saline (SC).
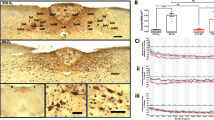
2. Analysis of the staining intensity and pattern demonstrated that injection of both KA and physiological saline elicited significant and long-lasting increase of pNFP and npNFP immunoreactivity, at the ipsilateral, and to lesser extent at the contralateral side of lesion.
3. Kainate intoxication induced abundant expression of pNFP and npNFP in cerebellar white matter, as well as in all layers of perilesioned cortex. Higher pNFP expression was evidenced in the Purkinje cell layer, particularly at cell bodies, initial segments, and proximal dendrites, which normally do not contain pNFP. In addition, synaptophysin immunocytochemistry was used as a marker of synaptogenesis and plasticity.
4. Spatio-temporal pattern of NFP and synaptophysin expression suggests that perilesioned cortex undergoes dynamic changes following brain demage and possess a reparative capacity to abridge the consequences of brain trauma.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Angaut, P., Alvarado-Mallart, R. M., and Sotelo, C. (1982). Ultrastructural evidence for compensatory sprouting of climbing and mossy afferents to the cerebellar hemisphere after ipsilateral pedunculotomy in the newborn rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 205:101-111.
Azizi, S. A., and Woodward, D. J. (1987). Inferior olivary nuclear complex of the rat: Morphology and comments on the principle of organization within the olivocerebellar system. J. Comp. Neurol. 263:467-484.
Bidmon, H. J., Jancsik, V., Schleicher, A., Hagemann, G., Witte, O. W., Woodhams, P., and Zilles, K. (1997). Structural alterations and changes in cytoskeletal proteins and proteoglycans after focal cortical ischemia. Neuroscience 82:397-420.
Black, M. M., and Lee, V. M. Y. (1988). Phosphorylation of neurofilament proteins in intact neurons: Demonstration of phosphorylation in cell bodies and axons. J. Neurosci. 8:3296-3305.
Chen, S., and Hillman, E. D. (1982). Plasticity of the parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapse takeover and new synapse formation in the adult rat. Brain Res. 240:205-220.
Chen, S., Pickard, J. D., and Harris, N. G. (2003). Time course of cellular pathology after control cortical impact injury. Exp. Neurol. 182:87-102.
Deller, T., Haas, C. A., and Frotscher, M. (2000). Reorganization of the rat fascia dentate after unilateral entorhinal cortex lesion. Role of the extracellular matrix. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 911:207-220.
De Waegh, S. M., Lee, V. M. Y., and Brady, S. T. (1992). Local modulation of neurofilament phosphorylation, axonal calibre and slow axonal transport by myelinating Schwann cells. Cell 68:451-463.
Elhanany, E., Jaffe, H., Link, W. T., Shelly, D. M., Gainer, H., and Pant, H. C. (1994). Identification of endogenously phosphorylated KSP sites in the high molecular weight rat neurofilament protein. J. Neurochem. 63:2324-2335.
Foster, A. C., and Roberts, J. P. (1980). Morphological and biochemical changes in the cerebellum induced kainic acid in vivo. J. Neurochem. 34:1191-1200.
Grant, P., Sharma, P., and Pant, H. C. (2001). Cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (Cdk5) and the regulation of neurofilament metabolism. Eur. J. Biochem. 268:1534-1546.
Hayes, R. L., Yang, K., Whitson, J. S., and Postmantur, R. (1995). Cytoskeletal derangements following central nervous system injury: Modulation by neurotrophic gene transfection. J. Neurotrauma 12:933-941.
Hicks, R. R., Smith, H. D., and McIntosh, K. T. (1995). Temporal response and effects of excitatory amino acid antagonism on MAP2 protein immunoreactivity following experimental brain injury in rats. Brain Res. 678:151-160.
Hugon, J., and Vallat, J. M. (1990). Abnormal distribution of phosphorylated neurofilaments in neuronal degeneration induced by kainic acid. Neurosci. Lett. 119:45-48.
Krapfenbauer, K., Berger, M., Lubec, G., and Fountoulakis, M. (2001). Changes in the brain protein levels following administration of kainic acid. Electrophoresis 22:2086-2091.
Laskawi, R., and Wolff, J. R. (1996). Changes in the phosphorylation of neurofilament proteins in facial motoneurons following various types of nerve lesion. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 58:13-22.
Lees, J. F., Shneidman, P. S., Skuntz, S. F., Carden, M. J., and Lazzarini, R. A. (1988). The gene structure of the largest human neurofilament subunit (NF-H) predicts a protein with multiple repeated sites for in vivo phosphorylation. EMBO J. 7:1947-1955.
Leterrier, J. F., Hartwig, J., Kas, J., Vegners, R., and Janmey, P. A. (1996). Mechanical effects of neurofilament cross bridges: Modulation by phosphorylation, lipids and interactions with F-actin. J. Biol. Chem. 271:15687-15694.
Li, B.-S., Daniels, M. P., and Pant, H. C. (2001). Integrins stimulate phosphorylation of neurofilament NF-M subunit KSP repeats through activation of extracellular regulated-kinases (Erk1/Erk2) in cultured motoneurons and transfected NIH 3T3 cells. J. Neurochem. 76:703-710.
Li, B.-S., Veeranna, G. J., Grant, P., and Pant, H. C. (1999). Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (Erk1 and erk2) cascade results in phosphorylation of NF-M tail domains in transfected NIH 3T3 cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 262:211-217.
Liu, M. H., Lei, D. L., and Yang, L. D. (1996). Kainate-induced brain lesion: Similar local and remote histopathologic and molecular changes as in ischemic brain infarct. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 55:787-797.
