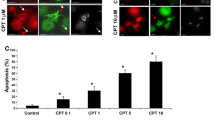
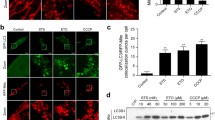
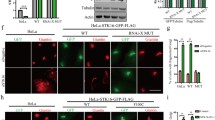
Abstract
Changes in cell shape can lead to detachment and cell death, and the disruption in the actin cytoskeletal network, as one marker of cell shape changes, can itself induce apoptosis. In this study, the effects of cytochalasin B on the apoptosis-related proteins, protein kinase B and survivin were investigated. Apoptosis induced by disruption of microfilaments with cytochalasin B was found, although it happened at a low level, to simultaneously occur with G2/M arrest in 50% of the cytochalasin B-treated cells. During apoptosis, PKB phosphorylation and survivin expression was decreased by cytochalasin B, and the decline in survivin expression were preceded by PKB dephosphorylation, which implicated that survivin may be a target of PKB protein. The G2/M arrest of cytochalasin B-treated cells may be the direct function of cytochalasin B to microfilaments or the subsequent inhibition of survivin expression, or both. These results suggest that PKB/survivin signaling pathway may be responsible for the apoptosis induced by the disruption of actin cytoskeleton.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frisch SM, Screaton RA: Anoikis mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13: 555-562, 2001
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM, Kaufmann SH: Mammalian caspases: Structure, activation, substrates, and functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem 68: 383-424, 1999
Shi Y: Mechanisms of caspase activation and inhibition during apoptosis. Mol Cell 9: 459-470, 2002
Alessi DR, Cohen P: Mechanism of activation and function of protein kinase B. Curr Opin Genet Dev 8: 55-62, 1998
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG: The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal 14: 381-395, 2002
Andjelkovic M, Alessi DR, Meier R, Fernandez A, Lamb NJ, Frech M, Cron P, Cohen P, Lucocq JM, Hemmings BA: Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. J Biol Chem 272: 31515-31524, 1997
Hemmings BA: PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 gets its message across. Science 277: 534, 1997
Datta K, Franke TF, Chan TO, Makris A, Yang SI, Kaplan DR, Morrison DK, Golemis EA, Tsichlis PN: AH/PH domain-mediated interaction between Akt molecules and its potential role in Akt regulation. Mol Cell Biol 15: 2304-2310, 1995
Dufner A, Andjelkovic M, Burgering BM, Hemmings BA, Thomas G: Protein kinase B localization and activation differentially affect S6 kinase 1 activity and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 9: 4525-4534, 1999
Filippa N, Sable CL, Hemmings BA, Van Obberghen E: Effect of phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 on protein kinase B translocation and its subsequent activation. Mol Cell Biol 20: 5712-5721, 2000
Borgatti P, Martelli AM, Bellacosa A, Casto R, Massari L, Capitani S, Neri LM: Translocation of Akt/PKB to the nucleus of osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells exposed to proliferative growth factors. FEBS Lett 477: 27-32, 2000
Brazil DP, Hemmings BA: Ten years of protein kinase B signalling: A hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem Sci 26: 657-664, 2001
Reed JC: The survivin saga goes in vivo. J Clin Invest 108: 965-969, 2001
Suzuki A, Ito T, Kawano H, Hayashida M, Hayasaki Y, Tsutomi Y, Akahane K, Nakano T, Miura M, Shiraki K: Survivin initiates procaspase 3/p21 complex formation as a result of interaction with Cdk4 to resist Fas-mediated cell death. Oncogene 19: 1346-1353, 2000
Altieri DC, Marchisio PC, Marchisio C: Survivin apoptosis: An interloper between cell death and cell proliferation in cancer. Lab Invest 79: 1327-1333, 1999
Reed JC, Bischoff JR: BIRinging chromosomes through cell division — and survivin' the experience. Cell 102:545-548, 2000
Fortugno P, Wall NR, Giodini A, O'Connor DS, Plescia J, Padgett KM, Tognin S, Marchisio PC, Altieri DC: Survivin exists in immunochemically distinct subcellular pools and is involved in spindle microtubule function. J Cell Sci 115: 575-585, 2002