Nakagawa, T., Chen, J., Zhang, Z., Kanai, Y., and Hirokawa, N. (1995). Two distinct functions of the carboxyl-terminal tail domain of NF-M upon neurofilament assembly: Cross-bridge formation and longitudinal elongation of filaments. J. Cell Biol. 129:387-395.
O'Ferrall, E. K., Robertson, J., and Mushynski, W. E. (2000). Inhibition of aberrant and constitutive phosphorylation of the high-molecular-mass neurofilament subunit by CEP-1347 (KT7515), an inhibitor of the stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J. Neurochem. 75:2358-2367.
Paxinos, G., and Watson, C. (1983). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Academic Press, New York.
Petzold, A., Baker, D., Pryce, G., Kier, G., Thompson, E. J., and Giovannoni, G. (2003). Quantification of neurodegeneration by measurement of brain-specific proteins. J. Neuroimmun. 138:45-48.
Pollanen, M. S., Bergeron, C., and Weyer, L. (1994). Characterisation of a shared epitope in cortical Lewy body fibrils and Alzheimer paired helical filaments. Acta Neuropathol. 88:1-6.
Popa-Wagner, A., Schroeder, E., Schmoll, H., Walker, L. C., and Kessler, C. (1999). Upregulation of MAP1B and MAP2 in the rat brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion: Effect of age. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 19:425-434.
Roberts-Lewis, J. M., Savage, M. J., Marcy, V. R., Pinsker, L. R., and Siman, R. (1994). Immunolocalisation of calpain I-mediated spectrin degradation to vulnerable neurons in the ischemic gerbil brain. J. Neurosci. 14:3934-3944.
Rossi, F., Borsello, T., and Strata, P. (1993b). Exposure to kainic acid mimics the effects of axotomy in cerebellar Purkinje cells of the adult rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 6:392-402.
Rossi, F., Borsello, T., Vaudano, E., and Strata, P. (1993a). Regressive modifications of climbing fibers following Purkinje cell degeneration in the cerebellar cortex of the adult rat. Neuroscience 53:759-778.
Rossi, F., JankovskI, A., and Sotelo, C. (1995). Differential regenerative capacity in two systems of injured adult cerebellar axons confronted to embryonic grafts. J. Comp. Neurol. 359:663-677.
Rossi, F., and Strata, P. (1995). Reciprocal trophic interactions in the adult climbing fiber-Purkinje cell system. Prog. Neurobiol. 47:341-369.
Schgroeder, E., Vogelgesang, S., Popa-Wagner, A., and Kessler, C. (2003). Neurofilament expression in the rat brain after cerebral infarctation: Effect of age. Neurobiol. Aging 24:135-145.
Shetty, K. A., and Turner, A. D. (1995). Intracerebroventricular kainic acid administration in adult rat alters hippocampal calbindin and non-phosphorylated neurofilament expression. J. Comp. Neurol. 363:581-599.
Shinozaki, H. (1994). Neuron damage induced by some potent kainoids and neuroprotective action of new agonist for metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur. Neurol. 34:2-9.
Sternberger, L. A., and Sterneberger, N. H. (1983). Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms of neurofilaments in situ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80:6126-6130.
Stone, J. D., Peterson, A. P., Eyer, J., Oblak, G., and Sickles, D. W. (2001). Neurofilaments are nonessential to the pathogenesis of toxicant-induced axonal degeneration. J. Neurosci. 21:2278-2287.
Terro, F., Lesort, M., Dussartre, C., Barthe, D., and Hugon, J. (1996). Phosphorylated neurofilament expression and resistance to kainate toxicity. Brain Res. Bull. 41:231-235.
Trojanowski, J. Q., Obrocka, M. A., and Lee, V. M.-Y. (1985). Distribution of neurofilament subunits in neurons and neuronal processes. Immunocytochemical studies of bovine cerebellum with subunit specific monoclonal antibodies. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 33:557-563.
Vartiainen, N., Tikka, T., Keinanen, R., Chan, P. H., and Koistinaho, J. (1999). Glutamatergic receptors regulate expression, phosphorylation and accumulation of neurofilaments in spinal cord neurons. Neuroscience 93:1123-1133.
Vickers, J. C., and Costa, M. (1992). The neurofilament triplets are present in distinct subpopulations of neurons in the central nervous system of the guinea-pig. Neuroscience 49:73-100.
Wang, S., Hamberger, A., Ding, M., and Haglid, K. G. (1992). In vivo activation of kainate receptors induces dephosphorylation of the heavy neurofilament subunit. J. Neurochem. 59:1975-1978.
Wang, S., Hamberger, A., Yang, Q., and Haglid, K. G. (1994). Changes in neurofilament protein NF-L and NF-H immunoreactivity following kainic acid-induced seizures. J. Neurochem. 62:739-748.
Xu, S., Cork, L. C., Griffin, J. W., and Cleveland, D. W. (1993). Increased expression of neurofilaments subunit NF-L produces morphological alterations that resembles the pathology of human motor neuron disease. Cell 73:23-33.
Yang, Q., Wang, S., Hamberger, A., and Haglid, K. S. (1996). Plasticity of granule cell-mossy fiber system following kainic acid induced seizures: An immunocytochemical study on neurofilament proteins. Neurosci. Res. 26:57-64.
Zhang, H., Sternberger, N. H., Rabinstein, L. J., Herman, M. H., Binder, L. I., and Sternberger, L. A. (1989). Abnormal processing of multiple proteins in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86:8045-8049.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milenkovic, I., Filipovic, R., Nedeljkovic, N. et al. Spatio-Temporal Changes in Neurofilament Proteins Immunoreactivity Following Kainate-Induced Cerebellar Lesion in Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 24, 367–378 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CEMN.0000022769.44211.2b
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CEMN.0000022769.44211.2b