Li F, Ackermann EJ, Bennett CF, Rothermel AL, Plescia J, Tognin S, Villa A, Marchisio PC, Altieri DC: Pleiotropic cell-division defects and apoptosis induced by interference with survivin function. Nat Cell Biol 1: 461-466, 1999
Antoccia A, Tanzarella C, Modesti D, Degrassi F: Cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay with kinetochore detection in colchicine-treated human fibroblasts. Mutat Res 287: 93-99, 1993
Kulms D, Dussmann H, Poppelmann B, Stander S, Schwarz A, Schwarz T: Apoptosis induced by disruption of the actin cytoskeleton is mediated via activation of CD95 (Fas/APO-1). Cell Death Differ 9: 598-608, 2002
Cimini D, Fioravanti D, Tanzarella C, Degrassi F: Simultaneous inhibition of contractile ring and central spindle formation in mammalian cells treated with cytochalasin B. Chromosoma 107: 479-485, 1998
Hermanto U, Zong CS, Li W, Wang LH: RACK1, an insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptor-interacting protein, modulates IGF-I-dependent integrin signaling and promotes cell spreading and contact with extracellular matrix. Mol Cell Biol 22: 2345-2365, 2002
Kim KY, Rhim T, Choi I, Kim SS: N-acetylcysteine induces cell cycle arrest in hepatic stellate cells through its reducing activity. J Biol Chem 276: 40591-40598, 2001
Wang E: Senescent human fibroblasts resist programmed cell death, and failure to suppress bcl2 is involved. Cancer Res 55: 2284-2292, 1995
Flusberg DA, Numaguchi Y, Ingber DE: Cooperative control of Akt phosphorylation, bcl-2 expression, and apoptosis by cytoskeletal microfilaments and microtubules in capillary endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 12: 3087-3094, 2001
Fujio Y, Walsh K: Akt mediates cytoprotection of endothelial cells by vascular endothelial growth factor in an anchorage-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 274: 16349-16354, 1999
King WG, Mattaliano MD, Chan TO, Tsichlis PN, Brugge JS: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is required for integrin-stimulated AKT and Raf-1/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway activation. Mol Cell Biol 17: 4406-4418, 1997
Downward J: Mechanisms and consequences of activation of protein kinase B/Akt. Curr Opin Cell Biol 10: 262-267, 1998
Deveraux QL, Reed JC: IAP family proteins — suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13: 239-252, 1999
Lodish H, Baltimore D, Berk A, Zipursky SL, Matsudaira P, Darnell J: In: Molecular Cell Biology, 3rd edn. Scientific American Books, Inc., New York, 1995, pp. 991-1050
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Sirugo G, Altieri DC: Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell proliferation by survivin gene targeting. J Biol Chem 273: 11177-11182, 1998
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J, Tognin S, Marchisio PC, Altieri DC: Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature 396: 580-584, 1998
Olie RA, Simoes-Wust AP, Baumann B, Leech SH, Fabbro D, Stahel RA, Zangemeister-Wittke U: A novel antisense oligonucleotide targeting survivin expression induces apoptosis and sensitizes lung cancer cells to chemotherapy. Cancer Res 60: 2805-2809, 2000
Papapetropoulos A, Fulton D, Mahboubi K, Kalb RG, O'Connor DS, Li F, Altieri DC, Sessa WC: Angiopoietin-1 inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis via the Akt/survivin pathway. J Biol Chem 275: 9102-9105, 2000
Li F, Altieri DC: Transcriptional analysis of human survivin gene expression. Biochem J 344: 305-311, 1999
Verdecia MA, Huang H, Dutil E, Kaiser DA, Hunter T, Noel JP: Structure of the human anti-apoptotic protein survivin reveals a dimeric arrangement. Nat Struct Biol 7: 602-608, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, YL., Wang, LY., Wu, H. et al. PKB phosphorylation and survivin expression are cooperatively regulated by disruption of microfilament cytoskeleton. Mol Cell Biochem 254, 257–263 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027385417793
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027385417793